
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically live in compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Corals species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton.

Coral Gables, officially the City of Coral Gables, is a city in Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States, located southwest of Downtown Miami. The United States Census Bureau estimates conducted in 2017 yielded the city had a population of 51,095. Coral Gables is home to the University of Miami.

Antipatharians, also known as Black corals, are an order of deep-water tree-like corals. Black corals were previously classified in the taxon Ceriantipatharia with the ceriantharians, but were later reclassified under Hexacorallia.

Scleractinia, also called stony corals or hard corals, are marine animals in the phylum Cnidaria that build themselves a hard skeleton. The individual animals are known as polyps and have a cylindrical body crowned by an oral disc in which a mouth is fringed with tentacles. Although some species are solitary, most are colonial. The founding polyp settles and starts to secrete calcium carbonate to protect its soft body. Solitary corals can be as much as 25 cm (10 in) across but in colonial species the polyps are usually only a few millimetres in diameter. These polyps reproduce asexually by budding, but remain attached to each other, forming a multi-polyp colony of clones with a common skeleton, which may be up to several metres in diameter or height according to species.

Coral Ridge Mall is an enclosed super-regional shopping mall located just south of Interstate 80 in Coralville, Iowa. The mall's primary trade area includes Iowa City, Cedar Rapids, and other parts of eastern Iowa. It is owned and managed by Brookfield Properties Retail Group, which acquired the original developer of the mall, General Growth Properties, in 2018.

Brain coral is a common name given to various corals in the families Mussidae and Merulinidae, so called due to their generally spheroid shape and grooved surface which resembles a brain. Each head of coral is formed by a colony of genetically identical polyps which secrete a hard skeleton of calcium carbonate; this makes them important coral reef builders like other stony corals in the order Scleractinia. Brain corals are found in shallow warm-water coral reefs in all the world's oceans. They are part of the phylum Cnidaria, in a class called Anthozoa or "flower animals". The lifespan of the largest brain corals is 900 years. Colonies can grow as large as 1.8 m (6 ft) or more in height.

White band disease is a coral disease that affects acroporid corals and is distinguishable by the white band of dead coral tissue that it forms. The disease completely destroys the coral tissue of Caribbean acroporid corals, specifically elkhorn coral and staghorn coral. The disease exhibits a pronounced division between the remaining coral tissue and the exposed coral skeleton. These symptoms are similar to white plague, except that white band disease is only found on acroporid corals, and white plague has not been found on any acroporid corals. It is part of a class of similar disease known as "white syndromes", many of which may be linked to species of Vibrio bacteria. While the pathogen for this disease has not been identified, Vibrio carchariae may be one of its factors. The degradation of coral tissue usually begins at the base of the coral, working its way up to the branch tips, but it can begin in the middle of a branch.

The staghorn coral is a branching, stony coral with cylindrical branches ranging from a few centimetres to over two metres in length and height. It occurs in back reef and fore reef environments from 0 to 30 m depth. The upper limit is defined by wave forces, and the lower limit is controlled by suspended sediments and light availability. Fore reef zones at intermediate depths 5–25 m (16–82 ft) were formerly dominated by extensive single-species stands of staghorn coral until the mid-1980s. This coral exhibits the fastest growth of all known western Atlantic fringe corals, with branches increasing in length by 10–20 cm (3.9–7.9 in) per year. This has been one of the three most important Caribbean corals in terms of its contribution to reef growth and fishery habitat.
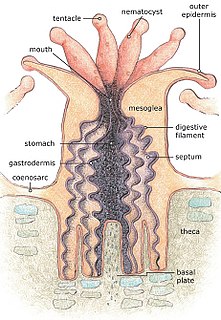
A corallite is the skeletal cup, formed by an individual stony coral polyp, in which the polyp sits and into which it can retract. The cup is composed of aragonite, a crystalline form of calcium carbonate, and is secreted by the polyp. Corallites vary in size, but in most colonial corals they are less than 3 mm (0.12 in) in diameter. The inner surface of the corallite is known as the calyx. The vertical blades inside the calyx are known as septa and in some species, these ridges continue outside the corallite wall as costae. Where there is no corallite wall, the blades are known as septocostae. The septa, costae and septocostae may have ornamentation in the form of teeth and may be thick, thin or variable in size. Sometimes there are paliform lobes, in the form of rods or blades, rising from the inner margins of the septa. These may form a neat circle called the paliform crown. The septa do not usually unite in the centre of the corallite, instead they form a columella, a tangled mass of intertwined septa, or a dome-shaped or pillar-like projection. In the living coral, the lower part of the polyp is in intimate contact with the corallite, and has radial mesenteries between the septa which increase the surface area of the body cavity and aid digestion. The septa, palliform lobes and costae can often be seen through the coenosarc, the layer of living tissue that covers the coenosteum, the part of the skeleton between the corallites.

