
Svalbard ( SVAHL-bar, Urban East Norwegian: [ˈsvɑ̂ːɫbɑr]; prior to 1925 known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. Situated north of mainland Europe, it is about midway between continental Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. While part of the Kingdom of Norway since 1925, Svalbard is not part of geographical Norway; administratively, the archipelago is not part of any Norwegian county, but forms an unincorporated area administered by a governor appointed by the Norwegian government, and a special jurisdiction subject to the Svalbard Treaty that is outside of the Schengen Area, the Nordic Passport Union and the European Economic Area.
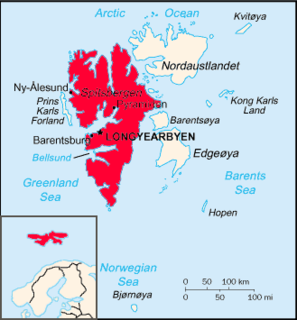
Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of 37,673 km2 (14,546 sq mi), making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in 21,977 km2 (8,485 sq mi) of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area.

Operation Gauntlet was an Allied Combined Operation from 25 August until 3 September 1941, during the Second World War. Canadian, British and Free Norwegian Forces landed on the Norwegian island of Spitsbergen in the Svalbard Archipelago, 650 mi (1,050 km) south of the North Pole.

Johan Oskar Backlund was a Swedish-Russian astronomer. His name is sometimes given as Jöns Oskar Backlund, however even contemporary Swedish sources give "Johan". In Russia, where he spent his entire career, he is known as Oskar Andreevich Baklund. Russian sources sometimes give his dates of birth and death as 16 April 1846 and 16 August 1916, since Russia still used the Julian calendar at the time.

The Svalbard Treaty recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and not all Norwegian law applies. The treaty regulates the demilitarisation of the archipelago. The signatories were given equal rights to engage in commercial activities on the islands. As of 2012, Norway and Russia are making use of this right.

Operation Zitronella, also known as Unternehmen Sizilien (Sicily), was an eight-hour German raid on Spitzbergen, in the Svalbard Archipelago, on 8 September 1943. The battleships Tirpitz and Scharnhorst, plus nine destroyers, sailed to the archipelago, bombarded settlements in Isfjorden and covered a landing party. Six Norwegians were killed and 31 were taken prisoner; one German died of wounds and fifteen were wounded.

The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the Atlantic Ocean. However, definitions of the Arctic Ocean and its seas tend to be imprecise or arbitrary. In general usage the term "Arctic Ocean" would exclude the Greenland Sea. In oceanographic studies the Greenland Sea is considered part of the Nordic Seas, along with the Norwegian Sea. The Nordic Seas are the main connection between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans and, as such, could be of great significance in a possible shutdown of thermohaline circulation. In oceanography the Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas are often referred to collectively as the "Arctic Mediterranean Sea", a marginal sea of the Atlantic.

Sør-Spitsbergen National Park encompasses the southern end of Spitsbergen island in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. The park was opened in 1973 and includes Wedel Jarlsberg Land, Torell Land and Sørkapp Land. Over 65% of the region is ice cap, with much of the rest tundra.

Operation Haudegen was the name of a German operation during the Second World War to establish meteorological stations on Svalbard. In September 1944, the submarine U-307 and the supply ship Carl J. Busch transported the men of Unternehmen Haudegen to the island. The station was active from 9 September 1944 to 4 September 1945 but lost radio contact in May 1945. The soldiers were capable of asking for support only in August 1945 and on 4 September, were picked up by a Norwegian seal hunting vessel and surrendered to its captain. The group of men were the last German troops to surrender after the Second World War.

Pytine is an extinct genus of asaphid trilobites. Species lived during the later part of the Arenig stage of the Ordovician Period, approximately 478 to 471 million years ago. Various species are found in the Svalbard, Valhallfonna Formation, Olenidsletta, Member, of Spitzbergen, Norway, the Megistaspis (Paramegistaspis) planilimbata Zone of the 'Shumardia Shale' of Sweden, Jujuy Province, Argentina, early Arenig-aged strata of Jiangxi province, China, and Darriwilian-aged strata in Western Hunan province, China. The type species, P. graia, has seven thorax segments, and lacks the rapier-like glabellar spine, that occurs in many other raphiophorids. The Chinese species, by contrast, have only six thoracic segments. So far, only the type species, and one of the Chinese species, P. laevigata, are known from complete specimens.

