Related Research Articles

In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if their intersection forms right angles at the point of intersection called a foot. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the perpendicular symbol, ⟂. Perpendicular intersections can happen between two lines, between a line and a plane, and between two planes.

Coxa vara is a deformity of the hip, whereby the angle between the head and the shaft of the femur is reduced to less than 120 degrees. This results in the leg being shortened and the development of a limp. It may be congenital and is commonly caused by injury, such as a fracture. It can also occur when the bone tissue in the neck of the femur is softer than normal, causing it to bend under the weight of the body. This may either be congenital or the result of a bone disorder. The most common cause of coxa vara is either congenital or developmental. Other common causes include metabolic bone diseases, post-Perthes deformity, osteomyelitis, and post traumatic. Shepherd's Crook deformity is a severe form of coxa vara where the proximal femur is severely deformed with a reduction in the neck shaft angle beyond 90 degrees. It is most commonly a sequela of osteogenesis imperfecta, Paget's disease, osteomyelitis, tumour and tumour-like conditions.

In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxa(pl.: coxae) in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis.

Proximal femoral focal deficiency (PFFD), also known as Congenital Femoral Deficiency (CFD), is a rare, non-hereditary birth defect that affects the pelvis, particularly the hip bone, and the proximal femur. The disorder may affect one side or both, with the hip being deformed and the leg shortened.

Slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a medical term referring to a fracture through the growth plate (physis), which results in slippage of the overlying end of the femur (metaphysis).

The upper extremity, proximal extremity or superior epiphysis of the femur is the part of the femur closest to the pelvic bone and the trunk. It contains the following structures:
Wayne Orin Southwick was an American surgeon and academic. He was the first chairman of the Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation at Yale University from 1958 to 1979. Southwick trained more future orthopaedic chairmen than any other chairman in the history of orthopaedics.

Bicycle and motorcycle geometry is the collection of key measurements that define a particular bike configuration. Primary among these are wheelbase, steering axis angle, fork offset, and trail. These parameters have a major influence on how a bike handles.

Pigeon toe, also known as in-toeing, is a condition which causes the toes to point inward when walking. It is most common in infants and children under two years of age and, when not the result of simple muscle weakness, normally arises from underlying conditions, such as a twisted shin bone or an excessive anteversion resulting in the twisting of the thigh bone when the front part of a person's foot is turned in.

Orthopaedic Studio is an application designed to help orthopaedic specialists perform several common quantitative hip examinations that are based on standard x-ray images.
SUFE may refer to:

Orthopedic surgery is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal injuries, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, bone tumours, and congenital limb deformities. Trauma surgery and traumatology is a sub-specialty dealing with the operative management of fractures, major trauma and the multiply-injured patient.
Perkin's line is a line drawn on an AP radiograph of the pelvis perpendicular to Hilgenreiner's line at the lateral aspects of the triradiate cartilage of the acetabulum.
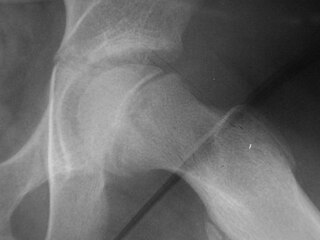
Klein's line or the line of Klein is a virtual line that can be drawn on an X-ray of an adolescent's hip parallel to the anatomically upper edge of the femoral neck. It was the first tool to aid in the early diagnosis of a slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), which if treated late or left untreated leads to crippling arthritis, leg length discrepancy and lost range of motion. It is named after the American orthopedic surgeon Armin Klein at Harvard University, who published its description and usefulness in 1952. Subsequent modification of its use has increased the sensitivity and reliability of the tool.

Trethowan's sign is when Klein's line does not intersect the lateral part of the superior femoral epiphysis on an AP radiograph of the pelvis.

Pain in the hip is the experience of pain in the muscles or joints in the hip/ pelvic region, a condition commonly arising from any of a number of factors. Sometimes it is closely associated with lower back pain.
G-arm medical imaging systems are based on fluoroscopic X-ray and are used for a variety of diagnostic imaging and minimally invasive surgical procedures. The name is derived from the G-shaped arm used to connect two X-ray generators and two X-ray detectors, image intensifiers or digital flat panel detectors, to one another. The main advantage of the G-arm, compared to a conventional C-arm system, is that it combines a pair of X-ray chains facilitating simultaneous views in two perpendicular planes, also called G-arm imaging.
The Drehmann sign describes a clinical test of examining orthopedic patients and is widely used in the functional check of the hip joint. It was first described by Gustav Drehmann.
X-rays of hip dysplasia are one of the two main methods of medical imaging to diagnose hip dysplasia, the other one being medical ultrasonography. Ultrasound imaging yields better results defining the anatomy until the cartilage is ossified. When the infant is around 3 months old a clear roentgenographic image can be achieved. Unfortunately the time the joint gives a good x-ray image is also the point at which nonsurgical treatment methods cease to give good results.
References
- Loder, R.; "Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis." American Family Physician 1998 57: 2135.