
A frontier is the political and geographical area near or beyond a boundary. A frontier can also be referred to as a "front". The term came from French in the 15th century, with the meaning "borderland"—the region of a country that fronts on another country. Unlike a border—a rigid and clear-cut form of state boundary—in the most general sense a frontier can be fuzzy or diffuse. For example, the frontier between the Eastern United States and the Old West in the 1800s was an area where European American settlements gradually thinned out and gave way to Native American settlements or uninhabited land. The frontier was not always a single continuous area, as California and various large cities were populated before the land that connected those to the East.

Kaskaskia is a village in Randolph County, Illinois. Having been inhabited by indigenous peoples, it was settled by France as part of the Illinois Country. Its population peaked at about 7,000 in the 18th century, when it was a regional center. During the American Revolutionary War, the town, which by then had become an administrative center for the British Province of Quebec, was taken by the Virginia militia during the Illinois campaign. It was designated as the county seat of Illinois County, Virginia, after which it became part of the Northwest Territory in 1787. Kaskaskia was later named as the capital of the United States' Illinois Territory, created on February 3, 1809. In 1818, when Illinois became the 21st U.S. state, the town briefly served as the state's first capital until 1819, when the capital was moved to more centrally located Vandalia.

The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest, Desert Southwest, or simply The Southwest, is the informal name for a region of the western United States. Definitions of the region's boundaries vary a great deal and have never been standardized, though many boundaries have been proposed. For example, one definition includes the stretch from the Mojave Desert in California to Carlsbad, New Mexico, and from the Mexico–United States border to the southern areas of Colorado, Utah, and Nevada. The largest metropolitan areas are centered around Phoenix, Las Vegas, Tucson, Albuquerque, and El Paso. Those five metropolitan areas have an estimated total population of more than 9.6 million as of 2017, with nearly 60 percent of them living in the two Arizona cities—Phoenix and Tucson.

The Western United States is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As European settlement in the U.S. expanded westward through the centuries, the meaning of the term the West changed. Before about 1800, the crest of the Appalachian Mountains was seen as the western frontier. The frontier moved westward and eventually the lands west of the Mississippi River were considered the West.

The American frontier includes the geography, history, folklore, and cultural expression of life in the forward wave of American expansion that began with English colonial settlements in the early 17th century and ended with the admission of the last remaining western territories as states in 1912. This era of massive migration and settlement was particularly encouraged by President Thomas Jefferson following the Louisiana Purchase, giving rise to the expansionist philosophy known as "Manifest Destiny".
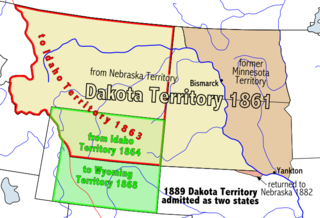
The Territory of Dakota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1861, until November 2, 1889, when the final extent of the reduced territory was split and admitted to the Union as the states of North and South Dakota.
Southwest is a compass point.

The Treaty of Greenville, formally titled Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., was a 1795 treaty between the United States and Indians of the Northwest Territory including the Wyandot and Delaware, which redefined the boundary between Indian lands and Whiteman's lands in the Northwest Territory.

The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi and the eastern half became the Alabama Territory until its admittance to the Union as the State of Alabama on December 14, 1819.
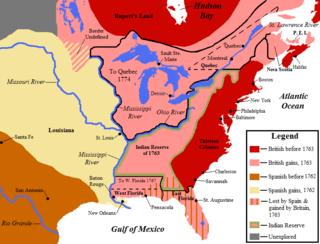
This is a list of historic regions of the United States that existed at some time during the territorial evolution of the United States and its overseas possessions, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today.
Northwest is a compass point.
The "Old Southwest" is an informal name for the southwestern frontier territories of the United States from the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) through the early 19th century, at the point when the territorial lands were organized into states.
The Natchez District was one of two areas established in the Kingdom of Great Britain's West Florida colony during the 1770s – the other being the Tombigbee District. The first Anglo settlers in the district came primarily from other parts of British America. The district was recognized to be the area east of the Mississippi River from Bayou Sara in the south and Bayou Pierre in the north.
West is a cardinal direction or compass point.

The Frontier Culture Museum, located in Staunton, Virginia is a living history museum that tells the story of the people who migrated from the Old World to America and the life they created in the Shenandoah Valley. The Museum is made up of original or reproduced examples of traditional buildings from the Old World and America.

Davidsonville Historic State Park is a 163-acre (66 ha) Arkansas state park in Randolph County, Arkansas in the United States. Situated on a border between The Ozarks and the Arkansas Delta, the park preserves the remains of the abandoned frontier town of Davidsonville. The town was one of Arkansaw Territory's first settlements when founded in 1815, serving as an important river port town on the Black River. The former townsite was made into a state park in 1957 and a monument was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.

The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of back-and-forth raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1795 between the Cherokee and American settlers on the frontier. Most of the events took place in the Upper South. While the fighting stretched across the entire period, there were times of little or no action, at times spanning several months.
The timeline of Kansas details past events that happened in what is present day Kansas. Located on the eastern edge of the Great Plains, the U.S. state of Kansas was the home of sedentary agrarian and hunter-gatherer Native American societies, many of whom hunted American bison. The region first appears in western history in the 16th century at the time of the Spanish conquest of Mexico, when Spanish conquistadores explored the unknown land now known as Kansas. It was later explored by French fur trappers who traded with the Native Americans. It became part of the United States in the Louisiana Purchase of 1803. In the 19th century, the first American explorers designated the area as the "Great American Desert."
The Chickamauga Cherokee were a group that separated from the greater body of the Cherokee tribes during the American Revolutionary War. The majority of the Cherokee people wished to make peace with the Americans near the end of 1776 following several military setbacks and the reprisals that followed. The Chickamauga followers of headman Dragging Canoe moved with him down the Tennessee River away from their historic Overhill Cherokee towns in the winter of 1776–77. Relocated in a more isolated area, they established 11 new towns in order to gain distance from colonists' encroachments. The frontier Americans associated Dragging Canoe and his band with their new town on the Chickamauga Creek and began to refer to them as the Chickamaugas. Five years later, the Chickamaugas moved further west and southwest into present-day Alabama, establishing five larger settlements. They were then more commonly known as the Lower Cherokee. This term was closely associated with the people of these "Five Lower Towns".
Julian Smith is an American author and journalist. He wrote Crossing the Heart of Africa, published in 2010 by Harper Perennial, and co-authored Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne Firefighters, published in 2015 by William Morrow. Smith and David Wolman are also co-authors of Aloha Rodeo: Three Hawaiian Cowboys, the World's Greatest Rodeo, and a Hidden History of the American West, coming May 28, 2019 from William Morrow.












