
Juglone, also called 5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione (IUPAC) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C10H6O3. In the food industry, juglone is also known as C.I. Natural Brown 7 and C.I. 75500. It is insoluble in benzene but soluble in dioxane, from which it crystallizes as yellow needles. It is an isomer of lawsone, which is the staining compound in the henna leaf.
The Bucherer reaction in organic chemistry is the reversible conversion of a naphthol to a naphthylamine in the presence of ammonia and sodium bisulfite. The reaction is widely used in the synthesis of dye precursors aminonaphthalenesulfonic acids.
The Étard reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the direct oxidation of an aromatic or heterocyclic bound methyl group to an aldehyde using chromyl chloride. For example, toluene can be oxidized to benzaldehyde.
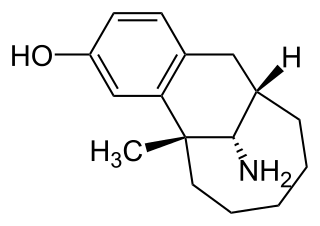
Dezocine is a marketed opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan group. First synthesized in 1970, it acts as a modulator of mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors. Dezocine is a mixed agonist/antagonist of opioid receptors. It is related to other benzomorphans such as pentazocine, with a similar profile of effects that include analgesia and euphoria. Unlike many other benzomorphans however, it is a silent antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor, and in accordance, does not produce side effects such as dysphoria or hallucinations at any dose.

Tetraethylammonium bromide (TEAB) is a quaternary ammonium compound with the chemical formula C8H20N+Br−, often written as "Et4N+Br−" in the chemical literature. It has been used as the source of tetraethylammonium ions in pharmacological and physiological studies, but is also used in organic chemical synthesis.

Xylaria hypoxylon is a species of fungus in the genus Xylaria. It is known by a variety of common names, such as the candlestick fungus, the candlesnuff fungus, carbon antlers, or the stag's horn fungus. The fruit bodies, characterized by erect, elongated black branches with whitened tips, typically grow in clusters on decaying hardwood. The fungus can cause a root rot in hawthorn and gooseberry plants.
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a fluorescent organic compound with the formula C10H7OH. It is a white solid. It is an isomer of 2-naphthol differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol, with the hydroxyl group being more reactive than in the phenols. Both isomers are soluble in simple alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds. Naphthols (both 1 and 2 isomers) are used as biomarkers for livestock and humans exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.

Tametraline (CP-24,441) is the parent of a series of chemical compounds investigated at Pfizer that eventually led to the development of sertraline (CP-51,974-1).
A dihydroxyanthraquinone is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula C
14H
8O
4, formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. Dihyroxyantraquinones have been studied since the early 1900s, and include some compounds of historical and current importance. The isomers differ in the position of the hydroxyl groups, and of the carbonyl oxygens (=O) of the underlying anthraquinone.
A hydroxynaphthoquinone is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of a naphthoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).
A dihydroxynaphthoquinone is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of naphthoquinone through replacement of two hydrogen atoms (H) by hydroxyl groups (OH).

Naphthazarin, often called 5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone or 5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione (IUPAC), is a naturally occurring organic compound with formula C
10H
6O
4, formally derived from 1,4-naphthoquinone through replacement of two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is thus one of many dihydroxynaphthoquinone structural isomers.
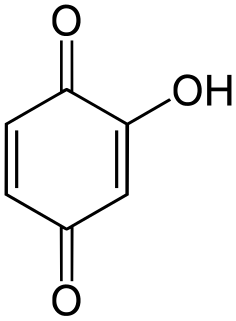
Hydroxyquinone often refers to a hydroxybenzoquinone, any organic compound with formula C
6H
4O
3 which can be viewed as a derivative of a benzoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH). When unqualified, the terms usually mean specifically the compound 2-hydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, derived from 1,4-benzoquinone or para-benzoquinone.
A hydroxyanthraquinone (formula: C14H9O2(OH)) is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of an anthraquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).
The IUPAC nomenclature recommends hydroxyanthracenedione.

A walnut is the nut of any tree of the genus Juglans, particularly the Persian or English walnut, Juglans regia.

Sodium bisulfite (or sodium bisulphite, sodium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NaHSO3. Sodium bisulfite is a food additive with E number E222. This salt of bisulfite can be prepared by bubbling sulfur dioxide in a solution of sodium carbonate in water. Sodium bisulfite in contact with chlorine bleach (aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite) will generate heat and form sodium bisulfate and sodium chloride.

Phenylpropanoic acid or hydrocinnamic acid is a carboxylic acid with the formula C9H10O2 belonging to the class of phenylpropanoids. It is a white, crystalline solid with a sweet, floral scent at room temperature. Phenylpropanoic acid has a wide variety of uses including cosmetics, food additives, and pharmaceuticals.
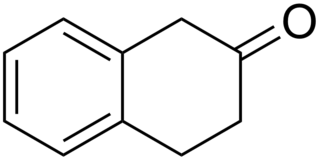
2-Tetralone is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C10H10O. This colourless oil is an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is a ketone derivative of tetralin, a hydrogenated derivative of naphthalene. A related compound is 1-tetralone.

1-Tetralone is a bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with an α-keto group and can also be regarded as benzo-fused cyclohexanone. It is used as starting material for agricultural and pharmaceutical agents.











