Mass media in Venezuela comprise the mass and niche news and information communications infrastructure of Venezuela. Thus, the media of Venezuela consist of several different types of communications media: television, radio, newspapers, magazines, cinema, and Internet-based news outlets and websites. Venezuela also has a strong music industry and arts scene.

The Bolivarian Revolution is an ongoing political process in Venezuela that was started by Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez, the founder of the Fifth Republic Movement and later the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV), and his successor Nicolás Maduro. The Bolivarian Revolution is named after Simón Bolívar, an early 19th-century Venezuelan revolutionary leader, prominent in the Spanish American wars of independence in achieving the independence of most of northern South America from Spanish rule. According to Chávez and supporters, the Bolivarian Revolution seeks to build an inter-American coalition to implement Bolivarianism, nationalism and a state-led economy.

The Bolivarian National Intelligence Service is the premier intelligence agency in Venezuela. SEBIN is an internal security force subordinate to the Vice President of Venezuela since 2012 and is dependent on Vice President Delcy Rodríguez. SEBIN has been described as the political police force of the Bolivarian government.

Telesur is a Latin American terrestrial and satellite news television network headquartered in Caracas, Venezuela and sponsored by the governments of Venezuela, Cuba and Nicaragua.

Corporación Venezolana de Televisión or VTV is a state-run television station based in Caracas, Venezuela, which can be seen throughout the capital and surrounding areas on channel 8. Programs that can be seen on VTV included Aló Presidente and Telesur Noticias.

The Cabinet of Ministers of Venezuela (Spanish: Gabinete de Ministros de Venezuela is one of the bodies that make up the Venezuelan executive in that country's presidential system, alongside the Council of Ministers. The Cabinet is headed by the president of Venezuela, and his corresponding vice president. The purpose of the ministries is to create, adopt, follow and evaluate policies, strategies, programs and projects in accordance with the constitution and the laws of the republic.

The United Socialist Party of Venezuela is a left-wing to far-left socialist political party which has been the ruling party of Venezuela since 2007. It was formed from a merger of some of the political and social forces that support the Bolivarian Revolution led by President Hugo Chávez.

Bolivarian propaganda is a form of nationalist propaganda, especially in Venezuela and associated with chavismo, Venezuelan socialism. This type of propaganda has been associated with Hugo Chávez's Bolivarian Revolution, which used emotional arguments to gain attention, exploit the fears of the population, create external enemies for scapegoat purposes, and produce nationalism within the population, causing feelings of betrayal for support of the opposition.

Colectivos are far-left Venezuelan armed paramilitary groups that support the Bolivarian government, the Great Patriotic Pole (GPP) political alliance and Venezuela's ruling party, and the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV). Colectivo has become an umbrella term for irregular armed groups that operate in poverty-stricken areas.

Ernesto Emilio Villegas Poljak is a journalist, politician, and writer from Venezuela.
The Units of Battle Hugo Chávez (UBCh) is a collection of organizations with multiple members of PSUV involved that has both military and political characteristics.
The Cartel of the Suns is a Venezuelan organization supposedly headed by high-ranking members of the Armed Forces of Venezuela who are involved in international drug trade. According to Héctor Landaeta, journalist and author of Chavismo, Narco-trafficking and the Military, the phenomenon began when Colombian drugs began to enter into Venezuela from corrupt border units and the "rot moved its way up the ranks."

In Venezuela, a cult of personality has been created around the late President Hugo Chávez, where his supporters venerate him. Chávez largely received his support through his charisma and by spending Venezuela's oil funds on the poor.

2016 protests in Venezuela began in early January following controversy surrounding the 2015 Venezuelan parliamentary elections and the increasing hardships felt by Venezuelans. The series of protests originally began in February 2014 when hundreds of thousands of Venezuelans protested due to high levels of criminal violence, inflation, and chronic scarcity of basic goods because of policies created by the Venezuelan government though the size of protests had decreased since 2014.

Presidential elections were held in Venezuela on 20 May 2018, with incumbent Nicolás Maduro being declared re-elected for a second six-year term. The original electoral date was scheduled for December 2018 but was subsequently pulled ahead to 22 April before being pushed back to 20 May. Some analysts described the poll as a sham election, as many prominent opposition parties had been barred from participating in it. The elections had the lowest voter turnout in Venezuela's democratic era.
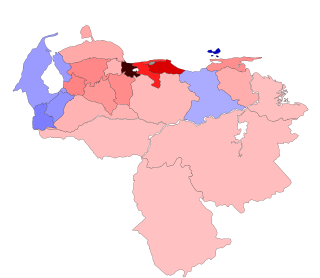
Regional elections were held in Venezuela on 15 October 2017 to elect the executive position of all 23 federal entities. This marked the first state executive election not held on the same date as elections for state legislatures, and the second separate from municipal elections. They were the 9th regional elections held in Venezuela since 1989.

Constituent Assembly elections were held in Venezuela on 30 July 2017 to elect the members of the 2017 Constituent National Assembly. Unlike the 1999 Constituent National Assembly, which was assembled following a referendum, the 2017 election was convened by the presidential decree of President Nicolás Maduro. Smartmatic, the Venezuelan-owned company which provided the voting machines, stated that the results were tampered with by the CNE, and that the turnout was off by at least one million votes.

On 27 June 2017, there was an incident involving a police helicopter at the Supreme Tribunal of Justice (TSJ) and Interior Ministry in Caracas, Venezuela. Claiming to be a part of an anti-government coalition of military, police and civilians, the occupants of the helicopter allegedly launched several grenades and fired at the building, although no one was injured or killed. President Nicolás Maduro called the incident a "terrorist attack". The helicopter escaped and was found the next day in a rural area. On 15 January 2018, Óscar Pérez, the pilot and instigator of the incident, was killed during a military raid by the Venezuelan army that was met with accusations of extrajudicial killing.

The Constituent National Assembly was a constituent assembly elected in 2017 to draft a new constitution for Venezuela. Its members were elected in a special 2017 election that was condemned by over forty mostly Latin American and Western states. The Democratic Unity Roundtable—the opposition to the incumbent ruling party—also boycotted the election claiming that the Constituent Assembly was "a trick to keep [the incumbent ruling party] in power." Since the opposition did not participate in the election, the incumbent Great Patriotic Pole, dominated by the United Socialist Party of Venezuela, won almost all seats in the assembly by default.
The Supreme Tribunal of Justice of Venezuela (TSJ) in exile is an institution that some, including the Organization of American States, consider to be the legitimate highest court of law in Venezuela and the head of the judicial branch, as opposed to the Supreme Tribunal of Justice. It was established on 21 July 2017 following the 2017 Venezuelan constitutional crisis. The TSJ's 33 members have been based in Chile, Colombia, Panama, and the United States due to the political crisis in Venezuela.














