Frank Donald Drake is an American astronomer and astrophysicist. He is involved in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence, including the founding of SETI, mounting the first observational attempts at detecting extraterrestrial communications in 1960 in Project Ozma, developing the Drake equation, and as the creator of the Arecibo Message, a digital encoding of an astronomical and biological description of the Earth and its lifeforms for transmission into the cosmos.

Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1932, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories observed radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy.

The Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) is a centimeter-wavelength radio astronomy observatory located in central New Mexico on the Plains of San Agustin, between the towns of Magdalena and Datil, ~40 miles (64 km) west of Socorro. The VLA comprises twenty-seven 25-meter radio telescopes deployed in a Y-shaped array and all the equipment, instrumentation, and computing power to function as an interferometer. Each of the massive telescopes is mounted on double parallel railroad tracks, so the radius and density of the array can be transformed to adjust the balance between its angular resolution and its surface brightness sensitivity. Astronomers using the VLA have made key observations of black holes and protoplanetary disks around young stars, discovered magnetic filaments and traced complex gas motions at the Milky Way's center, probed the Universe's cosmological parameters, and provided new knowledge about the physical mechanisms that produce radio emission.

Grote Reber was a pioneer of radio astronomy, which combined his interests in amateur radio and amateur astronomy. He was instrumental in investigating and extending Karl Jansky's pioneering work, and conducted the first sky survey in the radio frequencies.

The McDonald Observatory is an astronomical observatory located near the unincorporated community of Fort Davis in Jeff Davis County, Texas, United States. The facility is located on Mount Locke in the Davis Mountains of West Texas, with additional facilities on Mount Fowlkes, approximately 1.3 kilometers (0.81 mi) to the northeast. The observatory is part of the University of Texas at Austin. It is an organized research unit of the College of Natural Sciences.
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO)'s radio astronomy observatories are collectively known as the Australia Telescope National Facility (ATNF), with the facility supporting Australia's research in radio astronomy.

The Mullard Radio Astronomy Observatory (MRAO) is located near Cambridge, UK and is home to a number of the largest and most advanced aperture synthesis radio telescopes in the world, including the One-Mile Telescope, 5-km Ryle Telescope, and the Arcminute Microkelvin Imager. It was founded by the University of Cambridge and is an institute of the Cambridge University Astronomy Department.

Owens Valley Radio Observatory (OVRO) is a radio astronomy observatory located near Big Pine, California (US) in Owens Valley. It lies east of the Sierra Nevada approximately 350 kilometers (220 mi) north of Los Angeles and 20 kilometers (12 mi) southeast of Bishop. It was established in 1958, and is owned and operated by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The Owens Valley Solar Array portion of the observatory has been operated by New Jersey Institute of Technology since the transfer in 1997.

The Hat Creek Radio Observatory (HCRO) is operated by SRI International in the Western United States. The observatory is home to the Allen Telescope Array designed and owned by the SETI Institute in Mountain View, CA.
The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), with its headquarters in Bangalore, is a premier National Research Institute of India. IIA conducts research primarily in the areas of astronomy, astrophysics and related subjects. It is widely recognised as a leading research center for Astrophysics in India.
Paolo Padovani is an Italian astronomer working at the European Southern Observatory, specializing in the study of Active galactic nuclei including the study of quasars and blazars, evolution and multifrequency studies and extragalactic backgrounds. In 2004 he and several other astronomers discovered 30 supermassive blackholes at the European Astrophysical Virtual Observatory using pioneering techniques.

The Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory (HartRAO) is a radio astronomy observatory, located in a natural bowl of hills at Hartebeesthoek just south of the Magaliesberg mountain range, Gauteng, South Africa, about 50 km west of Johannesburg. It is a National Research Facility run by South Africa's National Research Foundation. HartRAO was the only major radio astronomy observatory in Africa until the construction of the KAT-7 test bed for the future MeerKAT array.

MeerKAT, originally the Karoo Array Telescope, is a radio telescope consisting of 64 antennas now being tested and verified in the Northern Cape of South Africa. When fully functional it will be the largest and most sensitive radio telescope in the southern hemisphere until the Square Kilometre Array is completed in approximately 2024. The telescope will be used for research into cosmic magnetism, galactic evolution, the large-scale structure of the cosmos, dark matter and the nature of transient radio sources. It will also serve as a technology demonstrator for South Africa's bid to host the Square Kilometer Array. First light was on 16 July 2016. As of May 2018, all sixty-four 13.5-meter diameter dish antennae have been completed and are currently undergoing verification tests.

Pushchino Radio Astronomy Observatory is a Russian radio astronomy observatory. It was developed by Lebedev Physical Institute (LPI), Russian Academy of Sciences within a span of twenty years. It was founded on April 11, 1956, and currently occupies 70 000 square meters.

Bohyeonsan or Bohyeon Mountain or Mount Bohyeon is located in the province of Gyeongsangbuk-do, eastern South Korea. Its peak has an elevation of 1,121 metres (3,678 ft), and is near the city of Yeongcheon.
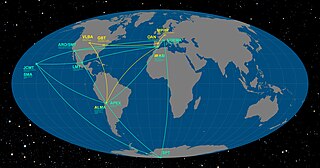
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a project to create a large telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes and combining data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around the Earth. The aim is to observe the immediate environment of the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* at the center of the Milky Way, as well as the even larger black hole in the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, with angular resolution comparable to the black hole's event horizon.
Patrick Thaddeus was the Robert Wheeler Willson Professor of Applied Astronomy Emeritus at Harvard University. He is best known for mapping carbon monoxide in the Milky Way galaxy and was responsible for the construction of the CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope.

The Korean VLBI Network (KVN) is a radio astronomy observatory located in South Korea. It comprises three 21-meter radio telescopes that function as an interferometer, using the technique of very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI).