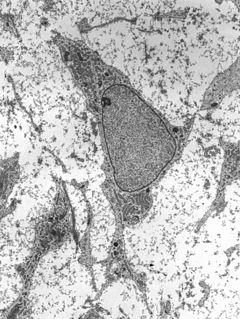
Multiple myeloma, also known as plasma cell myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell normally responsible for producing antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. When advanced, bone pain, bleeding, frequent infections, and anemia may occur. Complications may include amyloidosis.
Bone marrow suppression also known as myelotoxicity or myelosuppression, is the decrease in production of cells responsible for providing immunity (leukocytes), carrying oxygen (erythrocytes), and/or those responsible for normal blood clotting (thrombocytes). Bone marrow suppression is a serious side effect of chemotherapy and certain drugs affecting the immune system such as azathioprine. The risk is especially high in cytotoxic chemotherapy for leukemia.
Filgrastim, sold under the brand name Neupogen among others, is a medication used to treat low blood neutrophils. Low neutrophils may occur with HIV/AIDS, following chemotherapy or radiation poisoning, or be of an unknown cause. It may also be used to increase white blood cells for gathering during leukapheresis. It is given either by injection into a vein or under the skin.

Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood. It may be autologous, allogeneic or syngeneic.
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a medical complication following the receipt of transplanted tissue from a genetically different person. GvHD is commonly associated with stem cell transplants such as those that occur with bone marrow transplants. GvHD also applies to other forms of transplanted tissues such as solid organ transplants.
Cell therapy is therapy in which cellular material is injected into a patient; this generally means intact, living cells. For example, T cells capable of fighting cancer cells via cell-mediated immunity may be injected in the course of immunotherapy.
The National Marrow Donor Program (NMDP) is a nonprofit organization founded in 1986 and based in Minneapolis, Minnesota that operates the Be The Match Registry of volunteer hematopoietic cell donors and umbilical cord blood units in the United States.

Plerixafor is an immunostimulant used to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells in cancer patients into the bloodstream. The stem cells are then extracted from the blood and transplanted back to the patient. The drug was developed by AnorMED, which was subsequently bought by Genzyme.
Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) is a serious chronic leukemia that affects children mostly aged 4 and younger. The name JMML now encompasses all diagnoses formerly referred to as juvenile chronic myeloid leukemia (JCML), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia of infancy, and infantile monosomy 7 syndrome. The average age of patients at diagnosis is 2 years old. The World Health Organization has included JMML in the category of myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative disorders.
A micrometastasis is a small collection of cancer cells that has been shed from the original tumor and spread to another part of the body through the lymphovascular system. Micrometastases are too few, in size and quantity, to be picked up in a screening or diagnostic test, and therefore cannot be seen with imaging tests such as a mammogram, MRI, ultrasound, PET, or CT scans. These migrant cancer cells may group together to form a second tumor, which is so small that it can only be seen under a microscope. Approximately ninety percent of people who die from cancer die from metastatic disease, since these cells are so challenging to detect. It is important for these cancer cells to be treated immediately after discovery, in order to prevent the relapse and the likely death of the patient.
Autologous stem-cell transplantation is autologous transplantation of stem cells—that is, transplantation in which stem cells are removed from a person, stored, and later given back to that same person.
Dose-dense chemotherapy is a chemotherapy treatment plan in which drugs are given with less time between treatments than in a standard chemotherapy treatment plan.
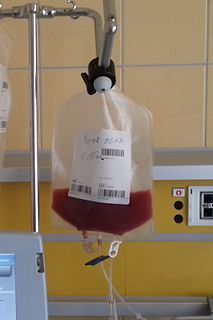
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT), also called "Peripheral stem cell support", is a method of replacing blood-forming stem cells destroyed, for example, by cancer treatment. PBSCT is now a much more common procedure than its bone marrow harvest equivalent, this is in-part due to the ease and less invasive nature of the procedure. Studies suggest that PBSCT has a better outcome in terms of the number of hematopoietic stem cell yield.

The Gift of Life Marrow Registry is a public bone marrow and blood stem cell registry headquartered in Boca Raton, Florida. Gift of Life facilitates transplants for children and adults suffering from life-threatening illnesses, including leukemia, lymphoma, other cancers and genetic diseases.

Childhood leukemia is leukemia that occurs in a child and is a type of childhood cancer. Childhood leukemia is the most common childhood cancer, accounting for 29% of cancers in children aged 0–14 in 2018. There are multiple forms of leukemia that occur in children, the most common being acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) followed by acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Survival rates vary depending on the type of leukemia, but may be as high as 90% in ALL.
Bone marrow failure occurs in individuals who produce an insufficient amount of red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets. Red blood cells transport oxygen to be distributed throughout the body’s tissue. White blood cells fight off infections that enter the body. Bone marrow also contains platelets, which trigger clotting, and thus help stop the blood flow when a wound occurs.
High-dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant (HDC/BMT), also high-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow transplant, was a treatment regimen for metastatic breast cancer, and later high-risk breast cancer, that was considered promising during the 1980s and 1990s. It was ultimately determined to be no more effective than normal treatment, and to have significantly higher side effects, including treatment-related death.
Guo Mei is a hematologist and associate director of 307th Hospital of Chinese People’s Liberation Army and deputy director of Radiation Research Institute.
Andrew Louis Pecora is an American hematologist and oncologist who has been involved in the research on the use of stem cells and oncolytic viruses to treat diseases, including cancer. He currently serves as chief innovations officer, professor and vice president of cancer services at the John Theurer Cancer Center, part of the Hackensack University Medical Center.