
BBC Red Button is a branding used for digital interactive television services provided by the BBC, and broadcast in the United Kingdom. The services replaced Ceefax, the BBC's analogue teletext service. BBC Red Button's text services were due to close on 30 January 2020, but the switch off was suspended on 29 January 2020 following protests.

Closed captioning (CC) and subtitling are both processes of displaying text on a television, video screen, or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information. Both are typically used as a transcription of the audio portion of a program as it occurs, sometimes including descriptions of non-speech elements. Other uses have included providing a textual alternative language translation of a presentation's primary audio language that is usually burned-in to the video and unselectable.
In a raster graphics display, the vertical blanking interval (VBI), also known as the vertical interval or VBLANK, is the time between the end of the final visible line of a frame or field and the beginning of the first visible line of the next frame. It is present in analog television, VGA, DVI and other signals.
Teletext Ltd was the provider of teletext and digital interactive services for ITV, Channel 4 and Five in the United Kingdom. Teletext Ltd currently runs Teletext Holidays and Teletext Cars only.
Zenith Electronics, LLC is an American research and development company that develops ATSC and digital rights management technologies. It is owned by the South Korean company LG Electronics. Zenith was previously an American brand of consumer electronics, a manufacturer of radio and television receivers and other consumer electronics, and was headquartered in Glenview, Illinois. After a series of layoffs, the consolidated headquarters moved to Lincolnshire, Illinois. For many years, their famous slogan was "The quality goes in before the name goes on". LG Electronics acquired a controlling share of Zenith in 1995; Zenith became a wholly owned subsidiary in 1999. Zenith was the inventor of subscription television and the modern remote control, and the first to develop High-definition television (HDTV) in North America.

TeleVideo Corporation was a U.S. company that achieved its peak of success in the early 1980s producing computer terminals. TeleVideo was founded in 1979 by K. Philip Hwang, a Utah State University graduate born in North Korea who had run a business producing CRT monitors for arcade games since 1975. The company was headquartered in San Jose, California.
MovieBeam was a video-on-demand service started by The Walt Disney Company, specifically its subsidiary Buena Vista Datacasting, LLC. Movies were sent wirelessly into the subscriber's home by embedding digital data (datacasting) within local Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) stations' analog TV (NTSC) broadcast to deliver the movies to a set-top box. The data was embedded using dNTSC technology licensed from Dotcast, and distributed to TV stations via National Datacast. Up to 10 new movies were delivered to the player each week. The player also contained free movie trailers, previews, and other extras.
NABTS, the North American Broadcast Teletext Specification, is a protocol used for encoding NAPLPS-encoded teletext pages, as well as other types of digital data, within the vertical blanking interval (VBI) of an analog video signal. It is standardized under standard EIA-516, and has a rate of 15.6 kbit/s per line of video.
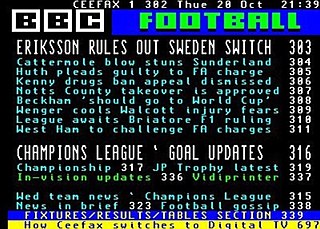
Teletext, or broadcast teletext, is a videotex standard for displaying text and rudimentary graphics on suitably equipped television sets. Teletext sends data in the broadcast signal, hidden in the invisible vertical blanking interval area at the top and bottom of the screen. The teletext decoder in the television buffers this information as a series of "pages", each given a number. The user can display chosen pages using their remote control.
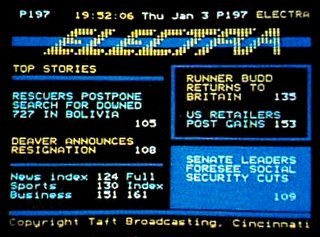
Electra was a teletext service in the United States that was in operation from the early 1980s up until 1993, when it was shut down due to a lack of funding, and discontinuation of teletextapable television sets by the only US television manufacturer offering teletext capability at the time, Zenith. It was owned, operated and maintained by Cincinnati-based Taft Broadcasting and Tulsa, Oklahoma-based Satellite Syndicated Systems (SSS), in cooperation with cable/satellite TV station Superstation WTBS, who carried Electra's data on their vertical blanking interval. The service was also available to C-band satellite dish users via the Galaxy 1 and Satcom 3R satellites.
ITV Nightscreen is a scheduled programme on the ITV television network, consisting of a sequence of animated pages of information about ITV's upcoming programmes, features and special events, with an easy listening music soundtrack. The programme is used to fill the station's overnight downtime, where a closedown would have once been used at the end of programmes. The programme is generally shown 7 days a week with the typical weekday show airing from 3:50 am – 5:05 am daily.

Channel Four Television Corporation is a publicly owned media company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. Its original and principal activity is the British national television network Channel 4.

ExtraVision was a short-lived teletext service created and operated by the American television network CBS in the early to mid-1980s. It was carried in the vertical blanking interval of the video from local affiliate stations of the CBS network. It featured CBS program information, news, sports, weather, even subtitling for CBS programming. ExtraVision could also have its pages customized by the local affiliate station carrying it, for such things as program schedules, local community announcements, and station promotions.

World System Teletext (WST) is the name of a standard for encoding and displaying teletext information, which is used as the standard for teletext throughout Europe today. It was adopted into the international standard CCIR 653 of 1986 as CCIR Teletext System B.
Norpak Corporation was a company headquartered in Kanata, Ontario, Canada, that specialized in the development of systems for television-based data transmission. In 2010, it was acquired by Ross Video Limited of Iroquois and Ottawa, Ontario.
Televideo is the teletext service broadcast on all RAI television channels in Italy, and also available in its entirety on the Internet.
Teletext is a television information retrieval service developed in the United Kingdom in the early 1970s. It offers a range of text-based information, typically including national, international and sporting news, weather and TV schedules. Subtitle information is also transmitted in the teletext signal, typically on page 888 or 777.
MediaCorp Teletext was a Singaporean teletext information service provided by MediaCorp. It was carried on MediaCorp's Channel 5, Channel 8 and Channel NewsAsia. On top of the standard information carried by most teletext providers, it also carried information unique to Singapore, such as COE and ERP rates, announcements from selected ministries in Singapore and lottery results.
SWISS TXT is a subsidiary and the centre of multimedia expertise of the Swiss Broadcasting Corporation.







