
A dye is a colored substance that has an affinity to the substrate to which it is being applied. The dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution, and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. This is achieved through either absorption or adsorption with the adsorbing substance becoming physically changed somewhat. This could be an increase in volume, boiling point, viscosity, or other physical characteristic or property of the substance, as water molecules can become suspended between the substance's molecules in the process.

Fiber or fibre is a natural or synthetic substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene.

Glass fiber is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.
Fiberglass (US) or fibreglass (UK) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet, or woven into a fabric. The plastic matrix may be a thermoset polymer matrix—most often based on thermosetting polymers such as epoxy, polyester resin, or vinylester—or a thermoplastic.

Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibres from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Many kinds of paper are made from wood with nothing else mixed into them. This includes newspapers, magazines and even toilet paper. Pulp is one of the most abundant raw materials.

Paper engineering is a branch of engineering that deals with the usage of physical science and life sciences in conjunction with mathematics as applied to the converting of raw materials into useful paper products and co-products. The field applies various principles in process engineering and unit operations to the manufacture of paper, chemicals, energy and related materials. The following timeline shows some of the key steps in the development of the science of chemical and bioprocess engineering:
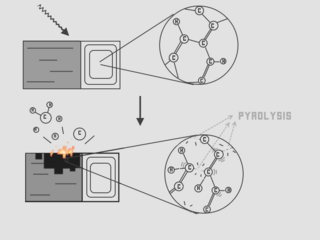
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. It involves the change of chemical composition and is irreversible. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements pyro "fire" and lysis "separating".
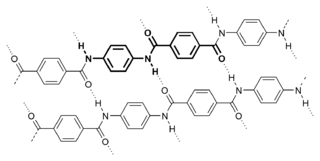
Aramid fibers are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers. They are used in aerospace and military applications, for ballistic-rated body armor fabric and ballistic composites, in bicycle tires, marine cordage, marine hull reinforcement, and as an asbestos substitute. The name is a portmanteau of "aromatic polyamide". The chain molecules in the fibers are highly oriented along the fiber axis. As a result, a higher proportion of the chemical bond contributes more to fiber strength than in many other synthetic fibers. Aramides have a very high melting point

Bagasse is the dry pulpy fibrous residue that remains after sugarcane or sorghum stalks are crushed to extract their juice. It is used as a biofuel for the production of heat, energy, and electricity, and in the manufacture of pulp and building materials.

The kraft process (also known as kraft pulping or sulfate process) is a process for conversion of wood into wood pulp, which consists of almost pure cellulose fibers, the main component of paper. The kraft process entails treatment of wood chips with a hot mixture of water, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and sodium sulfide (Na2S), known as white liquor, that breaks the bonds that link lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose. The technology entails several steps, both mechanical and chemical. It is the dominant method for producing paper. In some situations, the process has been controversial because kraft plants can release odorous products and in some situations produce substantial liquid wastes.

In industrial chemistry, black liquor is the waste product from the kraft process when digesting pulpwood into paper pulp removing lignin, hemicelluloses and other extractives from the wood to free the cellulose fibers.

Fragrance extraction refers to the separation process of aromatic compounds from raw materials, using methods such as distillation, solvent extraction, expression, sieving, or enfleurage. The results of the extracts are either essential oils, absolutes, concretes, or butters, depending on the amount of waxes in the extracted product.
Biological material may refer to:
The sulfite process produces wood pulp which is almost pure cellulose fibers by using various salts of sulfurous acid to extract the lignin from wood chips in large pressure vessels called digesters. The salts used in the pulping process are either sulfites (SO32−), or bisulfites (HSO3−), depending on the pH. The counter ion can be sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+) or ammonium (NH4+).

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter. In solids molecules are closely packed. It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice or irregularly. Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because in gases molecules are loosely packed.
Cellulose fibers are fibers made with ethers or esters of cellulose, which can be obtained from the bark, wood or leaves of plants, or from other plant-based material. In addition to cellulose, the fibers may also contain hemicellulose and lignin, with different percentages of these components altering the mechanical properties of the fibers.
In industrial paper-making processes, organosolv is a pulping technique that uses an organic solvent to solubilise lignin and hemicellulose. It has been considered in the context of both pulp and paper manufacture and biorefining for subsequent conversion of cellulose to fuel ethanol. The process was invented by Theodor Kleinert in 1968 as an environmentally benign alternative to kraft pulping.













