Tarsier is a group of small primates native to Southeast Asia.
Tarsier may also refer to:
- Tarsier Records, a record label in the Philippines
- Tarsier Studios, a Swedish video game developer
Tarsier is a group of small primates native to Southeast Asia.
Tarsier may also refer to:

Tarsiers are haplorhine primates of the family Tarsiidae, which is, itself, the lone extant family within the infraorder Tarsiiformes. Although the group was, prehistorically, more globally widespread, all of the species living today are restricted to Maritime Southeast Asia, predominantly being found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines.

Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini is a suborder of primates that includes the lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Africa, and the lorises from India and southeast Asia. Collectively they are referred to as strepsirrhines. Also belonging to the suborder are the extinct adapiform primates which thrived during the Eocene in Europe, North America, and Asia, but disappeared from most of the Northern Hemisphere as the climate cooled. Adapiforms are sometimes referred to as being "lemur-like", although the diversity of both lemurs and adapiforms does not support this comparison.

Prosimians are a group of primates that includes all living and extinct strepsirrhines, as well as the haplorhine tarsiers and their extinct relatives, the omomyiforms, i.e. all primates excluding the simians. They are considered to have characteristics that are more "primitive" than those of simians.

Haplorhini, the haplorhines or the "dry-nosed" primates is a suborder of primates containing the tarsiers and the simians, as sister of the Strepsirrhini ("moist-nosed"). The name is sometimes spelled Haplorrhini. The simians include catarrhines, and the platyrrhines.

Omomyidae is a group of early primates that radiated during the Eocene epoch between about 55 to 34 million years ago (mya). Fossil omomyids are found in North America, Europe & Asia, making it one of two groups of Eocene primates with a geographic distribution spanning holarctic continents, the other being the adapids. Early representatives of the Omomyidae and Adapidae appear suddenly at the beginning of the Eocene in North America, Europe, and Asia, and are the earliest known crown primates.

Tarsiiformes are a group of primates that once ranged across Europe, northern Africa, Asia, and North America, but whose extant species are all found in the islands of Southeast Asia. Tarsiers are the only living members of the infraorder; other members of Tarsiidae include the extinct Tarsius eocaenus from the Eocene, and Tarsius thailandicus from the Miocene. Two extinct genera, Xanthorhysis and Afrotarsius, are considered to be close relatives of the living tarsiers, and are generally classified within Tarsiiformes, with the former grouped within family Tarsiidae, and the latter listed as incertae sedis (undefined). Omomyids are generally considered to be extinct relatives, or even ancestors, of the living tarsiers, and are often classified within Tarsiiformes.

The Philippine tarsier, known locally as mawumag in Cebuano and other Visayan languages, and magô in Waray, is a species of tarsier endemic to the Philippines. It is found in the southeastern part of the archipelago, particularly on the islands of Bohol, Samar and Leyte. It is a member of the approximately 45-million-year-old family Tarsiidae, whose name is derived from its elongated "tarsus" or ankle bone. Formerly a member of the genus Tarsius, it is now listed as the only member of the genus Carlito, a new genus named after the conservationist Carlito Pizarras.

The Sangihe tarsier, also known as Sangihe Island tarsier, is a small primate found on Sangir Island, which is located about 200 kilometers north-east of the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. In 2008 a population of the Sangihe tarsier was determined to be a distinct species, the Siau Island tarsier. Locally in the Sangihe dialect of Sangir language, tarsiers are called Senggasi or Higo.

Horsfeld's tarsier is the only species of tarsier in the genus Cephalopachus. Named by American naturalist Thomas Horsfield, it is also referred to as western tarsier. The species occurs on Borneo, Sumatra and nearby islands and is, like other members of the group, entirely nocturnal.

The Peleng tarsier, or the Peleng Island tarsier, is a nocturnal primate found on the island of Peleng, just east of Sulawesi, Indonesia. In western Peleng, the animal is called Lakasinding, while in the east, Siling.

