
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word spectrum was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. As scientific understanding of light advanced, it came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum. It thereby became a mapping of a range of magnitudes (wavelengths) to a range of qualities, which are the perceived "colors of the rainbow" and other properties which correspond to wavelengths that lie outside of the visible light spectrum.
In linear algebra and functional analysis, a spectral theorem is a result about when a linear operator or matrix can be diagonalized. This is extremely useful because computations involving a diagonalizable matrix can often be reduced to much simpler computations involving the corresponding diagonal matrix. The concept of diagonalization is relatively straightforward for operators on finite-dimensional vector spaces but requires some modification for operators on infinite-dimensional spaces. In general, the spectral theorem identifies a class of linear operators that can be modeled by multiplication operators, which are as simple as one can hope to find. In more abstract language, the spectral theorem is a statement about commutative C*-algebras. See also spectral theory for a historical perspective.
In mathematics, the spectrum of a matrix is the set of its eigenvalues. More generally, if is a linear operator on any finite-dimensional vector space, its spectrum is the set of scalars such that is not invertible. The determinant of the matrix equals the product of its eigenvalues. Similarly, the trace of the matrix equals the sum of its eigenvalues. From this point of view, we can define the pseudo-determinant for a singular matrix to be the product of its nonzero eigenvalues.
Spectral analysis or spectrum analysis is analysis in terms of a spectrum of frequencies or related quantities such as energies, eigenvalues, etc. In specific areas it may refer to:
Spectral decomposition is any of several things:
In mathematics, spectral theory is an inclusive term for theories extending the eigenvector and eigenvalue theory of a single square matrix to a much broader theory of the structure of operators in a variety of mathematical spaces. It is a result of studies of linear algebra and the solutions of systems of linear equations and their generalizations. The theory is connected to that of analytic functions because the spectral properties of an operator are related to analytic functions of the spectral parameter.
In mathematics, spectral graph theory is the study of the properties of a graph in relationship to the characteristic polynomial, eigenvalues, and eigenvectors of matrices associated with the graph, such as its adjacency matrix or Laplacian matrix.
A computer font is implemented as a digital data file containing a set of graphically related glyphs. A computer font is designed and created using a font editor. A computer font specifically designed for the computer screen, and not for printing, is a screen font.
A spectrum is a condition or value that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum.
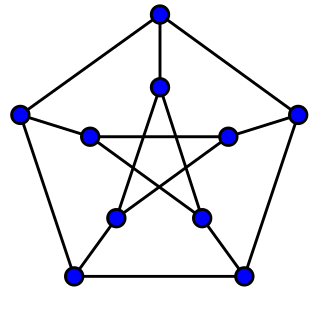
Algebraic graph theory is a branch of mathematics in which algebraic methods are applied to problems about graphs. This is in contrast to geometric, combinatoric, or algorithmic approaches. There are three main branches of algebraic graph theory, involving the use of linear algebra, the use of group theory, and the study of graph invariants.
In astronomy, a blueshift is a decrease in electromagnetic wavelength caused by the motion of a celestial object toward an observer.

Matrix digital rain, or Matrix code, is the computer code featured in the Ghost in the Shell series and the Matrix series. The falling green code is a way of representing the activity of the simulated reality environment of the Matrix on screen by kinetic typography. All four Matrix movies, as well as the spin-off The Animatrix episodes, open with the code. It is a characteristic mark of the franchise, similar to the opening crawl featured in the Star Wars franchise.
I is the ninth letter of the Latin alphabet.
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
In mathematics, the spectral abscissa of a matrix or a bounded linear operator is the greatest real part of the matrix's spectrum. It is sometimes denoted . As a transformation :\mathrm {M} ^{n}\rightarrow \mathbb {R} } , the spectral abscissa maps a square matrix onto its largest real eigenvalue.


