Terpene synthases include:
These synthases' structures may include:
Terpene synthases include:
These synthases' structures may include:

Terpenes are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes are further classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), etc. A well known monoterpene is alpha-pinene, a major component of turpentine.
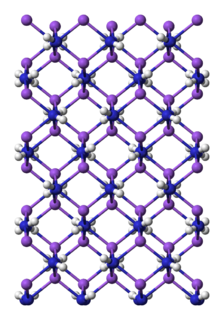
Sodium amide, commonly called sodamide, is the inorganic compound with the formula NaNH2. It is a salt composed of the sodium cation and the azanide anion. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is white, but commercial samples are typically gray due to the presence of small quantities of metallic iron from the manufacturing process. Such impurities do not usually affect the utility of the reagent. NaNH2 conducts electricity in the fused state, its conductance being similar to that of NaOH in a similar state. NaNH2 has been widely employed as a strong base in organic synthesis.
Diterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol. They are known to be antimicrobial and antiinflammatory.

Myrcene, or β-myrcene, is an alkene natural hydrocarbon. It is more precisely classified as a monoterpene. Monoterpenes are dimers of isoprenoid precursors, and myrcene is the primary component of the essential oil of the South African Adenandra villosa (50%), Myrcene is also found in bay, cannabis, and hops. It is produced mainly semi-synthetically from Myrcia, from which it gets its name. It is an intermediate in the production of several fragrances. α-Myrcene is the name for the structural isomer 2-methyl-6-methylene-1,7-octadiene, which has not been found in nature.

The epothilones are a class of potential cancer drugs. Like taxanes, they prevent cancer cells from dividing by interfering with tubulin, but in early trials epothilones have better efficacy and milder adverse effects than taxanes.

Fusicoccins are organic compounds produced by a fungus. It has detrimental effect on plants and causes their death.
Polyketide synthases (PKSs) are a family of multi-domain enzymes or enzyme complexes that produce polyketides, a large class of secondary metabolites, in bacteria, fungi, plants, and a few animal lineages. The biosyntheses of polyketides share striking similarities with fatty acid biosynthesis.
The long chain fatty acyl-CoA ligase is an enzyme of the ligase family that activates the oxidation of complex fatty acids. Long chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase catalyzes the formation of fatty acyl-CoA by a two-step process proceeding through an adenylated intermediate. The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction,

In molecular biology, Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase EC 2.3.1.41, is an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis. It typically uses malonyl-CoA as a carbon source to elongate ACP-bound acyl species, resulting in the formation of ACP-bound β-ketoacyl species such as acetoacetyl-ACP.

Cystathionine-β-synthase, also known as CBS, is an enzyme (EC 4.2.1.22) that in humans is encoded by the CBS gene. It catalyzes the first step of the transsulfuration pathway, from homocysteine to cystathionine:
Spermine synthase is an enzyme that converts spermidine into spermine. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

In enzymology, bornyl diphosphate synthase (BPPS) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Fatty-acyl-CoA Synthase, or more commonly known as yeast fatty acid synthase, is an enzyme complex responsible for fatty acid biosynthesis, and is of Type I Fatty Acid Synthesis (FAS). Yeast fatty acid synthase plays a pivotal role in fatty acid synthesis. It is a 2.6 MDa barrel shaped complex and is composed of two, unique multi-functional subunits: alpha and beta. Together, the alpha and beta units are arranged in an α6β6 structure. The catalytic activities of this enzyme complex involves a coordination system of enzymatic reactions between the alpha and beta subunits. The enzyme complex therefore consists of six functional centers for fatty acid synthesis.

The UDP-forming form of cellulose synthase is the main enzyme that produces cellulose. Systematically, it is known as UDP-glucose:(1→4)-β-D-glucan 4-β-D-glucosyltransferase in enzymology. It catalyzes the chemical reaction:

In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene and also part of the secondary metabolism. This entry will focus on the N terminal domain of the TPS protein.
In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene and also part of the secondary metabolism. This entry will focus on the C terminal domain of the TPS protein.
TPSC may refer to:
Sporulenol synthase (EC 4.2.1.137, sqhC (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name tetraprenyl-beta-curcumene—sporulenol cyclase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Tetraprenyl-beta-curcumene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name all-trans-heptaprenyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ATP synthase delta/epsilon subunit is a part of the ATP synthase and the F-ATPase family in general. It is known as the delta subunit in mitochondrial ATP syntheses, and the epsilon subunit in bacterial and chloroplastic ATP syntheses. It is part of the rotor between subunits F1 and FO. Its C terminal domain seems to inhibit ATPase activity of the synthase.