
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be specialized to develop flowers or short shoots or may have the potential for general shoot development. The term bud is also used in zoology, where it refers to an outgrowth from the body which can develop into a new individual.

In botany, an inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a plant's stem that is composed of a main branch or a system of branches. An inflorescence is categorized on the basis of the arrangement of flowers on a main axis (peduncle) and by the timing of its flowering.

Fruit tree pruning is the cutting and removing of selected parts of a fruit tree. It spans a number of horticultural techniques. Pruning often means cutting branches back, sometimes removing smaller limbs entirely. It may also mean removal of young shoots, buds, and leaves.

In botany and dendrology, a rhizome is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally. The rhizome also retains the ability to allow new shoots to grow upwards.

In botany, apical dominance is the phenomenon whereby the main, central stem of the plant is dominant over other side stems; on a branch the main stem of the branch is further dominant over its own side twigs.

Vascular plants with monopodial growth habits grow upward from a single point. They add leaves to the apex each year and the stem grows longer accordingly. The word Monopodial is derived from Greek "mono-", one and "podial", "foot", in reference to the fact that monopodial plants have a single trunk or stem.
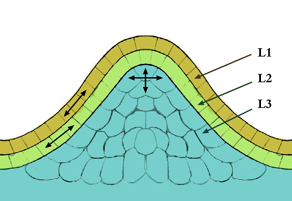
In cell biology, the meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until they become differentiated and lose the ability to divide.

A dichotomy is a partition of a whole into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be

In biology, stolons, also known as runners, are horizontal connections between parts of an organism. They may be part of the organism, or of its skeleton. Typically, animal stolons are exoskeletons.

The axillary bud is an embryonic or organogenic shoot located in the axil of a leaf. Each bud has the potential to form shoots, and may be specialized in producing either vegetative shoots or reproductive shoots (flowers). Once formed, a bud may remain dormant for some time, or it may form a shoot immediately.
Edible plant stems are a part of plants eaten by humans. Most plants are made up of stems, roots, leaves, flowers, and produce fruits containing seeds. Humans most commonly eat the seeds, fruit, flowers, leaves, roots, and stems (e.g. asparagus of many plants. There are also a few edible petioles such as celery or rhubarb.

In botany, secondary growth is the growth that results from cell division in the cambia or lateral meristems and that causes the stems and roots to thicken, while primary growth is growth that occurs as a result of cell division at the tips of stems and roots, causing them to elongate, and gives rise to primary tissue. Secondary growth occurs in most seed plants, but monocots usually lack secondary growth. If they do have secondary growth, it differs from the typical pattern of other seed plants.

A primordium in embryology, is an organ or tissue in its earliest recognizable stage of development. Cells of the primordium are called primordial cells. A primordium is the simplest set of cells capable of triggering growth of the would-be organ and the initial foundation from which an organ is able to grow. In flowering plants, a floral primordium gives rise to a flower.

Stigmaria is a form taxon for common fossils found in Carboniferous rocks. They represent the underground rooting structures of arborescent lycophytes such as Sigillaria and Lepidodendron under the order Lepidodendrales.
This page provides a glossary of plant morphology. Botanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. The accompanying page—Plant morphology—provides an overview of the science of the external form of plants. There is also an alphabetical list: Glossary of botanical terms. In contrast, this page deals with botanical terms in a systematic manner, with some illustrations, and organized by plant anatomy and function in plant physiology.
Important structures in plant development are buds, shoots, roots, leaves, and flowers; plants produce these tissues and structures throughout their life from meristems located at the tips of organs, or between mature tissues. Thus, a living plant always has embryonic tissues. By contrast, an animal embryo will very early produce all of the body parts that it will ever have in its life. When the animal is born, it has all its body parts and from that point will only grow larger and more mature. However, both plants and animals pass through a phylotypic stage that evolved independently and that causes a developmental constraint limiting morphological diversification.
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names.
Primary growth in plants is growth that takes place from the tips of roots or shoots. It leads to lengthening of roots and stems and sets the stage for organ formation. It is distinguished from secondary growth that leads to widening. Plant growth takes place in well defined plant locations. Specifically, the cell division and differentiation needed for growth occurs in specialized structures called meristems. These consist of undifferentiated cells capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until they differentiate and then lose the ability to divide. Thus, the meristems produce all the cells used for plant growth and function.

Dendrolycopodium obscurum, synonym Lycopodium obscurum, commonly called rare clubmoss, ground pine, or princess pine, is a North American species of clubmoss in the family Lycopodiaceae. It is a close relative of other species such as D. dendroideum and D. hickeyi, also treelike. It is native to the eastern United States and southeastern Canada from Georgia to Minnesota to Nova Scotia. It grows in the understory of temperate coniferous and deciduous forests, where it is involved in seral secondary succession, growing in clonal colonies some years after disturbance has occurred. It has also been found in Japan, Taiwan, Korea, Russian Far East, and northeastern China.
Topophysis occurs when scions, buddings, or root cuttings continue to grow in the same way after grafting as they had while growing on the ortet.
















