
Grandma's Reading Glass is a 1900 British short silent drama film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring a young Willy who borrows a huge magnifying glass to focus on various objects, which was shot to demonstrate the new technique of close-up. The film, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "was one of the first films to cut between medium shot and point-of-view close-up. It was destroyed in a fire at Warwick Trading Company's studio facility in 1912.

As Seen Through a Telescope is a 1900 British short silent comedy film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring an elderly gentleman getting a glimpse of a woman's ankle through a telescope. The three-shot comedy, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "uses a similar technique to that which G.A. Smith pioneered in Grandma's Reading Glass (1900)," and although, "the editing is unsophisticated, the film does at least show a very early example of how to make use of point-of-view close-ups in the context of a coherent narrative ." "Smith's experiments with editing," Brooke concludes, "were ahead of most contemporary film-makers, and in retrospect it can clearly be seen that he was laying the foundations of film grammar as we now understand it."

The Kiss in the Tunnel, also known as A Kiss in the Tunnel, is a 1899 film British short silent comedy film, produced and directed by George Albert Smith, showing a couple sharing a brief kiss as their train passes through a tunnel, which is said to mark the beginnings of narrative editing. The film is the first to feature Laura Bayley, Smith's wife.

Mary Jane's Mishap; or, Don't Fool with the Paraffin is a 1903 British short silent comedy film, directed by George Albert Smith, depicting disaster following when housemaid Mary Jane uses paraffin to light the kitchen stove. The trick film, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "is an example of Smith's interest in cinematic effects - including, here, the use of superimposition to suggest ghosts," which, "is notable for its then sophisticated mix of wide establishing shots and medium close-ups," and, "also contains two wipes to denote a change of scene."

Grandma Threading her Needle is a 1900 British short silent comedy film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring a grandma trying to get a thread though a needle. The sole purpose of the single-shot film, like the director's earlier Old Man Drinking a Glass of Beer (1898), according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "is to record changing facial expressions for the purposes of entertainment."
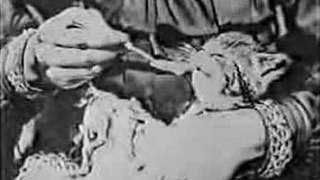
The Sick Kitten is a 1903 British short silent comedy film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring two young children tending to a sick kitten.

The House That Jack Built is a 1900 British short silent drama film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring a boy who knocks over a house made of bricks built by his sister and then rebuilds it when the original sequence is shown in reverse. "In addition to exploiting a popular cinematic trick," of, "reversing the film in the projector," and, "its audience's presumed knowledge of the technique," the director, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "was continuing his experiments with narrative forms," with the reversed sequence, "interpreted as wish-fulfilment on the part of the girl, hoping that time will literally turn back on itself to allow her house to be rebuilt," he, "demonstrates that while this is impossible in reality, it is easily achievable in cinema."

Tartans of Scottish Clans is a 1906 British short silent documentary film, directed by George Albert Smith as a test for his newly patented Kinemacolor system, which features a sequence of appropriately labelled Scottish tartan cloths, with an abundance of reds and greens, the two colours used by the system. The film, which was one of Smith's first Kinemacolor experiments, was according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "a very simple idea which nonetheless demanded colour in order to convey the necessary information."

Woman Draped in Patterned Handkerchiefs is a 1908 British short silent documentary film, directed by George Albert Smith as a showcase of his new Kinemacolor system, which features a woman displaying assorted tartan cloths, both draped on her body and waved semaphore-style. The patterned handkerchiefs are, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "presumably the same cloths featured in Tartans of Scottish Clans (1906), this time shown from various angles."

Spiders on a Web is a 1900 British short silent documentary film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring a single shot close-up of two spiders trapped in an enclosure. The film is, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "less formally ambitious," than the director's, "groundbreaking multiple close-up study Grandma's Reading Glass (1900), made the same year, but is nonetheless, "one of the earliest British examples of close-up natural history photography, predating Percy Smith's insect studies by a decade."

