
Martin Gardner was an American popular mathematics and popular science writer with interests also encompassing magic, scientific skepticism, micromagic, philosophy, religion, and literature – especially the writings of Lewis Carroll, L. Frank Baum, and G. K. Chesterton. He was a leading authority on Lewis Carroll; The Annotated Alice, which incorporated the text of Carroll's two Alice books, was his most successful work and sold over a million copies. He had a lifelong interest in magic and illusion and in 1999, MAGIC magazine named him as one of the "100 Most Influential Magicians of the Twentieth Century". He was considered the doyen of American puzzlers. He was a prolific and versatile author, publishing more than 100 books.

The Committee for Skeptical Inquiry (CSI), formerly known as the Committee for the Scientific Investigation of Claims of the Paranormal (CSICOP), is a program within the U.S. non-profit organization Center for Inquiry (CFI), which seeks to "promote scientific inquiry, critical investigation, and the use of reason in examining controversial and extraordinary claims." Paul Kurtz proposed the establishment of CSICOP in 1976 as an independent non-profit organization, to counter what he regarded as an uncritical acceptance of, and support for, paranormal claims by both the media and society in general. Its philosophical position is one of scientific skepticism. CSI's fellows have included notable scientists, Nobel laureates, philosophers, psychologists, educators, and authors. It is headquartered in Amherst, New York.

Scientific skepticism or rational skepticism, sometimes referred to as skeptical inquiry, is a position in which one questions the veracity of claims lacking empirical evidence. In practice, the term most commonly refers to the examination of claims and theories that appear to be beyond mainstream science, rather than the routine discussions and challenges among scientists. Scientific skepticism differs from philosophical skepticism, which questions humans' ability to claim any knowledge about the nature of the world and how they perceive it, and the similar but distinct methodological skepticism, which is a systematic process of being skeptical about the truth of one's beliefs.
Drunkard's Walk may refer to:

Deepak Chopra is an Indian-American author and alternative medicine advocate. A prominent figure in the New Age movement, his books and videos have made him one of the best-known and wealthiest figures in alternative medicine. His discussions of quantum healing have been characterised as technobabble – "incoherent babbling strewn with scientific terms" derided by those proficient in physics.

Yakov Grigorevich Sinai is a Russian–American mathematician known for his work on dynamical systems. He contributed to the modern metric theory of dynamical systems and connected the world of deterministic (dynamical) systems with the world of probabilistic (stochastic) systems. He has also worked on mathematical physics and probability theory. His efforts have provided the groundwork for advances in the physical sciences.

Leonard Mlodinow is an American theoretical physicist and mathematician, screenwriter and author. In physics, he is known for his work on the large N expansion, a method of approximating the spectrum of atoms based on the consideration of an infinite-dimensional version of the problem, and for his work on the quantum theory of light inside dielectrics.

Philip Julian Klass was a preeminent American aviation/aerospace journalist and UFO researcher, best known for his skepticism regarding UFOs. In the ufological and skeptical communities, Klass inspires polarized appraisals. He has been called the "Sherlock Holmes of UFOlogy". Klass demonstrated "the crusader's zeal for what seems 'right,' regardless of whether it brings popular acclaim," a trait he claimed his father instilled in him. "I've found," said Klass, "that roughly 97, 98 percent of the people who report seeing UFOs are fundamentally intelligent, honest people who have seen something—usually at night, in darkness—that is unfamiliar, that they cannot explain." The rest, he said, were frauds.
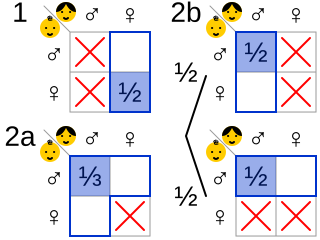
The Boy or Girl paradox surrounds a set of questions in probability theory, which are also known as The Two Child Problem, Mr. Smith's Children and the Mrs. Smith Problem. The initial formulation of the question dates back to at least 1959, when Martin Gardner featured it in his October 1959 "Mathematical Games column" in Scientific American. He titled it The Two Children Problem, and phrased the paradox as follows:

Alfred Paul "Al" Seckel was an American collector and popularizer of visual and other types of sensory illusions, who wrote books about them. Active in the Freethought movement as a skeptic in the 1980s, he was the co-founder and executive director of the Southern California Skeptics. News coverage arising from his connection to Jeffrey Epstein has stressed Seckel's misrepresentation of his education and credentials.

