
Tetraplegia, also known as quadriplegia, is defined as the dysfunction or loss of motor and/or sensory function in the cervical area of the spinal cord. A loss of motor function can present as either weakness or paralysis leading to partial or total loss of function in the arms, legs, trunk, and pelvis; paraplegia is similar but affects the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments of the spinal cord and arm function is spared. The paralysis may be flaccid or spastic. A loss of sensory function can present as an impairment or complete inability to sense light touch, pressure, heat, pinprick/pain, and proprioception. In these types of spinal cord injury, it is common to have a loss of both sensation and motor control.

Stoke Mandeville Hospital is a large National Health Service (NHS) hospital located on the parish borders of Aylesbury and Stoke Mandeville, Buckinghamshire, England. It is managed by Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust.
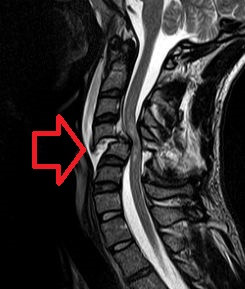
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be complete, with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or incomplete, meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems.

Evelina London Children's Hospital is a specialist NHS hospital in London. It is administratively a part of Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and provides teaching hospital facilities for London South Bank University and King's College London School of Medicine. Formerly housed at Guy's Hospital in Southwark, it moved to a new building alongside St Thomas' Hospital in Lambeth on 31 October 2005.

The Brain Tumour Charity is a UK-based, Charity Commission registered, charity dedicated to funding research, raising awareness of brain tumours, reducing diagnosis times and providing support and information for people with brain tumours, their families and friends.

The Paralyzed Veterans of America is a veterans' service organization in the United States of America, founded in 1946. The organization holds 33 chapters and 70 National Service Offices in the United States and Puerto Rico. It is based in Washington, D.C. The organization was founded in 1946 by a band of service members who came home from World War II with spinal cord injuries. These service members wanted to live with independence and dignity and as contributors to society, so they created the organization to be governed by its members, veterans of the armed forces living with spinal cord injury or disease such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease.

The Motor Neurone Disease Association focuses on improving access to care, research and campaigning for those people living with or affected by motor neurone disease (MND) in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. MND is also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or, in the United States, Lou Gehrig's disease.

Craig Hospital is a neurorehabilitation and research hospital in Englewood, Colorado specializing in spinal cord injury (SCI) and traumatic brain injury (TBI) rehabilitation and research. Craig is a 93-bed, private, not-for-profit, free-standing long-term acute care and rehabilitation hospital that provides a comprehensive system of inpatient and outpatient medical care, rehabilitation, neurosurgical rehabilitative care, and long-term follow-up services. Half of Craig's patients come from outside of Colorado each year, and in the past four years Craig has treated patients from all 50 states and several foreign countries. At any given time, the staff at Craig treats approximately 55 inpatients with spinal cord injuries, 30 with traumatic brain injuries, and 50-60 outpatients. Craig provides housing for out-of-state families and outpatients, including the first 30 days free for families of new inpatients.
Spinal Cord Injuries Australia (SCIA) is a non-government organisation which provides advocacy and services to people with spinal cord injury and similar conditions.
MedStar National Rehabilitation Network is located in Washington, D.C., and specializes in treating persons with physical disabilities, including spinal cord injury, brain injury, stroke, arthritis, amputation, multiple sclerosis, post-polio syndrome, orthopedic, and other neurological conditions. National Rehabilitation Hospital was founded in 1986 by Edward A. Eckenhoff, and is a member of the MedStar Health system, the Washington, D.C.-Baltimore region's largest non-profit healthcare organization.

