Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees, and are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their staff. Payroll taxes generally fall into two categories: deductions from an employee’s wages, and taxes paid by the employer based on the employee's wages. The first kind are taxes that employers are required to withhold from employees' wages, also known as withholding tax, pay-as-you-earn tax (PAYE), or pay-as-you-go tax (PAYG) and often covering advance payment of income tax, social security contributions, and various insurances. The second kind is a tax that is paid from the employer's own funds and that is directly related to employing a worker. These can consist of fixed charges or be proportionally linked to an employee's pay. The charges paid by the employer usually cover the employer's funding of the social security system, medicare, and other insurance programs. The economic burden of the payroll tax falls almost entirely on the worker, regardless of whether the tax is remitted by the employer or the employee, as the employers’ share of payroll taxes is passed on to employees in the form of lower wages than would otherwise be paid. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in human capital such as higher education.
The Federal Insurance Contributions Act is a United States federal payroll contribution directed towards both employees and employers to fund Social Security and Medicare—federal programs that provide benefits for retirees, people with disabilities, and children of deceased workers.
Tax brackets are the divisions at which tax rates change in a progressive tax system. Essentially, they are the cutoff values for taxable income—income past a certain point will be taxed at a higher rate.
In the United States income tax system, adjusted gross income (AGI) is an individual's total gross income minus specific deductions. Taxable income is adjusted gross income minus allowances for personal exemptions and itemized deductions. For most individual tax purposes, AGI is more relevant than gross income.
Three key types of withholding tax are imposed at various levels in the United States:

An S corporation, for United States federal income tax, is a closely held corporation that makes a valid election to be taxed under Subchapter S of Chapter 1 of the Internal Revenue Code. In general, S corporations do not pay any income taxes. Instead, the corporation's income or losses are divided among and passed through to its shareholders. The shareholders must then report the income or loss on their own individual income tax returns.
Taxation in France is determined by the yearly budget vote by the French Parliament, which determines which kinds of taxes can be levied and which rates can be applied.
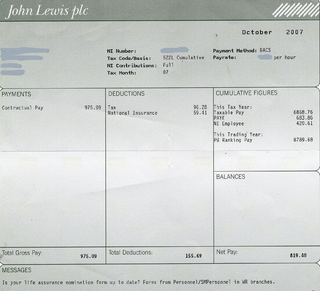
Compensation of employees (CE) is a statistical term used in national accounts, balance of payments statistics and sometimes in corporate accounts as well. It refers basically to the total gross (pre-tax) wages paid by employers to employees for work done in an accounting period, such as a quarter or a year.
Gross income is all a person's receipts and gains from all sources, before any deductions. The adjective "gross", as opposed to "net", generally qualifies a word referring to an amount, value, weight, number, or the like, specifying that necessary deductions have not been taken into account.
Income taxes in the United States are imposed by the federal, most state, and many local governments. The income taxes are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed, but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. An alternative tax applies at the federal and some state levels.
For the Old Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance (OASDI) tax or Social Security tax in the United States, the Social Security Wage Base (SSWB) is the maximum earned gross income or upper threshold on which a wage earner's Social Security tax may be imposed. The Social Security tax is one component of the Federal Insurance Contributions Act tax (FICA) and Self-employment tax, the other component being the Medicare tax. It is also the maximum amount of covered wages that are taken into account when average earnings are calculated in order to determine a worker's Social Security benefit.
The Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 was an Act of Congress providing for several kinds of economic stimuli intended to boost the United States economy in 2008 and to avert a recession, or ameliorate economic conditions. The stimulus package was passed by the U.S. House of Representatives on January 29, 2008, and in a slightly different version by the U.S. Senate on February 7, 2008. The Senate version was then approved in the House the same day. It was signed into law on February 13, 2008 by President Bush with the support of both Democratic and Republican lawmakers. The law provides for tax rebates to low- and middle-income U.S. taxpayers, tax incentives to stimulate business investment, and an increase in the limits imposed on mortgages eligible for purchase by government-sponsored enterprises. The total cost of this bill was projected at $152 billion for 2008.
Due to the absence of the tax code in Argentina, the tax regulation takes place in accordance with separate laws, which, in turn, are supplemented by provisions of normative acts adopted by the executive authorities. The powers of the executive authority include levying a tax on profits, property and added value throughout the national territory. In Argentina, the tax policy is implemented by the Federal Administration of Public Revenue, which is subordinate to the Ministry of Economy. The Federal Administration of Public Revenues (AFIP) is an independent service, which includes: the General Tax Administration, the General Customs Office and the General Directorate for Social Security. AFIP establishes the relevant legal norms for the calculation, payment and administration of taxes:
The economic impact of illegal immigrants in the United States is challenging to measure, and politically contentious. The scarcity of reliable statistics leaves room for many methods of study, leading to diverse conclusions.
Taxes has an important part in the Moroccan economy. The taxes are levied by the government and the organization responsible for tax policy on Morocco is called the “General Management of Taxes”.