Labour or labor may refer to:
Childbirth, also known as labour or delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies leaves the uterus by passing through the vagina or by Caesarean section. In 2015, there were about 135 million births globally. About 15 million were born before 37 weeks of gestation, while between 3 and 12% were born after 42 weeks. In the developed world most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing world most births take place at home with the support of a traditional birth attendant.
Do, DO or D.O. may refer to:
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and live birth, where the baby is born alive, if they die shortly after.
A stillborn is a baby born without signs of life.
Courier Mail may refer to:
Limelight is a type of stage lighting used during the nineteenth century.

The Kleihauer–Betke ("KB") test, Kleihauer–Betke ("KB") stain, Kleihauer test or acid elution test, is a blood test used to measure the amount of fetal hemoglobin transferred from a fetus to a mother's bloodstream. It is usually performed on Rh-negative mothers to determine the required dose of Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIg) to inhibit formation of Rh antibodies in the mother and prevent Rh disease in future Rh-positive children. It is named after Enno Kleihauer and Klaus Betke who described it in 1957.
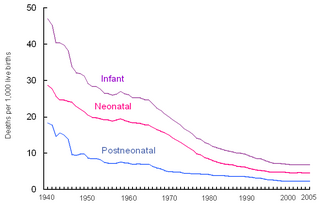
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion or exclusion of early fetal and late neonatal fatalities. The World Health Organization defines perinatal mortality as the "number of stillbirths and deaths in the first week of life per 1,000 total births, the perinatal period commences at 22 completed weeks of gestation, and ends seven completed days after birth", but other definitions have been used.

Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), also known as obstetric cholestasis, cholestasis of pregnancy, jaundice of pregnancy, and prurigo gravidarum, is a medical condition in which cholestasis occurs during pregnancy. It typically presents with itching and can lead to complications for both mother and baby.
Pregnant patients rights refers to the choices and legal rights available to a woman experiencing pregnancy or childbirth. Specifically those under medical care within a medical establishment or those under the care of a medical professional regardless of location.

Return to Zero is a drama film written and directed by Sean Hanish and stars Minnie Driver, Paul Adelstein, Alfred Molina, Connie Nielsen, Andrea Anders, Kathy Baker, and Sarah Jones with Peter Jason. It was first shown at the Cinequest Film Festival on March 8, 2014, then had an international premiere on the Lifetime Network on May 17, 2014. It was the first Lifetime original to receive a simultaneous international release.
Locked twins is a rare complication of multiple pregnancy where two fetuses become interlocked during presentation before birth. It occurs in roughly 1 in 1,000 twin deliveries and 1 in 90,000 deliveries overall. Most often, locked twins are delivered via Caesarean section, given that the condition has been diagnosed early enough. The fetal mortality rate is high for the twin that presents first, with over 50% being stillborn.
Toxic abortion is a medical phenomenon of spontaneous abortion, miscarriage, or stillbirth caused by toxins in the environment of the mother during pregnancy, especially as caused by toxic environmental pollutants, though sometimes reported as caused by naturally occurring plant toxins
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.




