Related Research Articles
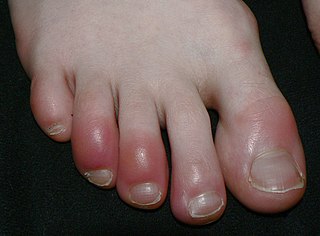
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue, resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly blisters.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The superficial fibular nerve is a mixed nerve that provides motor innervation to the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles, and sensory innervation to skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot.
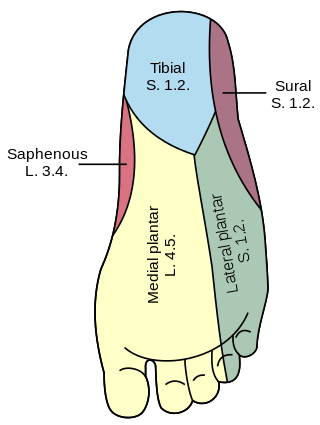
The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

The medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.

The intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, the smaller, passes along the lateral part of the dorsum of the foot, and divides into dorsal digital branches, which supply the contiguous sides of the third and fourth, and of the fourth and fifth toes.

The medial dorsal cutaneous nerve passes in front of the ankle-joint, and divides into two dorsal digital branches, one of which supplies the medial side of the great toe, the other, the adjacent side of the second and third toes.

Trachyonychia is a condition characterized by rough accentuated linear ridges on the nails of the fingers and toes. When the condition occurs on all the twenty nails of the fingers and toes, it is known as twenty-nail dystrophy, most evident in childhood, favoring males.

Dorsal digital nerves of foot are branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, sural nerve and deep fibular nerve.

Dermatitis repens is a rare, sterile, pustular eruption of the fingers and toes that slowly extends proximally.
Acral fibrokeratoma is a skin lesion characterized by a pinkish, hyperkeratotic, hornlike projection occurring on a finger, toe, or palm.

In racquet nails, the nail plate is flattened, the end of the thumb is widened and flattened, and the distal phalanx is abnormally short. In racquet nails, the width of the nail bed and nail plate is greater than their length. The condition is painless and asymptomatic.
Tricho–rhino–phalangeal syndrome type 2 is a genetic disorder consisting of fine and sparse scalp hair, thin nails, pear-shaped broad nose, and cone-shaped epiphyses of the middle phalanges of some fingers and toes.
A diabetic bulla is a cutaneous condition characterized by a noninflammatory, spontaneous, painless blister, often in acral locations, seen in diabetic patients.

An acral nevus is a cutaneous condition of the palms, soles, fingers, or toes, characterized by a skin lesion that is usually macular or only slightly elevated, and may display a uniform brown or dark brown color, often with linear striations.

Fibroma of tendon sheath is a benign tumor that presents as a small subcutaneous nodule that slowly increases in size. The tumors often have a multinodular growth pattern, with individual nodules being composed of bland, slender, spindle-shaped cells (myofibroblasts) in a dense, fibrous matrix.” A common microscopic finding is the presence of elongated, slit-like blood vessels. The lesions nearly always arise in the distal portions of the extremities. They often occur on the fingers, hands, toes, or feet. Although they are benign, they may recur in up to 40% of cases.
Runner's rump is a cutaneous condition characterized by a small ecchymoses in upper gluteal cleft caused by constant friction with each stride when running.
Progressive osseous heteroplasia is a cutaneous condition characterized by cutaneous or subcutaneous ossification.
Maternal autoimmune bullous disease is a blistering skin condition that presents at birth.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1371. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.