Related Research Articles

Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings, as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known branch of heraldry, concerns the design and transmission of the heraldic achievement. The achievement, or armorial bearings usually includes a coat of arms on a shield, helmet and crest, together with any accompanying devices, such as supporters, badges, heraldic banners and mottoes.

The coat of arms of the Kingdom of Sweden is the arms of dominion of the King of Sweden. It has a greater and a lesser version. The shield displays the "Three Crowns of Sweden" quartering the "Lion of Bjelbo", with an inescutcheon overall of the House of Vasa impaling the House of Bernadotte.

The Sun of May is a national symbol of Argentina and Uruguay, appearing on both of their flags.

Three Crowns is the national emblem of Sweden, present in the coat of arms of Sweden, and composed of three yellow or gilded coronets ordered two above and one below, placed on a blue background. Similar designs are found on a number of other coats of arms or flags.

Swedish heraldry encompasses heraldic achievements in modern and historic Sweden. Swedish heraldic style is consistent with the German-Nordic heraldic tradition, noted for its multiple helmets and crests which are treated as inseparable from the shield, its repetition of colours and charges between the shield and the crest, and its scant use of heraldic furs. Because the medieval history of the Nordic countries was so closely related, their heraldic individuality developed rather late. Swedish and Finnish heraldry have a shared history prior to the Diet of Porvoo in 1809; these, together with Danish heraldry, were heavily influenced by German heraldry. Unlike the highly stylized and macaronic language of English blazon, Swedish heraldry is described in plain language, using only Swedish terminology.

The coat of arms of Norway is the arms of dominion of King Harald V of Norway, and as such represents both the monarch and the kingdom. It depicts a standing golden lion on a red background, bearing a golden crown and axe with silver blade.

A Nordic cross flag is a flag bearing the design of the Nordic or Scandinavian cross, a cross symbol in a rectangular field, with the centre of the cross shifted towards the hoist.
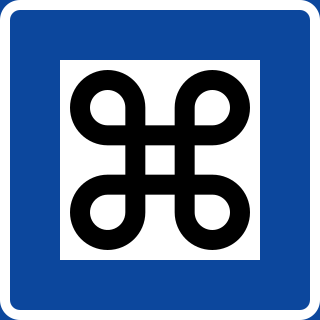
The looped square (⌘), also known as Saint John's Arms, Saint Hannes cross, and as the command-key symbol due to its use on the command key on Apple computer keyboards, is a symbol consisting of a square with outward pointing loops at its corners. It is referred to as a looped square, for example, in works regarding the Mississippian culture. It is also known as the place of interest sign when used on information signs, a practice that started in Finland in the 1950s, spreading to the other Nordic countries in the 1960s.

The Royal Standard of Norway is used by the King of Norway. Of historical origin, it was introduced by Cabinet Decision of 15 November 1905, following the plebiscite confirming the election of Prince Carl of Denmark to the vacant throne after the dissolution of the union between Sweden and Norway. Under his chosen name of Haakon VII, the new king arrived in the capital Kristiania on 25 November 1905 on a ship flying the royal standard for the first time.

Norwegian heraldry has roots in early medieval times, soon after the use of coats of arms first appeared in continental Europe. Some of the medieval coats of arms are rather simple of design, while others have more naturalistic charges. The king-granted coats of arms of later times were usually detailed and complex. Especially in the late 17th century and the 18th century, many ennobled persons and families received coats of arms with shields containing both two and four fields, and some even with an inescutcheon above these.
Danish heraldry has its roots in medieval times when coats of arms first appeared in Europe. Danish heraldry is a branch of the German-Nordic heraldic tradition.

Burgher arms or bourgeois arms are coats of arms borne by persons of the burgher social class of Europe since the Middle Ages. By definition, however, the term is alien to British heraldry, which follows other rules.

Norwegian Heraldry Society is a heraldry society located in Oslo, Norway, which was founded in 1969.

Icelandic heraldry is the study of coats of arms and other insignia used in Iceland. It belongs to the German-Nordic heraldic tradition, as the heraldry of Iceland has been primarily influenced by the heraldic traditions of Norway, Denmark and other Nordic countries. Iceland does not have a strong sense of heraldic tradition, however, because the country lacks a governing body to oversee this. As a result, coats of arms registered as such are virtually nonexistent in modern Iceland. While many municipalities use more or less heraldic logos, there are no heraldic standards to which these must adhere, and they are registered as graphic designs rather than as coats of arms.

A house mark was originally a mark of property, later also used as a family or clan emblem, incised on the facade of a building, on animals, in signet and similar in the farmer and burgher culture of Germany, the Netherlands and the Nordic countries.
St. John's Cross may refer to:
The Nordic diaspora may refer to:
For the purposes of this article, heraldry societies are defined as private associations of people who are interested in heraldry. Heraldic authorities, which have been established by reigning monarchs or governments, are dealt with in a separate article.
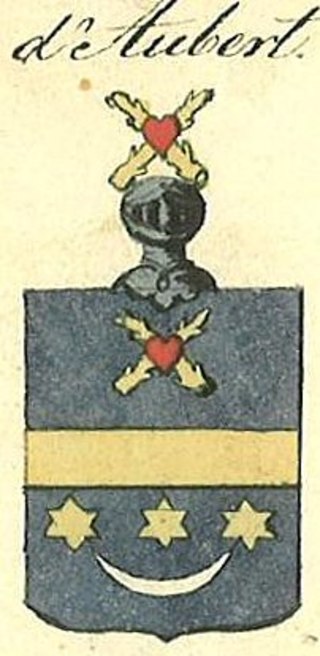
The d'Aubert family, or Aubert, is a family of the French nobility. Branches also belong to the Nobility of Denmark and to the Nobility of Norway. The family originates in the town of Thionville in Lothringen, where their progenitor Jean Aubert was a merchant. Today members live in France, in Denmark, in Norway, in Sweden, and in Germany.

Herman Leopoldus Løvenskiold, often known as Herman L. Løvenskiold, was a Norwegian ornithologist, photographer, government scholar and author on heraldry.
References
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(July 2024) |
- Heraldikkens femten glæder (The Fifteen Joys of Heraldry), 1971
- Alverdens heraldik i farver (Heraldry of the World - In Colours), translated, and edited from Carl Alexander von Volborth, 1972
- Danske adelsvåbener, en heraldisk nøgle (Danish Lordships Coats of Arms, a key to heraldry), 1973
- Symbols Around Us, 1978
- Danmarks kommunevåbener - samt Grønlands og Færøernes (Danish Municipal Heraldry, including Greenland and the Faeroe Islands), 1982
- Kroppens symbolik (Symbolics of the Body), 1983
- Symboler, hvad er det? (Symbols, what are they?), 1986