Alcyonacea, or soft corals, is an order of corals which do not produce calcium carbonate skeletons. Formerly known as gorgonians, they are sessile colonial cnidarians found throughout the oceans of the world, especially in the tropics and subtropics. Common names for subset of this order are sea fans and sea whips and are similar to the sea pen, a soft coral. Individual tiny polyps form colonies that are normally erect, flattened, branching, and reminiscent of a fan. Others may be whiplike, bushy, or even encrusting. A colony can be several feet high and across but only a few inches thick. They may be brightly coloured, often purple, red, or yellow. Photosynthetic gorgonians can be successfully kept in captive reef aquariums.

Precious coral, or red coral, is the common name given to a genus of marine corals, Corallium. The distinguishing characteristic of precious corals is their durable and intensely colored red or pink-orange skeleton, which is used for making jewelry.

Fire corals (Millepora) are a genus of colonial marine organisms that exhibit physical characteristics similar to that of coral. The name coral is somewhat misleading, as fire corals are not true corals but are instead more closely related to Hydra and other hydrozoans, making them hydrocorals. They make up the only genus in the monotypic family Milleporidae.

Elkhorn coral is a prominent Caribbean reef-building coral, although current populations are still struggling to recover from white band disease outbreak. This species is structurally complex with many large branches. The coral structure resembles that of elk antlers. These branches create habitats for many other reef species, such as lobsters, parrot-fish, snapper shrimps and other reef fish. Elkhorn coral colonies are incredibly fast-growing, with an average growth rate of 5 to 10 cm per year and can eventually grow up to 3.7 m (12 ft) in diameter. The color of this coral species ranges from brown to a yellowish-brown as a result of the symbiotic zooxanthellae living inside the tissue of this coral species. Zooxanthellae are a type of algae which photosynthesize to provide the coral with nutrients. The zooxanthellae are also capable of removing waste products from the coral. Historically, the majority of elkhorn coral reproduction has occurred asexually; this occurs when a branch of the coral breaks off and attaches to the substrate, forming a new colony, known as fragmentation. The degree to which local stands reproduce by fragmentation varies across the Caribbean, but on average, 50% of colonies are the result of fragmentation rather than sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction occurs once a year in August or September when coral colonies release millions of gametes by broadcast spawning.

Xeniidae is a family of soft coral in the order Alcyonacea.
Miracle Marketplace is a shopping mall in Miami, United States, which opened in March 1989. It is located at 3301 Coral Way, just a few blocks east of Douglas Road, east of Coral Gables.

Acroporidae is a family of small polyped stony corals in the phylum Cnidaria. The name is derived from the Greek "akron" meaning "summit" and refers to the presence of a corallite at the tip of each branch of coral. They are commonly known as staghorn corals and are grown in aquaria by reef hobbyists.

Catalaphyllia is a monotypic genus of stony coral in the family Euphylliidae from the western Pacific Ocean. It is represented by a single species, Catalaphyllia jardinei, commonly known as elegance coral. It was first described by William Saville-Kent in 1893 as Pectinia jardinei.
Sympodium is a genus of soft corals in the family Xeniidae.
















