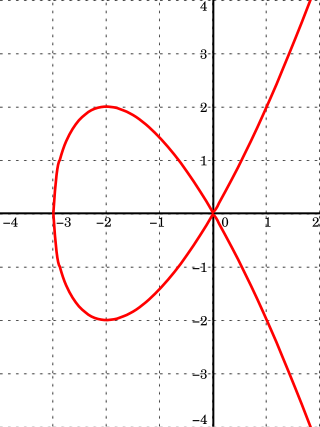In mathematics, a field F is algebraically closed if every non-constant polynomial in F[x] has a root in F. In other words, a field is algebraically closed if the fundamental theorem of algebra holds for it.

An algebraic number is a number that is a root of a non-zero polynomial in one variable with integer coefficients. For example, the golden ratio, , is an algebraic number, because it is a root of the polynomial x2 − x − 1. That is, it is a value for x for which the polynomial evaluates to zero. As another example, the complex number is algebraic because it is a root of x4 + 4.
In mathematics, a finite field or Galois field is a field that contains a finite number of elements. As with any field, a finite field is a set on which the operations of multiplication, addition, subtraction and division are defined and satisfy certain basic rules. The most common examples of finite fields are the integers mod p when p is a prime number.
In mathematics, particularly in algebra, a field extension is a pair of fields , such that the operations of K are those of L restricted to K. In this case, L is an extension field of K and K is a subfield of L. For example, under the usual notions of addition and multiplication, the complex numbers are an extension field of the real numbers; the real numbers are a subfield of the complex numbers.
In mathematics, in the area of abstract algebra known as Galois theory, the Galois group of a certain type of field extension is a specific group associated with the field extension. The study of field extensions and their relationship to the polynomials that give rise to them via Galois groups is called Galois theory, so named in honor of Évariste Galois who first discovered them.
In mathematics, an integral domain is a nonzero commutative ring in which the product of any two nonzero elements is nonzero. Integral domains are generalizations of the ring of integers and provide a natural setting for studying divisibility. In an integral domain, every nonzero element a has the cancellation property, that is, if a ≠ 0, an equality ab = ac implies b = c.

In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several factors, usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind. For example, 3 × 5 is an integer factorization of 15, and (x – 2)(x + 2) is a polynomial factorization of x2 – 4.
In algebraic number theory, an algebraic integer is a complex number that is integral over the integers. That is, an algebraic integer is a complex root of some monic polynomial whose coefficients are integers. The set of all algebraic integers A is closed under addition, subtraction and multiplication and therefore is a commutative subring of the complex numbers.

In mathematics, a root of unity, occasionally called a de Moivre number, is any complex number that yields 1 when raised to some positive integer power n. Roots of unity are used in many branches of mathematics, and are especially important in number theory, the theory of group characters, and the discrete Fourier transform.
In mathematics, an irreducible polynomial is, roughly speaking, a polynomial that cannot be factored into the product of two non-constant polynomials. The property of irreducibility depends on the nature of the coefficients that are accepted for the possible factors, that is, the ring to which the coefficients of the polynomial and its possible factors are supposed to belong. For example, the polynomial x2 − 2 is a polynomial with integer coefficients, but, as every integer is also a real number, it is also a polynomial with real coefficients. It is irreducible if it is considered as a polynomial with integer coefficients, but it factors as if it is considered as a polynomial with real coefficients. One says that the polynomial x2 − 2 is irreducible over the integers but not over the reals.
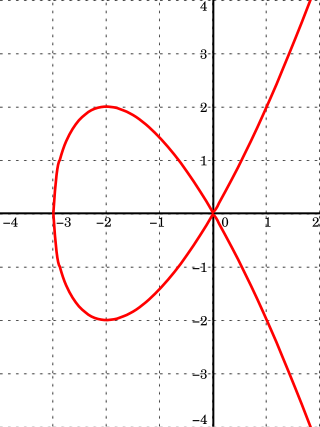
In mathematics, an affine algebraic plane curve is the zero set of a polynomial in two variables. A projective algebraic plane curve is the zero set in a projective plane of a homogeneous polynomial in three variables. An affine algebraic plane curve can be completed in a projective algebraic plane curve by homogenizing its defining polynomial. Conversely, a projective algebraic plane curve of homogeneous equation h(x, y, t) = 0 can be restricted to the affine algebraic plane curve of equation h(x, y, 1) = 0. These two operations are each inverse to the other; therefore, the phrase algebraic plane curve is often used without specifying explicitly whether it is the affine or the projective case that is considered.
In mathematics, especially in the field of algebra, a polynomial ring or polynomial algebra is a ring formed from the set of polynomials in one or more indeterminates with coefficients in another ring, often a field.
In mathematics, the ring of integers of an algebraic number field is the ring of all algebraic integers contained in . An algebraic integer is a root of a monic polynomial with integer coefficients: . This ring is often denoted by or . Since any integer belongs to and is an integral element of , the ring is always a subring of .
In abstract algebra, a normal extension is an algebraic field extension L/K for which every irreducible polynomial over K that has a root in L splits into linear factors in L. This is one of the conditions for an algebraic extension to be a Galois extension. Bourbaki calls such an extension a quasi-Galois extension. For finite extensions, a normal extension is identical to a splitting field.
In mathematics, the Hasse–Weil zeta function attached to an algebraic variety V defined over an algebraic number field K is a meromorphic function on the complex plane defined in terms of the number of points on the variety after reducing modulo each prime number p. It is a global L-function defined as an Euler product of local zeta functions.
In algebra, Gauss's lemma, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss, is a theorem about polynomials over the integers, or, more generally, over a unique factorization domain. Gauss's lemma underlies all the theory of factorization and greatest common divisors of such polynomials.
In mathematics and computer algebra, factorization of polynomials or polynomial factorization expresses a polynomial with coefficients in a given field or in the integers as the product of irreducible factors with coefficients in the same domain. Polynomial factorization is one of the fundamental components of computer algebra systems.
In field theory, a branch of mathematics, the minimal polynomial of an element α of an extension field of a field is, roughly speaking, the polynomial of lowest degree having coefficients in the smaller field, such that α is a root of the polynomial. If the minimal polynomial of α exists, it is unique. The coefficient of the highest-degree term in the polynomial is required to be 1.
In mathematics the Function Field Sieve is one of the most efficient algorithms to solve the Discrete Logarithm Problem (DLP) in a finite field. It has heuristic subexponential complexity. Leonard Adleman developed it in 1994 and then elaborated it together with M. D. Huang in 1999. Previous work includes the work of D. Coppersmith about the DLP in fields of characteristic two.
In mathematics, an algebraic number field is an extension field of the field of rational numbers such that the field extension has finite degree . Thus is a field that contains and has finite dimension when considered as a vector space over .