
The biceps is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes the forearm and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps unscrews the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion).

The recovery position refers to one of a series of variations on a lateral recumbent or three-quarters prone position of the body, in to which an unconscious but breathing casualty can be placed as part of first aid treatment.
In grammar, a supine is a form of verbal noun used in some languages. The term is most often used for Latin, where it is one of the four principal parts of a verb. The word refers to a position of lying on one's back, but there exists no widely accepted etymology that explains why or how the term came to be used to also describe this form of a verb.

The spread eagle is the position in which a person has their arms outstretched and legs apart, figuratively resembling an eagle with wings spread. It is a style that appears commonly in nature and geometry. In human style it is represented by the letter "X".

Prone position is a body position in which the person lies flat with the chest down and the back up. In anatomical terms of location, the dorsal side is up, and the ventral side is down. The supine position is the 180° contrast.

Inferior vena cava syndrome (IVCS) is a constellation of symptoms resulting from obstruction of the inferior vena cava. It can be caused by physical invasion or compression by a pathological process or by thrombosis within the vein itself. It can also occur during pregnancy. Pregnancy leads to high venous pressure in the lower limbs, decreased blood return to the heart, decreased cardiac output due to obstruction of the inferior vena cava, sudden rise in venous pressure which can lead to placental separation, and a decrease in kidney function. All of these issues can arise from lying in the supine position during late pregnancy which can cause compression of the inferior vena cava by the uterus. Symptoms of late pregnancy inferior vena cava syndrome consist of intense pain in the right hand side, muscle twitching, hypotension, and fluid retention.
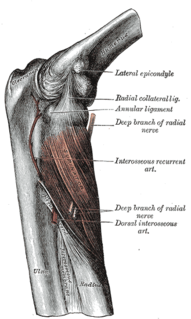
In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius. Its function is to supinate the forearm.
A peripheral vascular examination is a medical examination to discover signs of pathology in the peripheral vascular system. It is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with leg pain suggestive of a cardiovascular pathology.
Five temperaments is a theory in psychology, that expands upon the four temperaments proposed in ancient medical theory.

Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the joints. Anatomists use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing the uniqueness of the movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes.
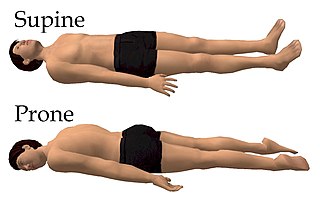
The supine position means lying horizontally with the face and torso facing up, as opposed to the prone position, which is face down. When used in surgical procedures, it allows access to the peritoneal, thoracic and pericardial regions; as well as the head, neck and extremities.

Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) is the volume of air present in the lungs at the end of passive expiration. At FRC, the opposing elastic recoil forces of the lungs and chest wall are in equilibrium and there is no exertion by the diaphragm or other respiratory muscles.
Nephroptosis, is an abnormal condition in which the kidney drops down into the pelvis when the patient stands up. It is more common in women than in men. It has been one of the most controversial conditions in terms of both its diagnosis and its treatments.
Aortocaval compression syndrome is compression of the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava by the gravid uterus when a pregnant woman lies on her back, i.e. in the supine position. It is a frequent cause of low maternal blood pressure (hypotension), which can result in loss of consciousness and in extreme circumstances fetal demise.

The bridge is a grappling move performed from a supine position, lying down face-up. It involves lifting the pelvis off the ground so that the body weight is supported on the shoulders at one end and on the feet at the other. This move is used in wrestling and other grappling and groundfighting sports, often combined with a twisting motion, to dislodge or flip an opponent who has established a position on top. The bridge is also a common exercise position. This maneuver can also be used to dodge pin attempts.

The Safe to Sleep campaign, formerly known as the Back to Sleep campaign, is an initiative backed by the US National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) at the US National Institutes of Health to encourage parents to have their infants sleep on their backs to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome, or SIDS. Since "Safe to Sleep" was launched in 1994, the incidence of SIDS has declined by more than 50%.

An abdominal x-ray is an x-ray of the abdomen. It is sometimes abbreviated to AXR, or KUB.
Tummy time is a colloquialism used to encourage parents to ensure that their infant children spend time in the prone position while awake and supervised.
The supine row is an exercise in weight training. It primarily works the muscles of the upper back—the trapezius and latissimus dorsi—as well as the biceps as a secondary muscle group. The supine row is normally carried out in three to five sets, but repetitions depend on the type of training a lifter is using to make their required gains.
Surgical positioning is the practice of placing a patient in a particular physical position during surgery. The goal in selecting and adjusting a particular surgical position is to maintain the patient's safety while allowing access to the surgical site. Often a patient must be placed in an unnatural position to gain access to the surgical site.











