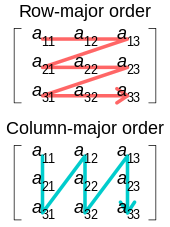
In linear algebra, an orthogonal matrix, or orthonormal matrix, is a real square matrix whose columns and rows are orthonormal vectors.

In numerical analysis and scientific computing, a sparse matrix or sparse array is a matrix in which most of the elements are zero. There is no strict definition regarding the proportion of zero-value elements for a matrix to qualify as sparse but a common criterion is that the number of non-zero elements is roughly equal to the number of rows or columns. By contrast, if most of the elements are non-zero, the matrix is considered dense. The number of zero-valued elements divided by the total number of elements is sometimes referred to as the sparsity of the matrix.
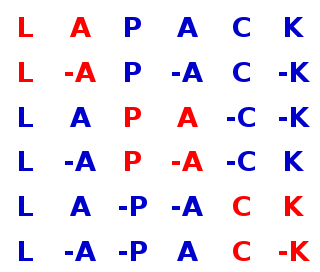
LAPACK is a standard software library for numerical linear algebra. It provides routines for solving systems of linear equations and linear least squares, eigenvalue problems, and singular value decomposition. It also includes routines to implement the associated matrix factorizations such as LU, QR, Cholesky and Schur decomposition. LAPACK was originally written in FORTRAN 77, but moved to Fortran 90 in version 3.2 (2008). The routines handle both real and complex matrices in both single and double precision. LAPACK relies on an underlying BLAS implementation to provide efficient and portable computational building blocks for its routines.
Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS) is a specification that prescribes a set of low-level routines for performing common linear algebra operations such as vector addition, scalar multiplication, dot products, linear combinations, and matrix multiplication. They are the de facto standard low-level routines for linear algebra libraries; the routines have bindings for both C and Fortran. Although the BLAS specification is general, BLAS implementations are often optimized for speed on a particular machine, so using them can bring substantial performance benefits. BLAS implementations will take advantage of special floating point hardware such as vector registers or SIMD instructions.
The GNU Scientific Library is a software library for numerical computations in applied mathematics and science. The GSL is written in C; wrappers are available for other programming languages. The GSL is part of the GNU Project and is distributed under the GNU General Public License.
dnAnalytics is an open-source numerical library for .NET written in C# and F#. It features functionality similar to BLAS and LAPACK.
The Portable, Extensible Toolkit for Scientific Computation, is a suite of data structures and routines developed by Argonne National Laboratory for the scalable (parallel) solution of scientific applications modeled by partial differential equations. It employs the Message Passing Interface (MPI) standard for all message-passing communication. PETSc is the world’s most widely used parallel numerical software library for partial differential equations and sparse matrix computations. PETSc received an R&D 100 Award in 2009. The PETSc Core Development Group won the SIAM/ACM Prize in Computational Science and Engineering for 2015.
JAMA is a software library for performing numerical linear algebra tasks created at National Institute of Standards and Technology in 1998 similar in functionality to LAPACK.
LAPACK++, the Linear Algebra PACKage in C++, is a computer software library of algorithms for numerical linear algebra that solves systems of linear equations and eigenvalue problems.
Numerical linear algebra, sometimes called applied linear algebra, is the study of how matrix operations can be used to create computer algorithms which efficiently and accurately provide approximate answers to questions in continuous mathematics. It is a subfield of numerical analysis, and a type of linear algebra. Computers use floating-point arithmetic and cannot exactly represent irrational data, so when a computer algorithm is applied to a matrix of data, it can sometimes increase the difference between a number stored in the computer and the true number that it is an approximation of. Numerical linear algebra uses properties of vectors and matrices to develop computer algorithms that minimize the error introduced by the computer, and is also concerned with ensuring that the algorithm is as efficient as possible.
Armadillo is a linear algebra software library for the C++ programming language. It aims to provide efficient and streamlined base calculations, while at the same time having a straightforward and easy-to-use interface. Its intended target users are scientists and engineers.
SLEPc is a software library for the parallel computation of eigenvalues and eigenvectors of large, sparse matrices. It can be seen as a module of PETSc that provides solvers for different types of eigenproblems, including linear and nonlinear, as well as the SVD. Recent versions also include support for matrix functions. It uses the MPI standard for parallelization. Both real and complex arithmetic are supported, with single, double and quadruple precision.

Eigen is a high-level C++ library of template headers for linear algebra, matrix and vector operations, geometrical transformations, numerical solvers and related algorithms. Eigen is open-source software licensed under the Mozilla Public License 2.0 since version 3.1.1. Earlier versions were licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License. Version 1.0 was released in Dec 2006.
Matrix Toolkit Java (MTJ) is an open-source Java software library for performing numerical linear algebra. The library contains a full set of standard linear algebra operations for dense matrices based on BLAS and LAPACK code. Partial set of sparse operations is provided through the Templates project. The library can be configured to run as a pure Java library or use BLAS machine-optimized code through the Java Native Interface.
Math.NET Numerics is an open-source numerical library for .NET and Mono, written in C# and F#. It features functionality similar to BLAS and LAPACK.
Parallel Colt is a set of multithreaded version of Colt. It is a collection of open-source libraries for High Performance Scientific and Technical Computing written in Java. It contains all the original capabilities of Colt and adds several new ones, with a focus on multi-threaded algorithms.
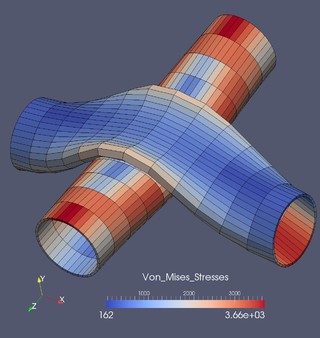
GetFEM++ is a generic finite element C++ library with interfaces for Python, Matlab and Scilab. It aims at providing finite element methods and elementary matrix computations for solving linear and non-linear problems numerically. Its flexibility in choosing among different finite element approximations and numerical integration methods is one of its distinguishing characteristics.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.