In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent called the mobile phase, which carries it through a system on which a material called the stationary phase is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation.
A cryopump or a "cryogenic pump" is a vacuum pump that traps gases and vapours by condensing them on a cold surface, but are only effective on some gases. The effectiveness depends on the freezing and boiling points of the gas relative to the cryopump's temperature. They are sometimes used to block particular contaminants, for example in front of a diffusion pump to trap backstreaming oil, or in front of a McLeod gauge to keep out water. In this function, they are called a cryotrap, waterpump or cold trap, even though the physical mechanism is the same as for a cryopump.

A rotary evaporator (rotovap) is a device used in chemical laboratories for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from samples by evaporation. When referenced in the chemistry research literature, description of the use of this technique and equipment may include the phrase "rotary evaporator", though use is often rather signaled by other language.

Column chromatography in chemistry is a chromatography method used to isolate a single chemical compound from a mixture. Chromatography is able to separate substances based on differential absorption of compounds to the adsorbent; compounds move through the column at different rates, allowing them to be separated into fractions. The technique is widely applicable, as many different adsorbents can be used with a wide range of solvents. The technique can be used on scales from micrograms up to kilograms. The main advantage of column chromatography is the relatively low cost and disposability of the stationary phase used in the process. The latter prevents cross-contamination and stationary phase degradation due to recycling. Column chromatography can be done using gravity to move the solvent, or using compressed gas to push the solvent through the column.
Scrubber systems are a diverse group of air pollution control devices that can be used to remove some particulates and/or gases from industrial exhaust streams. An early application of a carbon dioxide scrubber was in the submarine the Ictíneo I, in 1859; a role for which they continue to be used today. Traditionally, the term "scrubber" has referred to pollution control devices that use liquid to wash unwanted pollutants from a gas stream. Recently, the term has also been used to describe systems that inject a dry reagent or slurry into a dirty exhaust stream to "wash out" acid gases. Scrubbers are one of the primary devices that control gaseous emissions, especially acid gases. Scrubbers can also be used for heat recovery from hot gases by flue-gas condensation. They are also used for the high flows in solar, PV, or LED processes.

Solid-phase extraction (SPE) is a solid-liquid extractive technique, by which compounds that are dissolved or suspended in a liquid mixture are separated, isolated or purified, from other compounds in this mixture, according to their physical and chemical properties. Analytical laboratories use solid phase extraction to concentrate and purify samples for analysis. Solid phase extraction can be used to isolate analytes of interest from a wide variety of matrices, including urine, blood, water, beverages, soil, and animal tissue.
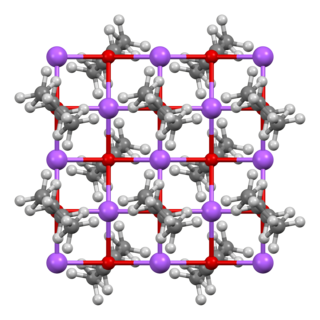
Sodium ethoxide, also referred to as sodium ethanolate, is the ionic, organic compound with the formula CH3CH2ONa, C2H5ONa, or NaOEt. It is a white solid, although impure samples appear yellow or brown. It dissolves in polar solvents such as ethanol. It is commonly used as a strong base.
Sigma-Aldrich is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company owned by the multinational chemical conglomerate Merck Group

The Schlenk line is a commonly used chemistry apparatus developed by Wilhelm Schlenk. It consists of a dual manifold with several ports. One manifold is connected to a source of purified inert gas, while the other is connected to a vacuum pump. The inert-gas line is vented through an oil bubbler, while solvent vapors and gaseous reaction products are prevented from contaminating the vacuum pump by a liquid-nitrogen or dry-ice/acetone cold trap. Special stopcocks or Teflon taps allow vacuum or inert gas to be selected without the need for placing the sample on a separate line.
Air sensitivity is a term used, particularly in chemistry, to denote the reactivity of chemical compounds with some constituent of air. Most often, reactions occur with atmospheric oxygen (O2) or water vapor (H2O), although reactions with the other constituents of air such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen (N2) are also possible.

