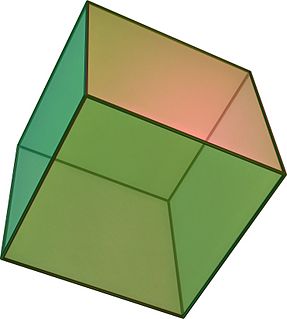
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex.

In mathematics, a group is a set equipped with a binary operation which combines any two elements to form a third element in such a way that four conditions called group axioms are satisfied, namely closure, associativity, identity and invertibility. One of the most familiar examples of a group is the set of integers together with the addition operation, but groups are encountered in numerous areas within and outside mathematics, and help focusing on essential structural aspects, by detaching them from the concrete nature of the subject of the study.

In mathematics and abstract algebra, group theory studies the algebraic structures known as groups.
The concept of a group is central to abstract algebra: other well-known algebraic structures, such as rings, fields, and vector spaces, can all be seen as groups endowed with additional operations and axioms. Groups recur throughout mathematics, and the methods of group theory have influenced many parts of algebra. Linear algebraic groups and Lie groups are two branches of group theory that have experienced advances and have become subject areas in their own right.

In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter.

In mathematics, a dihedral group is the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, which includes rotations and reflections. Dihedral groups are among the simplest examples of finite groups, and they play an important role in group theory, geometry, and chemistry.

Spontaneous symmetry breaking is a spontaneous process of symmetry breaking, by which a physical system in a symmetric state ends up in an asymmetric state. In particular, it can describe systems where the equations of motion or the Lagrangian obey symmetries, but the lowest-energy vacuum solutions do not exhibit that same symmetry. When the system goes to one of those vacuum solutions, the symmetry is broken for perturbations around that vacuum even though the entire Lagrangian retains that symmetry.

A wallpaper group is a mathematical classification of a two-dimensional repetitive pattern, based on the symmetries in the pattern. Such patterns occur frequently in architecture and decorative art, especially in textiles and tiles as well as wallpaper.

In crystallography, the terms crystal system, crystal family, and lattice system each refer to one of several classes of space groups, lattices, point groups, or crystals. Informally, two crystals are in the same crystal system if they have similar symmetries, although there are many exceptions to this.
Rotational symmetry, also known as radial symmetry in biology, is the property a shape has when it looks the same after some rotation by a partial turn. An object's degree of rotational symmetry is the number of distinct orientations in which it looks the same.

Floral symmetry describes whether, and how, a flower, in particular its perianth, can be divided into two or more identical or mirror-image parts.
In geometry, a point group in three dimensions is an isometry group in three dimensions that leaves the origin fixed, or correspondingly, an isometry group of a sphere. It is a subgroup of the orthogonal group O(3), the group of all isometries that leave the origin fixed, or correspondingly, the group of orthogonal matrices. O(3) itself is a subgroup of the Euclidean group E(3) of all isometries.

In physics, a symmetry of a physical system is a physical or mathematical feature of the system that is preserved or remains unchanged under some transformation.
In geometry, orbifold notation is a system, invented by William Thurston and popularized by the mathematician John Conway, for representing types of symmetry groups in two-dimensional spaces of constant curvature.
The advantage of the notation is that it describes these groups in a way which indicates many of the groups' properties: in particular, it describes the orbifold obtained by taking the quotient of Euclidean space by the group under consideration.
In geometry, Hermann–Mauguin notation is used to represent the symmetry elements in point groups, plane groups and space groups. It is named after the German crystallographer Carl Hermann and the French mineralogist Charles-Victor Mauguin. This notation is sometimes called international notation, because it was adopted as standard by the International Tables For Crystallography since their first edition in 1935.

Molecular symmetry in chemistry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can be used to predict or explain many of a molecule's chemical properties, such as its dipole moment and its allowed spectroscopic transitions. Many university level textbooks on physical chemistry, quantum chemistry, and inorganic chemistry devote a chapter to symmetry.

In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian is invariant under certain Lie groups of local transformations.

Time translation symmetry or temporal translation symmetry (TTS) is a mathematical transformation in physics that moves the times of events through a common interval. Time translation symmetry is the hypothesis that the laws of physics are unchanged, under such a transformation. Time translation symmetry is a rigorous way to formulate the idea that the laws of physics are the same throughout history. Time translation symmetry is closely connected, via the Noether theorem, to conservation of energy. In mathematics, the set of all time translations on a given system form a Lie group.












