
Symmetric multiprocessing or shared-memory multiprocessing (SMP) involves a multiprocessor computer hardware and software architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single, shared main memory, have full access to all input and output devices, and are controlled by a single operating system instance that treats all processors equally, reserving none for special purposes. Most multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture. In the case of multi-core processors, the SMP architecture applies to the cores, treating them as separate processors.

The VT100 is a video terminal, introduced in August 1978 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). It was one of the first terminals to support ANSI escape codes for cursor control and other tasks, and added a number of extended codes for special features like controlling the status lights on the keyboard. This led to rapid uptake of the ANSI standard, which became the de facto standard for hardware video terminals and later terminal emulators.
Sequent Computer Systems was a computer company that designed and manufactured multiprocessing computer systems. They were among the pioneers in high-performance symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) open systems, innovating in both hardware and software.

A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. Most early computers only had a front panel to input or display bits and had to be connected to a terminal to print or input text through a keyboard. Teleprinters were used as early-day hard-copy terminals and predated the use of a computer screen by decades. The computer would typically transmit a line of data which would be printed on paper, and accept a line of data from a keyboard over a serial or other interface. Starting in the mid-1970s with microcomputers such as the Sphere 1, Sol-20, and Apple I, display circuitry and keyboards began to be integrated into personal and workstation computer systems, with the computer handling character generation and outputting to a CRT display such as a computer monitor or, sometimes, a consumer TV, but most larger computers continued to require terminals.

The VT220 is a computer terminal introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in November 1983. The VT240 added monochrome ReGIS vector graphics support to the base model, while the VT241 did the same in color. The 200 series replaced the successful VT100 series, providing more functionality in a much smaller unit with a much smaller and lighter keyboard. Like the VT100, the VT200 series implemented a large subset of ANSI X.364. Among its major upgrades was a number of international character sets, as well as the ability to define new character sets.
Pyramid Technology Corporation was a computer company that produced a number of RISC-based minicomputers at the upper end of the performance range. It was based in the San Francisco Bay Area of California

The VT420 is an ANSI standard computer terminal introduced in 1990 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). The 420 is the only model in the 400 series, replacing the VT320. There are no color or graphics-capable 400 series terminals; the VT340 remained in production for those requiring ReGIS and Sixel graphics and color support. The entire lineup of VT300s and VT420 was eventually replaced by the relatively unknown VT500 series starting in 1993.

Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), also known as DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT) or terminal transferase, is a specialized DNA polymerase expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma cells. TdT adds N-nucleotides to the V, D, and J exons of the TCR and BCR genes during antibody gene recombination, enabling the phenomenon of junctional diversity. In humans, terminal transferase is encoded by the DNTT gene. As a member of the X family of DNA polymerase enzymes, it works in conjunction with polymerase λ and polymerase μ, both of which belong to the same X family of polymerase enzymes. The diversity introduced by TdT has played an important role in the evolution of the vertebrate immune system, significantly increasing the variety of antigen receptors that a cell is equipped with to fight pathogens. Studies using TdT knockout mice have found drastic reductions (10-fold) in T-cell receptor (TCR) diversity compared with that of normal, or wild-type, systems. The greater diversity of TCRs that an organism is equipped with leads to greater resistance to infection. Although TdT was one of the first DNA polymerases identified in mammals in 1960, it remains one of the least understood of all DNA polymerases. In 2016–18, TdT was discovered to demonstrate in trans template dependant behaviour in addition to its more broadly known template independent behaviour
Samuel Leroy Taylor, Jr., known as Sam "The Man" Taylor, was an American jazz, rhythm and blues, and blues tenor saxophonist.
The NAG Numerical Library is a software product developed and sold by The Numerical Algorithms Group Ltd. It is a software library of numerical analysis routines, containing more than 1,900 mathematical and statistical algorithms. Areas covered by the library include linear algebra, optimization, quadrature, the solution of ordinary and partial differential equations, regression analysis, and time series analysis.

The VT520 is an ANSI standard computer terminal introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1993 and 1994. The VT520 is a multi-session monochrome text-only terminal with a built-in 14" monitor. The VT510 was a single-session version, while the VT525 added color support and used a separate external monitor.
The National Replacement Character Set (NRCS) was a feature supported by later models of Digital's (DEC) computer terminal systems, starting with the VT200 series in 1983. NRCS allowed individual characters from one character set to be replaced by one from another set, allowing the construction of different character sets on the fly. It was used to customize the character set to different local languages, without having to change the terminal's ROM for different countries, or alternately, include many different sets in a larger ROM. Many 3rd party terminals and terminal emulators supporting VT200 codes also supported NRCS.

Krueppel-like factor 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF6 gene.

Multifunctional Information Distribution System (MIDS) is the NATO name for the communication component of Link-16.
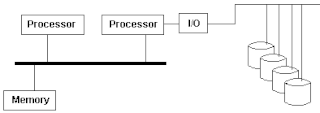
An asymmetric multiprocessing system is a multiprocessor computer system where not all of the multiple interconnected central processing units (CPUs) are treated equally. For example, a system might allow only one CPU to execute operating system code or might allow only one CPU to perform I/O operations. Other AMP systems might allow any CPU to execute operating system code and perform I/O operations, so that they were symmetric with regard to processor roles, but attached some or all peripherals to particular CPUs, so that they were asymmetric with respect to the peripheral attachment.
A terminal multiplexer is a software application that can be used to multiplex several separate pseudoterminal-based login sessions inside a single terminal display, terminal emulator window, PC/workstation system console, or remote login session, or to detach and reattach sessions from a terminal. It is useful for dealing with multiple programs from a command line interface, and for separating programs from the session of the Unix shell that started the program, particularly so a remote process continues running even when the user is disconnected.

The VT320 is an ANSI standard computer terminal introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1987. The VT320 is the text-only version, while the VT330 adds monochrome ReGIS, Sixel and Tektronix 4010 graphics, and the VT340 adds color.
SMP are an American industrial music group formed in Seattle, Washington. The original incarnation consisted of Jason Bazinet and Sean Ivy before Ivy left to join Christ Analogue in 1998, allowing SMP to function as a solo vehicle for Bazinet's musical output. The project was then put on hiatus in 2008, before being brought back in 2010. SMP continues to issue albums digitally with Hacked Vol. 2 being released in 2016 by Music Ration Entertainment.

Terminal is the third studio album by SMP, released in 2000 by Catastrophe Records. A critic at Last Sigh Magazine gave the album a positive review and called it "reminiscent of early nineties raves, in that it is intensely danceable with addictive hooks and crafted lyrics."

The Dream SMP was an invite-only survival multiplayer (SMP) Minecraft server. YouTubers Dream and GeorgeNotFound created a roleplay with Minecraft content creators. They played fictionalized versions of themselves in a loose storyline. Participants livestreamed on Twitch and YouTube. It became a popular Minecraft web series. The server was officially shut down on April 10, 2023.