The West Spitsbergen Current (WSC) is a warm, salty current that runs poleward just west of Spitsbergen,, in the Arctic Ocean. The WSC branches off the Norwegian Atlantic Current in the Norwegian Sea. The WSC is of importance because it drives warm and salty Atlantic Water into the interior Arctic. The warm and salty WSC flows north through the eastern side of Fram Strait, while the East Greenland Current (EGC) flows south through the western side of Fram Strait. The EGC is characterized by being very cold and low in salinity, but above all else it is a major exporter of Arctic sea ice. Thus, the EGC combined with the warm WSC makes the Fram Strait the northernmost ocean area having ice-free conditions throughout the year in all of the global ocean.
Virgohamna is a small bay on the northern coast of Danes Island, an island off the northwestern coast of Spitsbergen. Spitsbergen and Danes Island are islands of the Svalbard archipelago. The bay is named after SS Virgo, the vessel of Swedish engineer and explorer Salomon August Andrée's 1896 expedition. Virgohamna is located across a small strait from Smeerenburg, a historical whaling station on Amsterdam Island about 2 km to the north.
Sholto George Watson Douglas, 19th Earl of Morton, DL was a major landowner in Scotland, a businessman with mining investments in what is now Svalbard, Norway, and politician, serving as a representative peer (1886–1935) after being elected by the Peerage of Scotland.
Camp Morton was a coal mining encampment on Spitsbergen island in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. It was located on the northern shores of Van Mijenfjorden, near the sea entrance. It was part of an effort by British investors and entrepreneurs to extract resources from Spitsbergen, at that time open to various nations' claims for development.

Advent City is an abandoned settlement located on the east side of Adventfjorden on the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. It served as a coal mining camp from 1904 to 1917 operated by Spitzbergen Coal and Trading Company Limited of Sheffield, United Kingdom. A single mess was built the first year, and additional buildings followed in 1905, including a bakery and two streets. All remaining buildings were moved to Hiorthhamn in 1916 and 1917.
Quasianosteosaurus is an extinct genus of basal ichthyosaur known from the late Early Triassic of Spitsbergen of the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. It was first named by Michael W. Maisch and Andreas T. Matzke in 2003 and the type species is Quasianosteosaurus vikinghoegdai. The generic name is derived from Latin quasi, "almost", and Greek anosteos, "boneless" and sauros, "lizard", in reference to the preservation of the holotype which is almost exclusively a natural cast of the skull with very little original bone. The specific name is derived from Vikinghøgda, "Mount Viking", where the holotype was found. Quasianosteosaurus is known only from the holotype MNHN Nr. SVT 331, a partial three-dimensionally preserved skull consisting of the snout and orbital and postorbital regions. The skull is by far the largest Early Triassic ichthyosaur skull known, with estimated cranial length at 50 cm (20 in). It was collected from the lowermost Grippia Niveau of the Sticky Keep Formation, Sassendalen Group at Mount Viking, Sassendalen. A phylogenetic analysis performed by Maisch & Matzke (2003) found it to be a basal ichthyosaur, sister taxon to Hueneosauria.
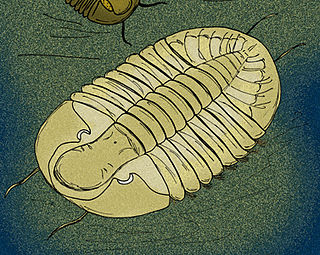
Gog is a genus of large, flattened asaphid trilobite from the Middle Arenig-aged Svalbard, Valhallfonna Formation, Olenidsletta, Member, of Spitzbergen, Norway, and the Upper Arenig-aged Dawan Formation in Hubei, China.

The Arctic desert ecoregion is a terrestrial ecoregion that covers the island groups of Svalbard, Franz Josef Land, Severny Island and Severnaya Zemlya in the Arctic Ocean, above 75 degrees north latitude. The region is covered with glaciers, snow, and bare rock in a harshly cold environment. The temperature does rise above freezing for short periods in the summer, so some ice melt occurs, and the area supports colonies of sea birds and mammals. It has an area of 161,400 square kilometres (62,300 sq mi).
Cornelis Giles, born in Den Helder around 1675 and died at sea on July 2, 1722, was a Dutch navigator and cartographer.











