
Tabula rasa is the idea of individuals being born empty of any built-in mental content, so that all knowledge comes from later perceptions or sensory experiences. Proponents typically form the extreme "nurture" side of the nature versus nurture debate, arguing that humans are born without any "natural" psychological traits and that all aspects of one's personality, social and emotional behaviour, knowledge, or sapience are afterwards imprinted by one's environment onto the mind as one would onto a wax tablet. This idea is the central view posited in the theory of knowledge known as empiricism. Empiricists disagree with the doctrines of innatism or rationalism, which hold that the mind is born already in possession of certain knowledge or rational capacity.

Zurab Zhvania was a Georgian politician, who served as Prime Minister of Georgia and Speaker of the Parliament of Georgia.

A-F Records was an American independent record label founded by punk rock band Anti-Flag – namely the band's drummer Pat Thetic, their rhythm guitarist Chris Head, and their lead vocalist Justin Sane – and based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was created to help expose more political punk bands to a larger audience.
"Tabula Rasa" is the eighth episode of season 6 of the television series Buffy the Vampire Slayer. The episode aired on November 13, 2001 on UPN. It explores the characters not as they are, but as they could be, after they lose their memory to a spell gone awry.

The Blank Slate: The Modern Denial of Human Nature is a best-selling 2002 book by the cognitive psychologist Steven Pinker, in which the author makes a case against tabula rasa models in the social sciences, arguing that human behavior is substantially shaped by evolutionary psychological adaptations. The book was nominated for the 2003 Aventis Prizes and was a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize.

allAfrica is a website that aggregates and produces news primarily on the African continent about all areas of African life, politics, issues and culture. It is owned by AllAfrica Global Media, a multi-media content service provider and the largest distributor of African news worldwide. The website operates from offices in Cape Town, Dakar, Abuja, Monrovia, Nairobi and Washington, D.C.. AllAfrica is the successor to Africa News Service.

Richard Garriott's Tabula Rasa was a MMORPG developed by Destination Games and published by NCsoft, designed in part by Richard Garriott. The game is a role-playing video game that blends certain shooter aspects into the combat system. It was officially released to retail on November 2, 2007, with customers that pre-ordered the game allowed access to the live servers from October 30, 2007. The development team released updates, called "Deployments," nearly every month following launch. The game required a monthly subscription.
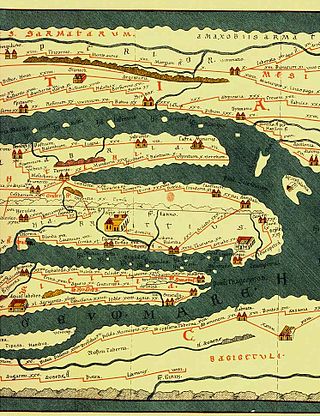
Tabula Peutingeriana, also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated itinerarium showing the layout of the cursus publicus, the road network of the Roman Empire.

Frontline is a fortnightly English language magazine published by The Hindu Group of publications headquartered in Chennai, India. Vaishna Roy is the editor of the magazine. It is a news and views magazine that provides in-depth coverage on various topics such as politics, world affairs, culture, science, health, business and personalities. Frontline gives coverage to developmental issues and issues related to the working classes, unorganized sectors, tribal regions and other under-served regions in India.

Top Channel is a national commercial television network based in Tirana, Albania. The network was founded by Dritan Hoxha in 2001, the network forms part of Top Media Group together with Top Albania Radio, Top Gold Radio, My Music Radio, daily newspaper Shqip, daily magazine Shqip Magazine, coffee producer Lori Caffe, Digitalb, Top News, VGA Studio, musicAL, and Imperial Cinemas.

The Tabula Cortonensis is a 2200-year-old, inscribed bronze tablet in the Etruscan language, discovered in Cortona, Italy. It may record for posterity the details of an ancient legal transaction which took place in the ancient Tuscan city of Cortona, known to the Etruscans as Curtun. Its 40-line, 200-word, two-sided inscription is the third longest inscription found in the Etruscan language, after the Liber Linteus Zagrabiensis and the Tabula Capuana, and the longest discovered in the 20th century.
"Tabula Rasa" is the third episode of the first season of Lost. It was directed by Jack Bender and written by Damon Lindelof. It first aired on October 6, 2004, on ABC.
Savatra, Sabatra, or Soatra was a city in the Roman province of Galatia, and subsequently the Byzantine province of Lycaonia.

Tabula, Inc., was an American fabless semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California. Founded in 2003 by Steve Teig, it raised $215 million in venture funding. The company designed and built three dimensional field programmable gate arrays and ranked third on the Wall Street Journal's annual "Next Big Thing" list in 2012.
Caenophrurium was a settlement in the Roman province of Europa, between Byzantium and Heraclea Perinthus. It appears in late Roman and early Byzantine accounts. Caenophrurium translates as the "stronghold of the Caeni", a Thracian tribe.

Full Measure is an American Sunday morning political affairs and investigative news magazine series hosted by investigative journalist Sharyl Attkisson. The program is produced, broadcast, and syndicated by the Sinclair Television Group. It is shown on most television stations operated by the Sinclair Broadcast Group division, initially broadcast at 9:30 a.m. Eastern Time on Sundays in some stations and later in the day by others. It is also streamed live-to-air on the program's website, FullMeasure.news. Topics often include coverage of government spending or actions considered inappropriate.

European Georgia is a political party in Georgia founded in Tbilisi in January 2017, primarily by prominent former members of the United National Movement. From 2017 to 2021 the party was chaired by Davit Bakradze. Since 2021, the chairman is Giga Bokeria who was chairman of the political council from 2017 to 2021.

Karine Jean-Pierre is an American political advisor who has been serving as the White House press secretary since May 13, 2022. She is the first black person and the first openly LGBT person to serve in the position. Previously, she served as the deputy press secretary to her predecessor Jen Psaki from 2021 to 2022 and as the chief of staff for U.S. Vice Presidential candidate Kamala Harris during the 2020 presidential campaign.

Parliamentary elections are scheduled to be held in Georgia on 26 October 2024.













