Thursday is the day of the week between Wednesday and Friday. According to the ISO 8601 international standard, it is the 4th day of the week. In countries which adopt the "Sunday-first" convention, it is the fifth day of the week.

Central Sulawesi is a province of Indonesia located at the centre of the island of Sulawesi. The administrative capital and largest city is located in Palu. The province borders the provinces of Gorontalo to the east, Southeast Sulawesi, South Sulawesi, and West Sulawesi to the south, and sharing maritime borders with East Kalimantan to the west, North Maluku to the east, and Malaysia and the Philippines to the north.

North Sulawesi is a province of Indonesia. It is mainly located on the Minahasa Peninsula of the island of Sulawesi, south of the Philippines and southeast of Sabah, Malaysia, but also includes various small archipelagoes situated between the Minahasa Peninsula and southern Philippines. It borders the Philippines province of Davao Occidental and Soccsksargen regions to the north, the Maluku Sea to the east, Gorontalo and the Celebes Sea to the west and the Gulf of Tomini to the southwest. The province's furthest extent, the outlying and isolated island of Miangas to its north, is the northernmost island of Indonesia that has the country's sole and only border with the Philippines.
In Modern English, the name of Sweden is derived from 17th century Middle Dutch and Middle Low German. In Old English, the country was named Swēoland and Swēorīċe ; the latter is cognate with Old Norse Svíaríki. Anglo-Norman of the 12th and 13th centuries used Suane and Swane. In Scots, Swane and Swaine appear in the 16th century. Early Modern English used Swedeland.

The Elder Futhark, also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Period. Inscriptions are found on artifacts including jewelry, amulets, plateware, tools, and weapons, as well as runestones, from the 1st to the 9th centuries.

The Kashia Band of Pomo Indians of the Stewarts Point Rancheria is a federally recognized tribe of Pomo people in Sonoma County, California. They are also known as the Kashaya Pomo.

Salaga is a town and is the capital of East Gonja district, a district in the Savannah Region of north Ghana. Salaga had a 2012 settlement population of 25,472 people. Salaga was the largest slave market in the 18th and 19th centuries.

Gorontalo is a city and the capital of the Gorontalo Province, Sulawesi, Indonesia. The city has an area of 79.59 km2 and had a population of 179,991 at the 2010 census and 198,539 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 205,390. Previously part of North Sulawesi, it became the capital of the newly-formed Gorontalo Province on 5 December 2000 when that province was separated from North Sulawesi. As the largest settlement and the only city in the province, it is the economic, political, and educational center of the province, hosting most of its universities and is the location of one of the only two public university in the province.
Haramaya is one of the woreda in the East Hararghe zone, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. It is named from the Haramaya lake that found in the woreda. The word Haramaya is come from two Oromo language word's[Hara and Maya] Hara means Lake and maya means name of person so Haramaya means the 'lake of maya'. Haramaya is bordered on the south by Kurfa Chele, on the west by Kersa, on the north by Dire Dawa, on the east by Kombolcha, and on the southeast by the Harari Region. The woreda has 33 rural keble and 4 administrative towns. Towns include Haramaya, Addele, Aweday and sharif kaled.

Bone Bolango is a regency of Gorontalo Province, Indonesia, on the island of Sulawesi. It was established in 2003 under Law Number 6/2003 from the former eastern districts of Gorontalo Regency. It has an area of 1,915.44 km2 and had a population of 141,915 at the 2010 Census and 162,778 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 172,301. The administrative centre of the regency is the town of Suwawa.
The Gorontalo–Mongondow languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia.
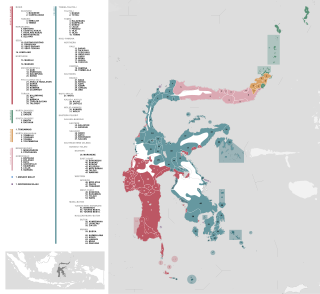
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.

Luwu Regency is a regency in South Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. On 20 April 1999, the northern districts of the original regency were separated to form North Luwu Regency. Subsequently, on 25 February 2003, some districts of North Luwu Regency were further split off to establish East Luwu Regency. Additionally, the former capital of Luwu Regency, Palopo, was designated as an independent municipality (city) on 10 April 2002.

Otanaha Fortress is one of the tourism site in Gorontalo province Suwalesi Island, Indonesia. It was built in 1522 by King Ilato from Gorontalo Kingdom and Portuguese sailors to strengthen the area security and defense. Located in Dembe Hill, this fort was made from mixture of sand, calcium, and eggs of Maleo birds. To reach the top of this fort, there are 348 steps, which separated into four stopovers: 52 steps from base to the first stopover, 83 steps from first to second stopover, 53 second to third stopover, and 89 steps from third to fourth stopover. From the last stopover, there are another 71 steps to reach the fort. From the top of this fortress, there are panoramic view of Limboto Lake and some part of Gorontalo region.
Ponosakan is a moribund Austronesian language spoken in the vicinity of the district of Belang, Southeast Minahasa, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. This language is almost extinct, with only four fluent speakers left as of November 2014.
Suwawa is a Philippine language spoken in North Sulawesi (Celebes), Indonesia. It is also known as Bonda, Bone, Bunda, Bune, Suvava, and Toewawa. The language mostly spoken in Suwawa District, Regency of Bone Bolango.

Gorontalo people, also known as Gorontalese, are an Austronesian ethnic group native to Gorontalo province. The Gorontalo people have traditionally been concentrated in the provinces of Gorontalo, North Sulawesi, and the northern part of Central Sulawesi.

The Mongondow or Bolaang Mongondow people are an Austronesian ethnic group native to western part of the North Sulawesi. The Mongondows are predominantly Muslim. They have traditionally been concentrated in the provinces of North Sulawesi and Gorontalo. This ethnic group used to be united by a single entity, the Kingdom of Bolaang Mongondow, which became the western regencies of North Sulawesi after the Indonesian independence.

Gorontalo is a province of Indonesia on the island of Sulawesi. Located on the Minahasa Peninsula, Gorontalo was formerly part of the province of North Sulawesi until its inauguration as a separate province on 5 December 2000. The province is bordered by the provinces of North Sulawesi to the east and Central Sulawesi to the west, as well sharing a maritime border with the Philippines in the Sulawesi Sea to the north, and a coastline on the Gulf of Tomini to the south. The provincial capital, as well as the main gateway to the province and its most populated city, is Gorontalo. The size is comparable to Vanuatu.












