The south Florida pine flatwoods are a flatwoods forest community found in central and southern Florida. [1]

Flatwoods, pineywoods, pine savannas and longleaf pine-wiregrass ecosystem are terms that refer to an ecological community in the Southeastern coastal plain of North America. Flatwoods are an ecosystem maintained by wildfire or prescribed fire and are dominated by longleaf pine, and slash pine in the tree canopy and saw palmetto, gallberry and other flammable evergreen shrubs in the understory, along with a high diversity of herb species. It was once one of the dominant ecosystem types of southeastern North America. Although grasses and pines are characteristic of this system, the precise composition changes from west to east, that is, from Texas to Florida. In Louisiana, savannas even differ between the east and west side of the Mississippi River. The key factor maintaining this habitat type is recurring fire. Without fire, the habitat is rapidly invaded by other species of woody plants.

Florida is the southernmost contiguous state in the United States. The state is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida. Florida is the 22nd-most extensive, the 3rd-most populous, and the 8th-most densely populated of the U.S. states. Jacksonville is the most populous municipality in the state and the largest city by area in the contiguous United States. The Miami metropolitan area is Florida's most populous urban area. Tallahassee is the state's capital.
These flatwoods have open canopies of slash pine ( Pinus elliottii var. densa) above a dense understory of low shrubs and grasses in places where low-intensity fires are frequent. Where fires have been suppressed, slash pine, shrubs, and saw palmetto ( Serenoa repens ) become more dense. [1]

Pinus elliottii, commonly known as slash pine, is a conifer tree in the Southeastern United States. Slash pine is named after the "slashes" – swampy ground overgrown with trees and bushes – that constitute its habitat. Other common names include swamp pine, yellow slash pine, and southern Florida pine. Historically, slash pine has been an important economic timber for naval stores, turpentine, and resin. Slash pine has two different varieties: Pinus elliottii var. elliottii and Pinus elliottii var. densa.
In addition to saw palmetto, the shrubs Appalachian tea ( Ilex glabra ), coastal plain staggerbush ( Lyonia fruticosa ), dwarf live oak ( Quercus minima ), shiny blueberry ( Vaccinium myrsinites ), and rosy camphorweed ( Pluchea rosea ) can be found in the flatwoods. Wiregrass ( Aristida beyrichiana ) is the dominant grass. [1]
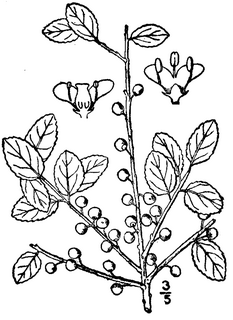
Ilex glabra, also known as Appalachian tea, dye-leaves, evergreen winterberry, gallberry, and inkberry, is a species of evergreen holly native to the coastal plain of eastern North America, from coastal Nova Scotia to Florida and west to Louisiana where it is most commonly found in sandy woods and peripheries of swamps and bogs. Ilex glabra is often found in landscapes of the middle and lower East Coast. It typically matures to 5–8 ft (1.5–2.4 m) tall, and can spread by root suckers to form colonies. It normally is cultivated as an evergreen shrub in USDA zones 6 to 10.

Lyonia fruticosa, the poor-grub or coastal plain staggerbush, is a plant species native to the US states of Florida, southern Georgia and the extreme southern part of South Carolina. It grows in pine woodlands and shrub bogs at elevations less than 100 meters.

Quercus minima, the dwarf live oak or minimal oak, is a North American species of shrubs in the beech family. It is native to the southeastern United States.
This system is similar to Florida dry prairie, but has taller and denser shrub cover. [1]
The Florida dry prairie is an herbaceous upland plant community found in subtropical southern Florida. It consists of plains covered in grasses, low shrubs, and few widely scattered trees. It was originally found on the plains near the Kissimmee River and Fisheating Creek connected to Lake Okeechobee, but its range has been reduced by conversion to agriculture and pasture. Frequent fires are necessary to maintain this system.