
A flavoring, also known as flavor or flavorant, is a food additive used to improve the taste or smell of food. It changes the perceptual impression of food as determined primarily by the chemoreceptors of the gustatory and olfactory systems. Along with additives, other components like sugars determine the taste of food.

Pizza cheese encompasses several varieties and types of cheeses and dairy products that are designed and manufactured for use specifically on pizza. These include processed and modified cheese, such as mozzarella-like processed cheeses and mozzarella variants. The term can also refer to any type of cheese suitable for use on pizza. The most popular cheeses used in the preparation of pizza are mozzarella, provolone, cheddar and Parmesan. Emmental, pecorino romano and ricotta are often used as toppings, and processed pizza cheeses manufactured specifically for pizza are mass-produced. Some mass-produced pizza cheeses are frozen after manufacturing and shipped frozen.
A quality management system (QMS) is a collection of business processes focused on consistently meeting customer requirements and enhancing their satisfaction. It is aligned with an organization's purpose and strategic direction. It is expressed as the organizational goals and aspirations, policies, processes, documented information, and resources needed to implement and maintain it. Early quality management systems emphasized predictable outcomes of an industrial product production line, using simple statistics and random sampling. By the 20th century, labor inputs were typically the most costly inputs in most industrialized societies, so focus shifted to team cooperation and dynamics, especially the early signaling of problems via a continual improvement cycle. In the 21st century, QMS has tended to converge with sustainability and transparency initiatives, as both investor and customer satisfaction and perceived quality are increasingly tied to these factors. Of QMS regimes, the ISO 9000 family of standards is probably the most widely implemented worldwide – the ISO 19011 audit regime applies to both and deals with quality and sustainability and their integration.

An application-specific integrated circuit is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec. Application-specific standard product chips are intermediate between ASICs and industry standard integrated circuits like the 7400 series or the 4000 series. ASIC chips are typically fabricated using metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, as MOS integrated circuit chips.

Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred to as a surface-mount device (SMD). In industry, this approach has largely replaced the through-hole technology construction method of fitting components, in large part because SMT allows for increased manufacturing automation which reduces cost and improves quality. It also allows for more components to fit on a given area of substrate. Both technologies can be used on the same board, with the through-hole technology often used for components not suitable for surface mounting such as large transformers and heat-sinked power semiconductors.

Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.

A frozen meal, prepackaged meal, ready-made meal, ready meal (UK), frozen dinner, and microwave meal is ultra-processed food portioned for an individual. A frozen meal in the United States and Canada usually consists of a type of meat, fish, or pasta for the main course, and sometimes vegetables, potatoes, and/or a dessert. Some frozen meals feature Indian, Chinese, Mexican, and other foods of international customs. Another form of convenience food, which is merely a refrigerated ready meal that requires less heating but expires sooner, is popular.

Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a coordinated system of preparing goods for transport, warehousing, logistics, sale, and end use. Packaging contains, protects, preserves, transports, informs, and sells. In many countries it is fully integrated into government, business, institutional, industrial, and for personal use.

A custom-built or home-built computer is a computer that is assembled by its user using commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components, rather than purchased as a complete and ready-to-use machine, also known as a "pre-built" or out-of-the-box system. Building a computer at home is generally considered a cost-effective alternative to buying a pre-built one because it excludes the assembly labor cost. However, the total cost of building a computer can vary based on an individual's budget, the quality and availability of the parts used, and the discounts offered by mass production. As a result, the final cost may potentially exceed that of typical pre-built computers. Home-built computers are often used at home, like home computers, but home computers are traditionally purchased already assembled by the manufacturer. Some suppliers provide both home and homebuilt computers, like the Newbear 77-68, which the owner was expected to assemble and use in their home.
A contract manufacturer (CM) is a manufacturer that contracts with a firm for components or products. It is a form of outsourcing. A contract manufacturer performing packaging operations is called copacker or a contract packager. Brand name companies focus on product innovation, design and sales, while the manufacturing takes place in independent factories.
A software factory is a structured collection of related software assets that aids in producing computer software applications or software components according to specific, externally defined end-user requirements through an assembly process. A software factory applies manufacturing techniques and principles to software development to mimic the benefits of traditional manufacturing. Software factories are generally involved with outsourced software creation.