The pygmy tarsier, also known as the mountain tarsier or the lesser spectral tarsier, is a nocturnal primate found in central Sulawesi, Indonesia, in an area with lower vegetative species diversity than the lowland tropical forests. The pygmy tarsier was believed to have become extinct in the early 20th century. Then, in 2000, Indonesian scientists accidentally killed one while trapping rats. The first pygmy tarsiers seen alive since the 1920s were found by a research team led by Dr. Sharon Gursky and Ph.D. student Nanda Grow from Texas A&M University on Mount Rore Katimbo in Lore Lindu National Park in August 2008. The two males and single female were captured using nets, and were radio collared to track their movements. As the first live pygmy tarsiers seen in 80-plus years, these captures dispelled the belief among some primatologists that the species was extinct.
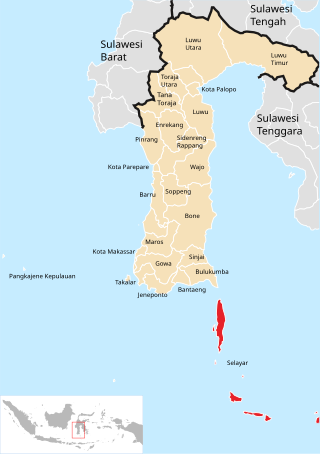
Spectral tarsier or Selayar tarsier is a species of tarsier found on the island of Selayar in Indonesia. It is apparently less specialized than the Philippine tarsier or Horsfield's tarsier; for example, it lacks adhesive toes. It is the type species for the genus Tarsius. While its range used to also include the population on nearby southwestern Sulawesi, this population has been reclassified as a separate species, Tarsius fuscus. Some of the earlier research published on Tarsius spectrum refers to the taxon that was recently reclassified and elevated to a separate species, the Gursky's spectral tarsier.
Carlito means "little Carlos". It may refer to:

The Siau Island tarsier is a species of tarsier from the tiny volcanic island of Siau in Indonesia. The T. tumpara species is one of 14 species and 7 subspecies in the tarsier family called "Tarsiidae". They belong to the Haplorrhini suborder, known as the "dry-nosed" primates. The tarsier's eyes are so big that they do not move in its socket and they are almost as big as its brain. Locally in the Siau dialect of Sangir language, the tarsiers are called Tumpara. The name differs from the Sangihe dialect which called tarsiers, Senggasi or Higo, these names are used for the Sangihe tarsier instead.
Animal suicide is when an animal intentionally ends its own life through its actions. It implies a wide range of higher cognitive capacities that experts have been wary to ascribe to nonhuman animals such as a concept of self, death, and future intention. There is currently not enough empirical data on the subject for there to be a consensus among experts. For these reasons, the occurrence of animal suicide is controversial among academics.

Tarsier Studios is a Swedish video game developer based in Malmö.
Wallace's tarsier, Tarsius wallacei, is a species of Sulawesi tarsier. It is found in the forests of what is referred to geologically as the neck of Sulawesi where there are two separate populations. It is a small brown arboreal primate of the infraorder Tarsiiformes less than 15 cm (6 in) long.

Brookland/Oaklyn is the only collaborative studio album by Alias & Tarsier. It was released on Anticon in 2006.
T. dentatus may refer to:

Archicebus is a genus of fossil primates that lived in the early Eocene forests of what is now Jingzhou in the Hubei Province in central China, discovered in 2003. The only known species, A. achilles, was a small primate, estimated to weigh about 20–30 grams (0.7–1.1 oz), and is the only known member of the family Archicebidae. When discovered, it was the oldest fossil haplorhine primate skeleton found, appearing to be most closely related to tarsiers and the fossil omomyids, although A. achilles is suggested to have been diurnal, whereas tarsiers are nocturnal. Resembling tarsiers and simians, it was a haplorhine primate, and it also may have resembled the last common ancestor of all haplorhines as well as the last common ancestor of all primates. Its discovery further supports the hypothesis that primates originated in Asia, not in Africa.