
Agrigento is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one of the leading cities of Magna Graecia during the golden age of Ancient Greece with population estimates in the range of 200,000 to 800,000 before 406 BC.

The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum, is a rectangular forum (plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancient city referred to this space, originally a marketplace, as the Forum Magnum, or simply the Forum.

The Capitolium or Capitoline Hill, between the Forum and the Campus Martius, is one of the Seven Hills of Rome.

The Palatine Hill, which is the centremost of the Seven Hills of Rome, is one of the most ancient parts of the city and has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire." It stands 40 metres above the Roman Forum, looking down upon it on one side, and upon the Circus Maximus on the other. From the time of Augustus Imperial palaces were built here. Prior to extensions to the Palace of Tiberius and the construction of the Domus Augustana by Domitian, 81-96 AD, the hill was mostly occupied by the houses of the rich. The perimeter measures 2,182 meters and the area is 255,801 square meters or 63 acres, with a circumference of 1,740 meters while the Regionary Catalogues of the fourth century give a perimeter of 11,510 feet or 3,402 meters (equals 131 acres.
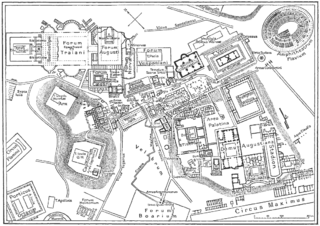
Vicus Tuscus was an ancient street in the city of Rome, running southwest out of the Roman Forum between the Basilica Julia and the Temple of Castor and Pollux towards the Forum Boarium and Circus Maximus via the west side of the Palatine Hill and Velabrum.

The Pantheon is a former Roman temple, now a church, in Rome, Italy, on the site of an earlier temple commissioned by Marcus Agrippa during the reign of Augustus. It was completed by the emperor Hadrian and probably dedicated about 126 AD. Its date of construction is uncertain, because Hadrian chose not to inscribe the new temple but rather to retain the inscription of Agrippa's older temple, which had burned down.
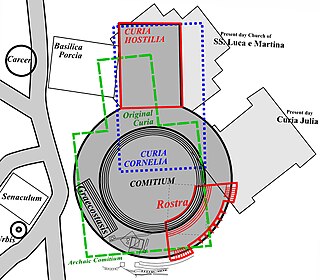
The Curia Hostilia was one of the original senate houses or "curia" of the Roman Republic. It is believed to have begun as a temple where the warring tribes laid down their arms during the reign of Romulus. During the early monarchy, the temple was used by senators acting as council to the king. Tullus Hostilius is believed to have replaced the original structure after fire destroyed the converted temple. It may have held historic significance as the location of an Etruscan mundus and altar. The Lapis Niger, a series of large black marble slabs, was placed over the altar where a series of monuments was found opposite the Rostra. This curia was enlarged in 80 BC by Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his renovations of the comitium. The building burned down in 53 BC when the supporters of the murdered Publius Clodius Pulcher used it as a pyre to cremate his body.

The Campus Martius was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about 2 square kilometres in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome. The IV rione of Rome, Campo Marzio, which covers a smaller section of the original area, bears the same name.

The Temple of Portunus or Temple of Fortuna Virilis is a Roman temple in Rome, Italy, one of the best preserved of all Roman temples. Its dedication remains unclear, as ancient sources mention several temples in this area of Rome, without saying enough to make it clear which this is. It was called the Temple of Fortuna Virilis from the Renaissance, and remains better known by this name. If dedicated to Portunus, the god of keys, doors and livestock, and so granaries, it is the main temple dedicated to the god in the city.

Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete state. Today they remain "the most obvious symbol of Roman architecture". Their construction and maintenance was a major part of ancient Roman religion, and all towns of any importance had at least one main temple, as well as smaller shrines. The main room (cella) housed the cult image of the deity to whom the temple was dedicated, and often a small altar for incense or libations. Behind the cella was a room or rooms used by temple attendants for storage of equipment and offerings. The ordinary worshiper rarely entered the cella, and most public ceremonies were performed outside, on the portico, with a crowd gathered in the temple precinct.

The Forum Holitorium was the site of a commercial marketplace (macellum) for vegetables, herbs and oil in ancient Rome. It was "oddly located" outside the Porta Carmentalis in the Campus Martius, crowded between the Forum Boarium and buildings located in the Circus Flaminius.

The Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, also known as the Temple of Jupiter Capitolinus was the most important temple in Ancient Rome, located on the Capitoline Hill. It had a cathedral-like position in the official religion of Rome, and was surrounded by the Area Capitolina, a precinct where certain assemblies met, and numerous shrines, altars, statues and victory trophies were displayed.

The Theatre of Pompey was a structure in Ancient Rome built during the latter part of the Roman Republican era by Pompey the Great. Completed in 55 BC, it was the first permanent theatre to be built in Rome.

The Tiber Island is the only island in the part of the Tiber which runs through Rome. Tiber Island is located in the southern bend of the Tiber.

The Temple of Vesta is an ancient edifice in Rome, Italy, located in the Roman Forum near the Regia and the House of the Vestal Virgins. The temple's most recognizable feature is its circular footprint. Since the worship of Vesta began in private homes, the architecture seems to be a reminder of its history. The extant temple used Greek architecture with Corinthian columns, marble, and a central cella. The remaining structure indicates that there were twenty Corinthian columns built on a podium fifteen meters in diameter. The roof probably had a vent at the apex to allow smoke release.

The Temple of Saturn was an ancient Roman temple to the god Saturn. Its ruins stand at the foot of the Capitoline Hill at the western end of the Roman Forum. The original dedication of the temple is traditionally dated to 497 BC, but ancient writers disagreed greatly about the history of this site.
Comana Pontica, was an ancient city located in ancient Pontus, now in modern Turkey.
The Battle of the Cremera was fought between the Roman Republic and the Etruscan city of Veii, in 477 BC.
Spes is the Roman goddess of hope.
