An NMR tube is a thin glass walled tube used to contain samples in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Typically NMR tubes come in 5 mm diameters but 10 mm and 3 mm samples are known. It is important that the tubes are uniformly thick and well-balanced to ensure that NMR tube spins at a regular rate, usually about 20 Hz in the NMR spectrometer.

A carbon dioxide scrubber is a piece of equipment that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2). It is used to treat exhaust gases from industrial plants or from exhaled air in life support systems such as rebreathers or in spacecraft, submersible craft or airtight chambers. Carbon dioxide scrubbers are also used in controlled atmosphere (CA) storage and carbon capture and storage processes.
Air-free techniques refer to a range of manipulations in the chemistry laboratory for the handling of compounds that are air-sensitive. These techniques prevent the compounds from reacting with components of air, usually water and oxygen; less commonly carbon dioxide and nitrogen. A common theme among these techniques is the use of a fine (100–10−3 Torr) or high (10−3–10−6 Torr) vacuum to remove air, and the use of an inert gas: preferably argon, but often nitrogen.
Analytical thermal desorption, known within the analytical chemistry community simply as "thermal desorption" (TD), is a technique that concentrates volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in gas streams prior to injection into a gas chromatograph (GC). It can be used to lower the detection limits of GC methods, and can improve chromatographic performance by reducing peak widths.
A polar organic chemical integrative sampler (POCIS) is a passive sampling device which allows for the in situ collection of a time-integrated average of hydrophilic organic contaminants developed by researchers with the United States Geological Survey in Columbia, Missouri. POCIS provides a means for estimating the toxicological significance of waterborne contaminants. The POCIS sampler mimics the respiratory exposure of organisms living in the aquatic environment and can provide an understanding of bioavailable contaminants present in the system. POCIS can be deployed in a wide range of aquatic environments and is commonly used to assist in environmental monitoring studies.
Nanoremediation is the use of nanoparticles for environmental remediation. It is being explored to treat ground water, wastewater, soil, sediment, or other contaminated environmental materials. Nanoremediation is an emerging industry; by 2009, nanoremediation technologies had been documented in at least 44 cleanup sites around the world, predominantly in the United States. In Europe, nanoremediation is being investigated by the EC funded NanoRem Project. A report produced by the NanoRem consortium has identified around 70 nanoremediation projects worldwide at pilot or full scale. During nanoremediation, a nanoparticle agent must be brought into contact with the target contaminant under conditions that allow a detoxifying or immobilizing reaction. This process typically involves a pump-and-treat process or in situ application.

A respirator cartridge or gas mask canister is a type of filter that removes gases, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other vapors from the air through adsorption, absorption, or chemisorption. It is one of two basic types of filters used by air-purifying respirators. The other is a mechanical filter, which removes only particulates. Hybrid filters combine the two.

Passive sampling is an environmental monitoring technique involving the use of a collecting medium, such as a man-made device or biological organism, to accumulate chemical pollutants in the environment over time. This is in contrast to grab sampling, which involves taking a sample directly from the media of interest at one point in time. In passive sampling, average chemical concentrations are calculated over a device's deployment time, which avoids the need to visit a sampling site multiple times to collect multiple representative samples. Currently, passive samplers have been developed and deployed to detect toxic metals, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, radionuclides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and other organic compounds in water, while some passive samplers can detect hazardous substances in the air.
Workplace exposure monitoring is the monitoring of substances in a workplace that are chemical or biological hazards. It is performed in the context of workplace exposure assessment and risk assessment. Exposure monitoring analyzes hazardous substances in the air or on surfaces of a workplace, and is complementary to biomonitoring, which instead analyzes toxicants or their effects within workers.

Lithium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of lithium and lactic acid with the formula CH3CH(OH)COOLi, an amorphous solid, very soluble in water.








