Related Research Articles
A fourth-generation programming language (4GL) is any computer programming language that belongs to a class of languages envisioned as an advancement upon third-generation programming languages (3GL). Each of the programming language generations aims to provide a higher level of abstraction of the internal computer hardware details, making the language more programmer-friendly, powerful, and versatile. While the definition of 4GL has changed over time, it can be typified by operating more with large collections of information at once rather than focusing on just bits and bytes. Languages claimed to be 4GL may include support for database management, report generation, mathematical optimization, GUI development, or web development. Some researchers state that 4GLs are a subset of domain-specific languages.
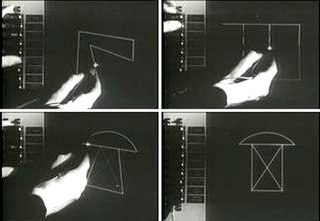
The history of the graphical user interface, understood as the use of graphic icons and a pointing device to control a computer, covers a five-decade span of incremental refinements, built on some constant core principles. Several vendors have created their own windowing systems based on independent code, but with basic elements in common that define the WIMP "window, icon, menu and pointing device" paradigm.

GNUstep is a free software implementation of the Cocoa Objective-C frameworks, widget toolkit, and application development tools for Unix-like operating systems and Microsoft Windows. It is part of the GNU Project.
HCL Notes and HCL Domino are the client and server, respectively, of a collaborative client-server software platform formerly sold by IBM, now by HCL Technologies.

Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) is the domain of software tools used to design and implement applications. CASE tools are similar to and were partly inspired by computer-aided design (CAD) tools used for designing hardware products. CASE tools are used for developing high-quality, defect-free, and maintainable software. CASE software is often associated with methods for the development of information systems together with automated tools that can be used in the software development process.
Oracle Forms is a software product for creating screens that interact with an Oracle database. It has an IDE including an object navigator, property sheet and code editor that uses PL/SQL. It was originally developed to run server-side in character mode terminal sessions. It was ported to other platforms, including Windows, to function in a client–server environment. Later versions were ported to Java where it runs in a Java EE container and can integrate with Java and web services.
Dataphor is an open-source truly-relational database management system (RDBMS) and its accompanying user interface technologies, which together are designed to provide highly declarative software application development. The Dataphor Server has its own storage engine or it can be a virtual, or federated, DBMS, meaning that it can utilize other database engines for storage.
A user interface markup language is a markup language that renders and describes graphical user interfaces and controls. Many of these markup languages are dialects of XML and are dependent upon a pre-existing scripting language engine, usually a JavaScript engine, for rendering of controls and extra scriptability.

Uniface is a low-code development and deployment platform for enterprise applications that can run in a large range of runtime environments, including mobile, mainframe, web, Service-oriented architecture (SOA), Windows, Java EE and .NET. Uniface is used to create mission-critical applications.
IBM InfoSphere DataStage is an ETL tool and part of the IBM Information Platforms Solutions suite and IBM InfoSphere. It uses a graphical notation to construct data integration solutions and is available in various versions such as the Server Edition, the Enterprise Edition, and the MVS Edition. It uses a client-server architecture. The servers can be deployed in both Unix as well as Windows.
OpenROAD stands for "Open Rapid Object Application Development". It is a software product of Actian Corporation.
Forté 4GL was a proprietary application server that was developed by Forté Software and used for developing scalable, highly available, enterprise applications.
LINC is a fourth-generation programming language, used mostly on Unisys computer systems.
IBM Informix C-ISAM is an X/Open standards-compliant Application programming interface (API) to an Indexed Sequential Access Method or ISAM.
Servoy is a development and deployment platform for enterprise applications, written itself in Java, and which uses JavaScript as its development language. It can adopt the native look and feel of any platform or the web, using HTML and CSS code. Servoy was created from the start to make business application development easy. It has introduced many innovations for that purpose: the use of JavaScript instead of Java, a comprehensive development framework with building blocks that are added through drag and drop, a web client, etc.
IBM's Cross System Product (CSP) was an application generator intended to create online systems on IBM's mainframe platforms. Introduced in 1981, CSP consisted of a set of source code generators that allowed developers to interactively define, test, generate, and execute application programs. CSP was composed of two products:
Informix Corporation was a software company located in Menlo Park, California. It was a developer of relational database software for computers using the Unix, Microsoft Windows, and Apple Macintosh operating systems.
Rocket U2 is a suite of database management (DBMS) and supporting software now owned by Rocket Software. It includes two MultiValue database platforms: UniData and UniVerse. Both of these products are operating environments which run on current Unix, Linux and Windows operating systems. They are both derivatives of the Pick operating system. The family also includes developer and web-enabling technologies including SystemBuilder/SB+, SB/XA, U2 Web Development Environment (WebDE), UniObjects and wIntegrate.
Forté is a proprietary application server that was developed by Forté Software and used for developing scalable, highly available, enterprise applications.
References
- ↑ 'Acquisition Announcement' Rocket Software