Santa Claus is an 1898 British short silent drama film, directed by George Albert Smith, which features Santa Claus visiting a house on Christmas Eve. The film, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "is believed to be the cinema's earliest known example of parallel action and, when coupled with double-exposure techniques that Smith had already demonstrated in the same year's The Mesmerist (1898) and Photographing a Ghost (1898), the result is one of the most visually and conceptually sophisticated British films made up to then." It has been described as the very first Christmas movie and a technical marvel of its time.

The X-Rays is an 1897 British short silent comedy film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring a courting couple exposed to X-rays. The trick film, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "contains one of the first British examples of special effects created by means of jump cuts" Smith employs the jump-cut twice; first to transform his courting couple via "X rays," dramatized by means of the actors donning black bodysuits decorated with skeletons and with the woman holding only the metal support work of her umbrella, and then to return them and the umbrella to normal. The couple in question were played by Smith's wife Laura Bayley and Tom Green.

Old Man Drinking a Glass of Beer is a 1897 British short silent comedy film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring a man drinking a glass of beer whose face and hands become increasingly lively as a result. The single-shot film shows comedian Tom Green, according to Bryony Dixon of BFIfilms, "performing what is known as a 'facial', that is a piece direct to camera showing changing facial expressions. The ability to get close up to the star was a great advantage that film had over the stage and early filmmakers were keen to exploit it."

The Big Swallow is a 1901 British short silent comedy film, directed by James Williamson, featuring a man, irritated by the presence of a photographer, who solves his dilemma by swallowing him and his camera whole. The three-shot trick film is, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "one of the most important early British films in that it was one of the first to deliberately exploit the contrast between the eye of the camera and of the audience watching the final film".

The Little Match Seller is a 1902 British short silent drama film, directed by James Williamson, retelling the classic 1845 Hans Christian Andersen fable of the sad life and tragic death of a little match seller. This major fiction film of the period was, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "a serious attempt at depicting a person's inner emotional life on film through purely visual means, using trick effects not to provoke laughter but for serious dramatic reasons."

Our New Errand Boy is a 1905 British short silent comedy film, directed by James Williamson, about a new errand boy, engaged by a grocer who soon regrets the appointment. This "relatively unambitious" chase comedy, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "is one of a number of Williamson films featuring a mischievous child, played by the director's son Tom." "Although essentially a series of sketches," this film, according to David Fisher, "demonstrates the extent to which Williamson had developed film technique For a start, the film has a title frame, which includes the logo of the Williamson Cinematograph Company," and, "the chase section anticipates the American comedies of the next decade."

Let Me Dream Again is a 1900 British short silent drama film, directed by George Albert Smith, featuring a man dreaming about an attractive young woman and then waking up next to his wife. The film stars Smith's real wife, Laura Bayley, as the woman of his fantasies. Bayley would later appear in Smith's 1906 film Mary Jane's Mishap. The film, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "is an excellent example of an early two-shot film, and is particularly interesting for the way it attempts a primitive dissolve by letting the first shot slip out of focus before cutting to the second shot, which starts off out of focus and gradually sharpens." This appears to be the first use of a dissolve transition to signify a movement of a dreaming state to one of reality.

The Man to Beat Jack Johnson is a 1910 British short black-and-white silent comedy film, produced by the Tyler Film Company, featuring four-year-old Willy Sanders demonstrating his boxing and wrestling skills against an adult opponent.

Comic Costume Race is an 1896 British short black-and-white silent actuality film, directed by Robert W. Paul, featuring comic costume scramble at the Music Hall Sports on 14 July 1896 at Herne Hill, London. The music hall sports day was an annual charity event consisting of other events such as egg and spoon races and three-legged races. The film is the best surviving pictorial record of the Music Hall Sports. It is not known who the race participants are.

Willie's Magic Wand is a 1907 British short silent comedy film, directed by Walter R. Booth, featuring a young boy terrorising the household with his father's magic wand. Similar to "earlier trick films The Haunted Curiosity Shop and Undressing Extraordinary ," this is, according to Michael Brooke of BFI Screenonline, "essentially a series of [loosely linked] special-effects set pieces," however, "the print in the National Film and Television Archive is incomplete, omitting amongst other things a come-uppance where Willie is punished for his misdemeanours by being turned into a girl, thus depriving him of more than one magic wand." A clip from the film is featured in Paul Merton's interactive guide to early British silent comedy How They Laughed on the BFI website.




















