
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering.

Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines to applied disciplines.

Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use.
Integration may refer to:
Software engineering is a field within computer science focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining of software applications. It involves applying engineering principles and computer programming expertise to develop software systems that meet user needs.

Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.

Computer engineering is a branch of electrical engineering that integrates several fields of electrical engineering, electronics engineering and computer science required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer engineering is referred to as Electrical and Computer engineering OR Computer Science and Engineering at some universities
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using dedicated software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online content. Desktop publishing software can generate page layouts and produce text and image content comparable to the simpler forms of traditional typography and printing. This technology allows individuals, businesses, and other organizations to self-publish a wide variety of content, from menus to magazines to books, without the expense of commercial printing.
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems comprise four components: task, people, structure, and technology. Information systems can be defined as an integration of components for collection, storage and processing of data, comprising digital products that process data to facilitate decision making and the data being used to provide information and contribute to knowledge.
A computer scientist is a scientist who specializes in the academic study of computer science.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design, and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human–computer interaction:
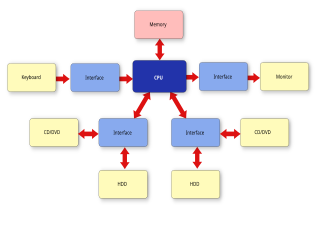
A system architecture is the conceptual model that defines the structure, behavior, and views of a system. An architecture description is a formal description and representation of a system, organized in a way that supports reasoning about the structures and behaviors of the system.

In engineering, hardware architecture refers to the identification of a system's physical components and their interrelationships. This description, often called a hardware design model, allows hardware designers to understand how their components fit into a system architecture and provides to software component designers important information needed for software development and integration. Clear definition of a hardware architecture allows the various traditional engineering disciplines to work more effectively together to develop and manufacture new machines, devices and components.
The School of Engineering and Applied Science (SEAS) at the George Washington University in Washington, D.C. is a technical school which specializes in engineering, technology, communications, and transportation. The school is located on the main campus of the George Washington University and offers both undergraduate and graduate programs.

Electrical/Electronics engineering technology (EET) is an engineering technology field that implements and applies the principles of electrical engineering. Like electrical engineering, EET deals with the "design, application, installation, manufacturing, operation or maintenance of electrical/electronic(s) systems." However, EET is a specialized discipline that has more focus on application, theory, and applied design, and implementation, while electrical engineering may focus more of a generalized emphasis on theory and conceptual design. Electrical/Electronic engineering technology is the largest branch of engineering technology and includes a diverse range of sub-disciplines, such as applied design, electronics, embedded systems, control systems, instrumentation, telecommunications, and power systems.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computer engineering:

Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow. Previously electrical engineering only used passive devices such as mechanical switches, resistors, inductors, and capacitors.
This glossary of computer science is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in computer science, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including terms relevant to software, data science, and computer programming.

Information engineering is the engineering discipline that deals with the generation, distribution, analysis, and use of information, data, and knowledge in electrical systems. The field first became identifiable in the early 21st century.










