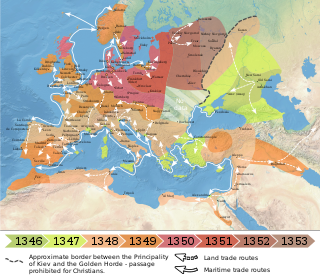
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as 50 million people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis and spread by fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history.

Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus, often anglicized as Galen or Galen of Pergamon, was a Roman and Greek physician, surgeon, and philosopher. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all medical researchers of antiquity, Galen influenced the development of various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and neurology, as well as philosophy and logic.

In astronomy, a conjunction occurs when two astronomical objects or spacecraft appear to be close to each other in the sky. This means they have either the same right ascension or the same ecliptic longitude, usually as observed from Earth.

The Canon of Medicine is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Muslim Persian physician-philosopher Avicenna and completed in 1025. It is among the most influential works of its time. It presents an overview of the contemporary medical knowledge of the Islamic world, which had been influenced by earlier traditions including Greco-Roman medicine, Persian medicine, Chinese medicine and Indian medicine. Its translation from Arabic to Latin in 12th century Toledo greatly influenced the development of medieval medicine. It became the standard textbook for teaching in European universities into the early modern period.

The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can cause disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade humans, other animals, and other living hosts. Their growth and reproduction within their hosts can cause disease. "Germ" refers to not just a bacterium but to any type of microorganism, such as protists or fungi, or other pathogens that can cause disease, such as viruses, prions, or viroids. Diseases caused by pathogens are called infectious diseases. Even when a pathogen is the principal cause of a disease, environmental and hereditary factors often influence the severity of the disease, and whether a potential host individual becomes infected when exposed to the pathogen. Pathogens are disease-carrying agents that can pass from one individual to another, both in humans and animals. Infectious diseases are caused by biological agents such as pathogenic microorganisms as well as parasites.

The miasma theory is an abandoned medical theory that held that diseases—such as cholera, chlamydia, or the Black Death—were caused by a miasma, a noxious form of "bad air", also known as night air. The theory held that epidemics were caused by miasma, emanating from rotting organic matter. Though miasma theory is typically associated with the spread of contagious diseases, some academics in the early nineteenth century suggested that the theory extended to other conditions as well, e.g. one could become obese by inhaling the odor of food.

Ergotism is the effect of long-term ergot poisoning, traditionally due to the ingestion of the alkaloids produced by the Claviceps purpurea fungus—from the Latin clava "club" or clavus "nail" and -ceps for "head", i.e. the purple club-headed fungus—that infects rye and other cereals, and more recently by the action of a number of ergoline-based drugs. It is also known as ergotoxicosis, ergot poisoning, and Saint Anthony's fire.

The Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems is a 1632 Italian-language book by Galileo Galilei comparing the Copernican system with the traditional Ptolemaic system. It was translated into Latin as Systema cosmicum in 1635 by Matthias Bernegger. The book was dedicated to Galileo's patron, Ferdinando II de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, who received the first printed copy on February 22, 1632.
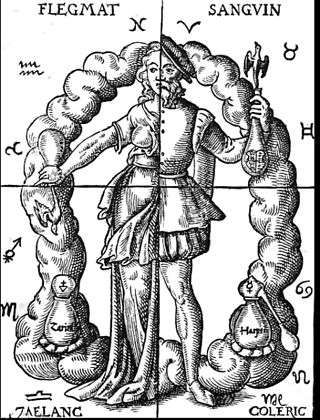
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, is a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.

Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Yaḥyà ibn aṣ-Ṣā’igh at-Tūjībī ibn Bājja, best known by his Latinised name Avempace, was an Andalusi polymath, whose writings include works regarding astronomy, physics, and music, as well as philosophy, medicine, botany, and poetry.

A great conjunction is a conjunction of the planets Jupiter and Saturn, when the two planets appear closest together in the sky. Great conjunctions occur approximately every 20 years when Jupiter "overtakes" Saturn in its orbit. They are named "great" for being by far the rarest of the conjunctions between naked-eye planets.

