Related Research Articles
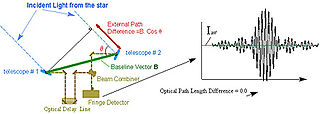
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and our galaxy, the Milky Way.

Ultraviolet astronomy is the observation of electromagnetic radiation at ultraviolet wavelengths between approximately 10 and 320 nanometres; shorter wavelengths—higher energy photons—are studied by X-ray astronomy and gamma ray astronomy. Ultraviolet light is not visible to the human eye. Most of the light at these wavelengths is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so observations at these wavelengths must be performed from the upper atmosphere or from space.
Photometry is a technique of astronomy concerned with measuring the flux, or intensity of an astronomical object's electromagnetic radiation. When photometry is performed over broad wavelength bands of radiation, where not only the amount of radiation but also its spectral distribution is measured, the term spectrophotometry is used.

The Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) was the first-ever space telescope to perform a survey of the entire night sky at infrared wavelengths.

The Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) is an orbiting ultraviolet space telescope launched on April 28, 2003, and operated until early 2012.
The Guide Star Catalog (GSC), also known as the Hubble Space Telescope, Guide Catalog (HSTGC), is a star catalog compiled to support the Hubble Space Telescope with targeting off-axis stars. GSC-I contained approximately 20,000,000 stars with apparent magnitudes of 6 to 15. GSC-II contains 945,592,683 stars out to magnitude 21. As far as possible, binary stars and non-stellar objects have been excluded or flagged as not meeting the requirements of Fine Guidance Sensors. This is the first full sky star catalog created specifically for navigation in outer space.

The European Space Research Organisation (ESRO) was an international organisation founded by 10 European nations with the intention of jointly pursuing scientific research in space. It was founded in 1964. As an organisation ESRO was based on a previously existing international scientific institution, CERN. The ESRO convention, the organisations founding document outlines it as an entity exclusively devoted to scientific pursuits. This was the case for most of its lifetime but in the final years before the formation of ESA, the European Space Agency, ESRO began a programme in the field of telecommunications. Consequently, ESA is not a mainly pure science focused entity but concentrates on telecommunications, earth observation and other application motivated activities. ESRO was merged with ELDO in 1975 to form the European Space Agency.

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.
Sir Robert Wilson was the son of a Durham miner. He studied physics at King's College, Durham and obtained his PhD in Edinburgh, where he worked at the Royal Observatory on stellar spectra. He was an astronomer, who fully embraced the opportunities provided by the space age and he was one of the pioneers who laid the groundwork for the development of the Great Space Observatories, such as the Hubble Space Telescope.

In astronomy, magnitude is a unitless measure of the brightness of an object in a defined passband, often in the visible or infrared spectrum, but sometimes across all wavelengths. An imprecise but systematic determination of the magnitude of objects was introduced in ancient times by Hipparchus.

SkyMapper is a fully automated 1.35 m (4.4 ft) wide-angle optical telescope at Siding Spring Observatory in northern New South Wales, Australia. It is one of the telescopes of the Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics of the Australian National University (ANU). The telescope has a compact modified Cassegrain design with a large 0.69 m secondary mirror, which gives it a very wide field of view: its single, dedicated instrument, a 268-million pixel imaging camera, can photograph 5.7 square degrees of sky. The camera has six light filters which span from ultraviolet to near infrared wavelengths.

The Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer (EUVE) was a space telescope for ultraviolet astronomy, launched on June 7, 1992. With instruments for ultraviolet (UV) radiation between wavelengths of 7 and 76 nm, the EUVE was the first satellite mission especially for the short-wave ultraviolet range. The satellite compiled an all-sky survey of 801 astronomical targets before being decommissioned on January 31, 2001. It re-entered the atmosphere on January 30, 2002.
HD 34557 is a double star in the northern constellation of Auriga. The fainter star has an angular separation of 0.380″ from the primary component. They have a combined apparent magnitude of 5.52, making HD 34557 faintly visible to the naked eye from dark skies. Based upon parallax measurements made with the Hipparcos satellite, this system is roughly 280 light years away. The primary component is spinning rapidly, with a projected rotational velocity of 217 km/s. It has a stellar classification of A3V, making it an A-type main sequence star.
Kosmos 215, also known as DS-U1-A No.1, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1968 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 385-kilogram (849 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used to study radiation and conduct optical observations of the Earth's atmosphere. It was equipped with eight telescopes for optical observation, and one for ultraviolet astronomy. It was primarily used to study the Sun, although several other X-ray emissions were detected.

The history of X-ray astronomy begins in the 1920s, with interest in short wave communications for the U.S. Navy. This was soon followed by extensive study of the earth's ionosphere. By 1927, interest in the detection of X-ray and ultraviolet (UV) radiation at high altitudes inspired researchers to launch Goddard's rockets into the upper atmosphere to support theoretical studies and data gathering. The first successful rocket flight equipped with instrumentation able to detect solar ultraviolet radiation occurred in 1946. X-ray solar studies began in 1949. By 1973 a solar instrument package orbited on Skylab providing significant solar data.

Spektr-RG is a Russian/German high-energy astrophysics space observatory planned to launch in June 2019. It will follow on from the Spektr-R satellite telescope launched in 2011.
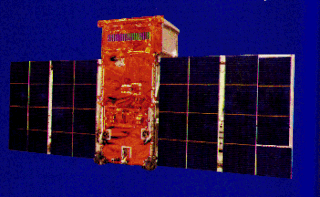
TD-1A, or Thor-Delta 1A, was a European astrophysical research satellite which was launched in 1972. Operated by the European Space Research Organisation, TD-1A made astronomical surveys primarily in the ultraviolet, but also using x-ray and gamma ray detectors.

ULTRASAT is a proposed astronomical satellite mission whose wide-angle UV telescope will detect and monitor transient astrophysical phenomena in the near-ultraviolet spectral region. ULTRASAT will observe a large patch of sky, more than 200 square degrees, alternating every six months between the southern and northern hemisphere. The satellite will orbit the Earth from an altitude of about 300 km above the geosynchronous orbit, getting a ‘ride’ as a secondary payload in the fairing of the rocket carrying a communications satellite. Upon detection of a transient event, ULTRASAT will provide alerts to other ground-based and space telescopes to be directed to the source for further observation of the event in other wavelength bands. A joint American-Israeli proposal for this project was submitted to NASA by a team from Caltech/JPL, the Weizmann Institute of Science and Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). The Israeli contribution will be funded by the Israel Space Agency and launch is expected in 2021/2022.
References
- ↑ "TD1 - TD1 Stellar Ultraviolet Fluxes Catalog" . Retrieved 5 April 2011.
- ↑ Thompson, G.I.; Nandy K.; Jamar C.; Monfils C.; Houziaux L.; Carnochan D.J.; Wilson R. (1978). "Catalogue of stellar ultraviolet fluxes (TD1): A compilation of absolute stellar fluxes measured by the Sky Survey Telescope (S2/68) aboard the ESRO satellite TD-1". The Science Research Council.
- ↑ "Citations history for 1978csuf.book.....T from the ADS Databases" . Retrieved 5 April 2011.