Mary Free Bed Rehabilitation Hospital is a 167-bed acute care inpatient rehabilitation hospital for children and adults who have experienced a brain injury, spinal cord injury, stroke, amputation, or other injury or illness requiring physical rehabilitation.
Magee Rehabilitation Hospital, part of Jefferson Health, founded in 1958, is a 96-bed specialty medical rehabilitation hospital providing physical and cognitive rehabilitation services. Magee's flagship facility is located in Center City Philadelphia. In addition to the main campus that offers comprehensive services for spinal cord injury, brain injury, stroke, orthopaedic replacement, amputation, pain management and work injury, Magee provides an expanding outpatient network serving the surrounding communities. In 1985, Magee's brain injury rehabilitation program became the first in the nation to be accredited by the Commission on the Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities. Magee partnered with Jefferson Hospital to create one of the nation's 14 federally designated centers for spinal cord injury rehabilitation. Magee has been rated one of America's leading rehabilitation hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Magee provides treatment to more than 5,000 individuals annually. Magee is authorized to treat wounded military personnel returning from war. Magee is not an Obligated Group Affiliate.
TIRR Memorial Hermann is a 134-bed rehabilitation hospital, rehabilitation and research center, outpatient medical clinic and network of outpatient rehabilitation centers in Houston, Texas that offers physical rehabilitation to patients following traumatic brain or spinal injury or to those suffering from neurologic illnesses.
The Canadian Spinal Research Organization (SCRO) is a nationally registered charity whose mission is to improve the physical quality of life for persons with spinal cord injuries (SCI) and related neurological deficits, as well as to reduce the number of spinal cord injuries through awareness and prevention programs.
Trust PA is a UK registered charity working to help those suffering from paralysis as a result of a spinal cord injury (SCI), funding research, as well as the work necessary to convert successful research into properly tested and approved treatments that can be freely available in UK NHS hospitals and across the world.
Southport and Ormskirk Hospital NHS Trust is the principal healthcare provider to 258,000 people across Southport, Formby and West Lancashire.
Although spinal cord injury (SCI) often causes sexual dysfunction, many people with SCI are able to have satisfying sex lives. Physical limitations acquired from SCI affect sexual function and sexuality in broader areas, which in turn has important effects on quality of life. Damage to the spinal cord impairs its ability to transmit messages between the brain and parts of the body below the level of the lesion. This results in lost or reduced sensation and muscle motion, and affects orgasm, erection, ejaculation, and vaginal lubrication. More indirect causes of sexual dysfunction include pain, weakness, and side effects of medications. Psycho-social causes include depression and altered self-image. Many people with SCI have satisfying sex lives, and many experience sexual arousal and orgasm. People with SCI may employ a variety of adaptations to help carry on their sex lives healthily, by focusing on different areas of the body and types of sexual acts. Neural plasticity may account for increases in sensitivity in parts of the body that have not lost sensation, so people often find newly sensitive erotic areas of the skin in erogenous zones or near borders between areas of preserved and lost sensation.
Spinal cord injury research seeks new ways to cure or treat spinal cord injury in order to lessen the debilitating effects of the injury in the short or long term. There is no cure for SCI, and current treatments are mostly focused on spinal cord injury rehabilitation and management of the secondary effects of the condition. Two major areas of research include neuroprotection, ways to prevent damage to cells caused by biological processes that take place in the body after the injury, and neuroregeneration, regrowing or replacing damaged neural circuits.

The Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System (VAHCS) is network of hospital and outpatient clinics based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA. It belongs to the VISN23 VA Midwest Health Care Network managed by the Veterans Health Administration of the Department of Veterans Affairs. The Minneapolis VAHCS provides healthcare for United States military veterans in areas such as medicine, surgery, psychiatry, physical medicine and rehabilitation, neurology, oncology, dentistry, geriatrics and extended care. As a teaching hospital, it operates comprehensive training programs for multiple treatment specialties. The Minneapolis VAHCS also hosts one of the largest research programs of any VA health care system and maintains research affiliations with the University of Minnesota.
The 2020 New Year Honours are appointments by some of the 16 Commonwealth realms to various orders and honours to recognise and reward good works by citizens of those countries. The New Year Honours are awarded as part of the New Year celebrations at the start of January and were officially announced in The London Gazette on 27 December 2019. Australia, an independent Realm, has a separate honours system and its first honours of the year, the 2020 Australia Day Honours, coincide with Australia Day on 26 January.