Design for manufacturability is the general engineering practice of designing products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture. The concept exists in almost all engineering disciplines, but the implementation differs widely depending on the manufacturing technology. DFM describes the process of designing or engineering a product in order to facilitate the manufacturing process in order to reduce its manufacturing costs. DFM will allow potential problems to be fixed in the design phase which is the least expensive place to address them. Other factors may affect the manufacturability such as the type of raw material, the form of the raw material, dimensional tolerances, and secondary processing such as finishing.
The process of establishing documentary evidence demonstrating that a procedure, process, or activity carried out in testing and then production maintains the desired level of compliance at all stages. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is very important that in addition to final testing and compliance of products, it is also assured that the process will consistently produce the expected results. The desired results are established in terms of specifications for outcome of the process. Qualification of systems and equipment is therefore a part of the process of validation. Validation is a requirement of food, drug and pharmaceutical regulating agencies such as the US FDA and their good manufacturing practices guidelines. Since a wide variety of procedures, processes, and activities need to be validated, the field of validation is divided into a number of subsections including the following:
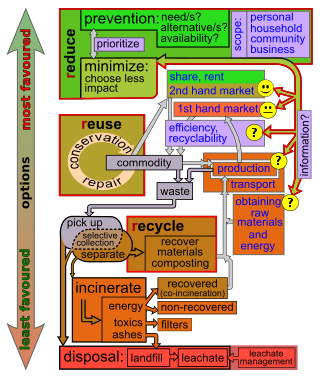
Waste minimisation is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. By reducing or eliminating the generation of harmful and persistent wastes, waste minimisation supports efforts to promote a more sustainable society. Waste minimisation involves redesigning products and processes and/or changing societal patterns of consumption and production.

An evaporator is a type of heat exchanger device that facilitates evaporation by utilizing conductive and convective heat transfer, which provides the necessary thermal energy for phase transition from liquid to vapor. Within evaporators, a circulating liquid is exposed to an atmospheric or reduced pressure environment, causing it to boil at a lower temperature compared to normal atmospheric boiling.

Open-end spinning is a technology for creating yarn without using a spindle. It was invented and developed in Czechoslovakia in Výzkumný ústav bavlnářský / Cotton Research Institute in Ústí nad Orlicí in 1963.

Package testing or packaging testing involves the measurement of a characteristic or property involved with packaging. This includes packaging materials, packaging components, primary packages, shipping containers, and unit loads, as well as the associated processes.

The Easy Serving Espresso pod, is a small packed coffee pod with a paper filter covering for use in a non-grinding espresso machine. The E.S.E. standard was created by Italian Illy in the 1970s and is maintained by the "Consortium for the Development and the Protection of the E.S.E. Standard." It is open to all coffee roasters and machine manufacturers, making it the self-acclaimed "only open system available to the sector for espresso coffee prepared with paper pods".

Combi steamers are combination ovens that expand upon standard convection ovens in that they can also generate conventional moist steam or superheated steam and are capable of shifting between cooking modes automatically during the cooking process. They can be used to simultaneously steam vegetables or potatoes quickly and gently, while also roasting or braising meat and fish, or baking bread. The appliance is fit for many culinary applications, including baking, roasting, grilling, steaming, braising, blanching and poaching. These devices are cooking appliances typically used in professional catering or food service operations. They help gastronomy-industry professionals bridge the gap between economy and menu diversity while also maintaining the desired food quality.
Tool management is needed in metalworking so that the information regarding the tools on hand can be uniformly organized and integrated. The information is stored in a database and is registered and applied using tool management. Tool data management consists of specific data fields, graphics and parameters that are essential in production, as opposed to managing general production equipment.














