
Bioenergy Europe is a European trade association open to national biomass associations and bioenergy companies active in Europe. It was founded in 1990 under the leadership of french senator Michel Souplet with the aim to promote energy generation from biomass - in all its forms: biopower, bioheat or biofuels for transport. Bioenergy Europe is the umbrella organisation of the European Pellet Council (EPC), and the International Biomass Torrefaction Council (IBTC)..

A biofuel is a fuel that is produced through contemporary biological processes, such as agriculture and anaerobic digestion, rather than a fuel produced by geological processes such as those involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as coal and petroleum, from prehistoric biological matter. If the source biomatter can regrow quickly, the resulting fuel is said to be a form of renewable energy.
A biorefinery is a refinery that converts biomass to energy and other beneficial byproducts. The International Energy Agency Bioenergy Task 42 defined biorefining as "the sustainable processing of biomass into a spectrum of bio-based products and bioenergy ". As refineries, biorefineries can provide multiple chemicals by fractioning an initial raw material (biomass) into multiple intermediates that can be further converted into value-added products..The use of biomass as feedstock can provide a benefit by reducing the impacts on the environment, as lower pollutants emissions and reduction in the emissions of hazard products. In addition, biorefineries are intended to achieve the following goals:
- Supply the current fuels and chemical building blocks
- Supply new building blocks for the production of novel materials with disruptive characteristics
- Creation of new jobs, including rural areas
- Valorization of waste

Pellet fuels are biofuels made from compressed organic matter or biomass. Pellets can be made from any one of five general categories of biomass: industrial waste and co-products, food waste, agricultural residues, energy crops, and virgin lumber. Wood pellets are the most common type of pellet fuel and are generally made from compacted sawdust and related industrial wastes from the milling of lumber, manufacture of wood products and furniture, and construction. Other industrial waste sources include empty fruit bunches, palm kernel shells, coconut shells, and tree tops and branches discarded during logging operations. So-called "black pellets" are made of biomass, refined to resemble hard coal and were developed to be used in existing coal-fired power plants. Pellets are categorized by their heating value, moisture and ash content, and dimensions. They can be used as fuels for power generation, commercial or residential heating, and cooking. Pellets are extremely dense and can be produced with a low moisture content that allows them to be burned with a very high combustion efficiency.

An energy crop is a plant grown as a low-cost and low-maintenance harvest used to make biofuels, such as bioethanol, or combusted for its energy content to generate electricity or heat. Energy crops are generally categorized as woody or herbaceous plants; many of the latter are grasses of the family Graminaceae.

Drax Group plc is a British electrical power generation company. The Group is made up of upstream and downstream enterprises. The principal downstream enterprises are based in the UK and include Drax Power Limited, which runs Europe’s biggest biomass-fuelled power station, Drax power station, near Selby in North Yorkshire – the UK’s largest decarbonisation project, as well as supplying between 7-8 per cent of the country’s electricity needs. Related businesses include Haven Power, a supplier of electricity to business. The group’s largest upstream enterprises are Drax Biomass, which sources sustainable biomass for Drax power station and Baton Rouge Transit, which handles storage and transport of finished biomass pellets from the Port of Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
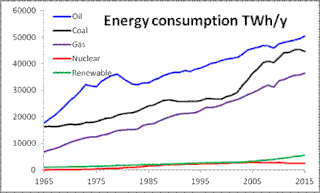
World energy consumption is the total energy used by the entire human civilization. Typically measured per year, it involves all energy harnessed from every energy source applied towards humanity's endeavours across every single industrial and technological sector, across every country. It does not include energy from food, and the extent to which direct biomass burning has been accounted for is poorly documented. Being the power source metric of civilization, World Energy Consumption has deep implications for humanity's socio-economic-political sphere.
On April 25, 2006, Executive Order S-06-06, the Bioenergy Action Plan was issued by the then governor of California, Arnold Schwarzenegger, outlining a set of target goals which would establish the increasing use and production of biofuels and biopower for both electricity generation and substitution of natural gas and petroleum within the state of California. The plan asked multiple state agencies to work towards the advancement of biomass programs in California. The order would also help provide statewide environmental protection, mitigation and economic advancement. The plan was passed on July 7, 2006 with progress reports issued in 2007 and 2009.

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. As of 2012, renewable energy accounts for about half of new nameplate electrical capacity installed and costs are continuing to fall.
Abengoa S.A. is a Spanish multinational corporation, which includes companies in the domains of energy, telecommunications, transportation, and the environment. The company was founded in 1941 by Javier Benjumea Puigcerver and José Manuel Abaurre Fernández-Pasalagua, and is based in Seville, Spain with U.S. headquarters in St. Louis, Missouri. It is a global biotechnology company specializing in the development of new technologies in producing biofuels and biochemicals and promoting sustainability of raw materials.

Renewable energy in Finland grew to 38.7% of total final energy consumption by year end 2014, achieving joint second position with Latvia in terms of renewable energy consumption by share amongst the EU-28 countries, behind its neighbour Sweden in first position on a 52.6% share. The 2014 share in Finland breaks down as renewable energy providing 52% of the heating and cooling sector, 31.4% of the electricity sector and 21.6% of the transport sector. By 2014 Finland had already exceeded its 2020 target for renewable energy use under the EU renewable energy directive as shown in the table of country targets.
The use of biofuels varies by region and with increasing oil prices there is a renewed interest in it as an energy source.

Renewable energy technologies provide about 17% of Canada’s total primary energy supply and about 65% of its electricity production as of 2016.
Bio-energy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) is a potential greenhouse gas mitigation technology which produces negative carbon dioxide emissions by combining bioenergy (energy from biomass) use with geologic carbon capture and storage. The concept of BECCS is drawn from the integration of trees and crops, which extract carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere as they grow, the use of this biomass in processing industries or power plants, and the application of carbon capture and storage via CO2 injection into geological formations. There are other non-BECCS forms of carbon dioxide removal and storage that include technologies such as biochar, carbon dioxide air capture and biomass burial and enhanced weathering.
Deploying Renewables 2011: Best and Future Policy Practice is a 2011 book by the International Energy Agency. The book analyses the recent successes in renewable energy, which now accounts for almost a fifth of all electricity produced worldwide, and addresses how countries can best capitalize on that growth to realise a sustainable energy future. The book says that renewable energy commercialization must be stepped up, especially given the world’s increasing appetite for energy and the need to meet this demand more efficiently and with low-carbon energy sources. Wind power and other renewable energy sources offer great potential to address issues of energy security and sustainability.

The International Energy Agency Solar Heating and Cooling Programme is one of over 40 multilateral Technology Collaboration Programmes of the International Energy Agency. It was one of the first of such programmes, founded in 1977. Its current mission is to "advance international collaborative efforts for solar energy to reach the goal set in the vision of contributing 50% of the low temperature heating and cooling demand by 2030.". Its international solar collector statistics Solar Heat Worldwide serve as a reference document for governments, financial institutions, consulting firms and non-profit organizations.
The World Bioenergy Association (WBA) is an international NGO and non-profit association that represents the bioenergy sector globally. The organisation works to promote the use of sustainable bioenergy which includes Biomass, Biofuels and Biogas. The secretariat of WBA is in Stockholm.