James E. Alcock is a Canadian educator. He has been a Professor of Psychology at York University (Canada) since 1973. Alcock is a noted critic of parapsychology and is a Fellow and Member of the Executive Council for the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry. He is a member of the Editorial Board of The Skeptical Inquirer, and a frequent contributor to the magazine. He has also been a columnist for Humanist Perspectives Magazine. In 1999, a panel of skeptics named him among the two dozen most outstanding skeptics of the 20th century. In May 2004, CSICOP awarded Alcock CSI's highest honor, the In Praise of Reason Award. Alcock is also an amateur magician and is a member of the International Brotherhood of Magicians. As of 2020, he is currently on leave from York University.

In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of definite pattern or predictability in information. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. Individual random events are, by definition, unpredictable, but if there is a known probability distribution, the frequency of different outcomes over repeated events is predictable. For example, when throwing two dice, the outcome of any particular roll is unpredictable, but a sum of 7 will tend to occur twice as often as 4. In this view, randomness is not haphazardness; it is a measure of uncertainty of an outcome. Randomness applies to concepts of chance, probability, and information entropy.

Critical Mass: How One Thing Leads to Another, a non-fiction book by English chemist and physicist Philip Ball originally published in 2004, discusses the concept of a "physics of society". Ball discusses thinkers such as Thomas Hobbes, Lewis Mumford, Emyr Hughes, and Gottfried Achenwall who have attempted to apply physics, chemistry, or mathematics in the study of mass social phenomena. He also discusses how the concept relates to recent research, including his own.

The Grand Design is a popular-science book written by physicists Stephen Hawking and Leonard Mlodinow and published by Bantam Books in 2010. The book examines the history of scientific knowledge about the universe and explains eleven-dimensional M-theory. The authors of the book point out that a Unified Field Theory may not exist.

The Hidden Reality: Parallel Universes and the Deep Laws of the Cosmos is a book by Brian Greene published in 2011 which explores the concept of the multiverse and the possibility of parallel universes. It has been nominated for the Royal Society Winton Prize for Science Books for 2012.
Model-dependent realism is a view of scientific inquiry that focuses on the role of scientific models of phenomena. It claims reality should be interpreted based upon these models, and where several models overlap in describing a particular subject, multiple, equally valid, realities exist. It claims that it is meaningless to talk about the "true reality" of a model as we can never be absolutely certain of anything. The only meaningful thing is the usefulness of the model. The term "model-dependent realism" was coined by Stephen Hawking and Leonard Mlodinow in their 2010 book, The Grand Design.

Donald Ross Prothero is an American geologist, paleontologist, and author who specializes in mammalian paleontology and magnetostratigraphy, a technique to date rock layers of the Cenozoic era and its use to date the climate changes which occurred 30–40 million years ago. He is the author or editor of more than 30 books and over 300 scientific papers, including at least 5 geology textbooks.
The Northeast Conference on Science and Skepticism is a four-day conference focusing on science and skepticism founded in 2009 and held annually in New York City. NECSS is jointly run by the New York City Skeptics (NYCS) and the New England Skeptical Society (NESS). The Society for Science-Based Medicine joined as a full sponsor of the conference in 2015. As of 2016, attendance was estimated at approximately 500 people.

CSICon or CSIConference is an annual skeptical conference typically held in the United States. CSICon is hosted by the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry (CSI), which is a program of the Center for Inquiry (CFI). CSI publishes the magazine Skeptical Inquirer.















