Related Research Articles

Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below princes and grand dukes. The title comes from French duc, itself from the Latin dux, 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank, and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word duchess is the female equivalent.

The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population of the Grand Duchy was about 1,815,000 inhabitants.
The Duchy of Savoy was a territorial entity of the Savoyard state that existed from 1416 until 1847 and was a possession of the House of Savoy.

Deux-Nèthes was a department of the First French Republic and of the First French Empire in present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. It was named after two branches of the river Nete. The southern part of its territory corresponds more or less with the present-day Belgian province of Antwerp. It was created on 1 October 1795, when the Austrian Netherlands were officially annexed by the French Republic. Its territory was the northern part of the former duchy of Brabant. After the annexation of the Kingdom of Holland in 1810, the department was expanded with the western half of the present-day Dutch province of North Brabant, itself historically part of the Duchy of Brabant.

Meuse-Inférieure was a department of the French First Republic and French First Empire in present-day Belgium, Netherlands and Germany. It was named after the river Meuse. Its territory corresponded largely with the present-day provinces of Belgian and Dutch Limburg. It was created on 1 October 1795, when the Austrian Netherlands and the Prince-Bishopric of Liège were officially annexed by the French Republic. Before this annexation, its territory was part of the County of Loon, the Austrian Upper Guelders, the Staats-Oppergelre, the County of Horne, the Abbacy of Thorn, Maastricht and part of the Lands of Overmaas. The original medieval Duchy of Limburg were associated with the Lands of Overmaas, lying to their south. The two regions had long been governed together and referred to collectively with both names, but the original Duchy lands were not part of this new entity.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm, which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

The Kingdom of Italy was a kingdom in Northern Italy that was a client state of Napoleon's French Empire. It was fully influenced by revolutionary France and ended with Napoleon's defeat and fall. Its government was assumed by Napoleon as King of Italy and the viceroyalty delegated to his stepson Eugène de Beauharnais. It covered some of Piedmont and the modern regions of Lombardy, Veneto, Emilia-Romagna, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Trentino, South Tyrol, and Marche. Napoleon I also ruled the rest of northern and central Italy in the form of Nice, Aosta, Piedmont, Liguria, Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, but directly as part of the French Empire, rather than as part of a vassal state.

Robert I ; 9 July 1848 – 16 November 1907) was the last sovereign Duke of Parma and Piacenza from 1854 until 1859, when the duchy was annexed to Sardinia-Piedmont during the Risorgimento. He was a member of the House of Bourbon-Parma and descended from Philip, Duke of Parma, the third son of King Philip V of Spain and Queen Elisabeth Farnese.

The Duchy of Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.

The Duchy of Amalfi or the Republic of Amalfi was a de facto independent state centered on the Southern Italian city of Amalfi during the 10th and 11th centuries. The city and its territory were originally part of the larger ducatus Neapolitanus, governed by a patrician, but it extracted itself from Byzantine vassalage and first elected a duke in 958.
The Vicariate Apostolic of Northern Germany, known for most of its existence as the Vicariate Apostolic of the NorthernMissions, was a Catholic missionary jurisdiction established on 28 April 1667. It belonged to a vicar apostolic in predominantly Protestant Northern Europe.
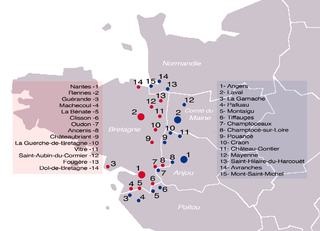
The Marches of Neustria were two marches created in 861 by the Carolingian king of West Francia Charles the Bald. They were ruled by officials appointed by the Monarchy of France, known as wardens, prefects or margraves. One march was created as a buffer against the Bretons and the other against the Norsemen.
Manso I or II was the Prefect of Amalfi from 898 to 914.
Lambert I was the Count of Nantes and Prefect of the Breton March between 818 and 831 and Duke of Spoleto between 834 and 836. Lambert succeeded his father Guy.

Guidobaldo II della Rovere was an Italian condottiero, who succeeded his father Francesco Maria I della Rovere as Duke of Urbino from 1538 until his death in 1574. He was a member of the House of La Rovere. Guidobaldo was an important patron of the arts in general, and of Titian in particular, commissioning his own portrait, and buying Titian's Venus of Urbino.

The March of Pannonia or Eastern March was a frontier march of the Carolingian Empire, named after the former Roman province of Pannonia and carved out of the preceding and larger Avar March.
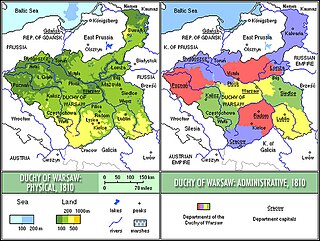
Subdivisions of the Duchy of Warsaw were based on departments that were headed by prefects. The subsidivions were based on the French model following the erection of the Duchy of Warsaw by Napoleon. The departments were in turn subdivided into traditional Polish powiats (counties). Initially six departments were created out of the province of South Prussia in the Kingdom of Prussia. After the 1809 Polish–Austrian War, and the Treaty of Schönbrunn, their number increased to ten. Each department was named after its capital city.
Flavianus was a Roman civil official who served as governor or prefect of Egypt from 364 to 366. He was a native of Illyricum, the only one since the emperor Constantine I to hold the office. Flavianus was apparently already serving in some administrative capacity in Egypt, perhaps as praeses, before succeeding Maximus as prefect in 364. On 5 May 365 he received from the emperor Valens an edict on banished bishops, and on 8 June he sent the emperor a report seeking instructions on how to deal with the trinitarian bishop Athanasius. On 5 October 365, Flavianus, alongside the dux Victorinus, tried to arrest Athanasius, who escaped. On 1 February 366, he was instructed, through the notary Brasidas, to desist and allow Athanasius to return. Flavianus was succeeded as prefect after 21 July by Proclianus.

The Principality of Lucca and Piombino was created in July 1805 by Napoleon I for his sister Elisa Bonaparte. It was a state located on the central Italian Peninsula and was a client state of Napoleonic France.

Pierre Dartout is a French civil servant who was the Minister of State of Monaco from 2020 to 2024 under Prince Albert II. He previously served as a prefect in France from 1997 to 2020. His first posting was in French Guiana. Upon the announcement of his appointment in Monaco, he was in office in Bouches-du-Rhône. Dartout held key positions in the prefecture corps from 1980.
References
- Skinner, Patricia. Family Power in Southern Italy: The Duchy of Gaeta and its Neighbours, 850-1139. Cambridge University Press: 1995.