The Plague of Athens was an epidemic that devastated the city-state of Athens in ancient Greece during the second year of the Peloponnesian War when an Athenian victory still seemed within reach. The plague killed an estimated 75,000 to 100,000 people, around 25% of the population, and is believed to have entered Athens through Piraeus, the city's port and sole source of food and supplies. Thucydides, an Athenian survivor, wrote that much of the eastern Mediterranean also saw an outbreak of the disease, albeit with less impact.
Aristotelian physics is the form of natural philosophy described in the works of the Greek philosopher Aristotle. In his work Physics, Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies, both living and inanimate, celestial and terrestrial – including all motion, quantitative change, qualitative change, and substantial change. To Aristotle, 'physics' was a broad field including subjects which would now be called the philosophy of mind, sensory experience, memory, anatomy and biology. It constitutes the foundation of the thought underlying many of his works.
In astrology, planets have a meaning different from the astronomical understanding of what a planet is. Before the age of telescopes, the night sky was thought to consist of two similar components: fixed stars, which remained motionless in relation to each other, and moving objects/"wandering stars", which moved relative to the fixed stars over the course of the year(s).
Planetary aspects are interchange of energies at great distances; the respective mass of each planet generates and radiates its own specific energy-field. At times these planetary aspects take a lead over planetary conjunctions. Planetary aspects play an important role in predicting future events. However, there are three great differences between Western astrology and Hindu astrology in computing these aspects - (1) in the former system the count is made from degree to degree, in the latter system the count is made from sign to sign, (2) in the former system the aspect will be mutually the same i.e. if Mars and Jupiter are in trine it can be expressed as either Mars Trine Jupiter or Jupiter Trine Mars, in the latter system if Jupiter is in Aries and Mars in Leo, Jupiter will have full aspect on Mars but Mars will have 50% aspect on Jupiter and, (3) in the former system certain aspects such as sextile are good whereas square and opposition are evil, the latter system does not have such classification in which system aspects by benefic planets and those owning trines i.e. the 5th and the 9th, are always good, and by malefic planets and those owning cadent houses i.e. the 6th, 8th or 12th, are always evil; moreover, the aspect of any planet on its own sign strengthens that house and causes no harm to its indications.
Sanyasa yoga in Hindu astrology are the peculiar planetary situations or combinations seen in certain horoscopes that indicate Sanyasa i.e. renunciation of worldly material life by persons born with those yogas. Sanyasa yogas are also known as Pravrajya yogas.
Dhana yogas are astrological combinations or yogas for wealth and prosperity which prove more fruitful if both the lagna and its lord are strong, and there are no Arista yogas present affecting the Dhana yoga - causing planets and the bhavas associated with earning, acquisition, and accumulation of wealth. Jupiter is one of the natural Dhana-karaka, a strong Jupiter gives lifelong prosperity and financial stability.
Maraka in Hindu astrology refers to the planet or planets that cause death at the end of a particular life-span; if the assessed life-span is not over they cause accident, ill-health, poverty and misery during the course of their dasha or antra-dasha or in the period of the planet associating/influenced by them. Each lagna has a fixed maraka or marakas. The two luminaries, the Sun and the Moon, and the lord of the 9th house generally do not become marakas. The lords of the 2nd and the 7th house, or the malefic planets occupying anyone of these named houses and associated with their lords are the Primary determinants of death. The Secondary determinants of death are the benefic planets in association with lords of 2nd and 7th house or the lords of the 3rd and 8th house, or the lord of the 3rd or the 8th associating with the lord of the 2nd or the 7th house. The Tertiary determinants of death are Saturn associating with any of the afore stated marakas, the lord of the 6th or the 8th associated with a maraka, and the least powerful planet in the horoscope. The transit influences of the Sun, Mars and Jupiter are taken into account for determining the time of death.
Jacques du Chevreul was a French mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher.
Secreta mulierum, also known as De secretis mulierum, is a natural philosophical text from the late thirteenth or early fourteenth century frequently attributed to Albertus Magnus, although it is more likely written by one of his followers. Originally written in Latin, the title translates as The Secrets of Women or Of the Secrets of Women. Drawing on Hippocratic, Galenic, and Aristotelian theories, this text discusses sexuality and reproduction from both a medical and philosophical perspective. Over eighty manuscript copies of the treatise have been identified, and it has been translated into multiple different languages over several centuries. This suggests that the ideas expressed in this work were hugely popular and influential. It was added to the Index librorum prohibitorum in 1605.











