
Brest, formerly Brest-Litovsk and Brest-on-the-Bug, is a city in Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the Polish town of Terespol, where the Bug and Mukhavets rivers meet, making it a border town. It serves as the administrative center of Brest Region and Brest District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2023, it has a population of 342,461.


The Warsaw Uprising, shortly after the war also known as the August Uprising, was a major World War II operation by the Polish underground resistance to liberate Warsaw from German occupation. It occurred in the summer of 1944, and it was led by the Polish resistance Home Army. The uprising was timed to coincide with the retreat of the German forces from Poland ahead of the Soviet advance. While approaching the eastern suburbs of the city, the Red Army halted combat operations, enabling the Germans to regroup and defeat the Polish resistance and to destroy the city in retaliation. The Uprising was fought for 63 days with little outside support. It was the single largest military effort taken by any European resistance movement during World War II.

Around six million Polish citizens are estimated to have perished during World War II. Most were civilians killed by the actions of Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, the Lithuanian Security Police, as well as the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists and its offshoots.

The German camps in occupied Poland during World War II were built by the Nazis between 1939 and 1945 throughout the territory of the Polish Republic, both in the areas annexed in 1939, and in the General Government formed by Nazi Germany in the central part of the country (see map). After the 1941 German attack on the Soviet Union, a much greater system of camps was established, including the world's only industrial extermination camps constructed specifically to carry out the "Final Solution to the Jewish Question".

Kovel is a city in Volyn Oblast, northwestern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Kovel Raion within the oblast. Population: 67,575.

Witold Pilecki was a Polish World War II cavalry officer, intelligence agent, and resistance leader.

The Tomb of the Unknown Soldier is a monument in Warsaw, Poland, dedicated to the unknown soldiers who have given their lives for Poland. It is one of many such national tombs of unknowns that were erected after World War I, and the most important such monument in Poland.

The Sikorski–Mayski agreement was a treaty between the Soviet Union and Poland that was signed in London on 30 July 1941. Its name is taken from its two most notable signatories: the prime minister of Poland, Władysław Sikorski, and the Soviet ambassador to the United Kingdom, Ivan Mayski.

In Poland, the resistance movement during World War II was led by the Home Army. The Polish resistance is notable among others for disrupting German supply lines to the Eastern Front, and providing intelligence reports to the British intelligence agencies. It was a part of the Polish Underground State.

The "cursed soldiers" or "indomitable soldiers" comprised a heterogeneous array of anti-Soviet-imperialist and anti-communist Polish resistance movements formed in the later stages of World War II and in its aftermath by members of the Polish Underground State. The above terms, introduced in the early 1990s, reflect the stance of many of the diehard soldiers.
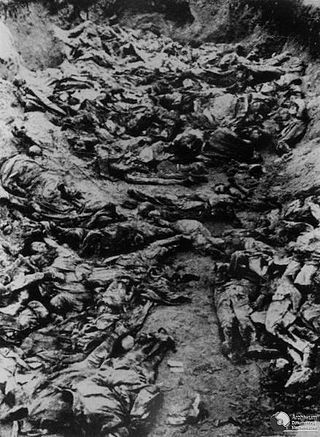
The Katyn massacre was a series of mass executions of nearly 22,000 Polish military officers and intelligentsia prisoners of war carried out by the Soviet Union, specifically the NKVD in April and May 1940. Though the killings also occurred in the Kalinin and Kharkiv prisons and elsewhere, the massacre is named after the Katyn forest, where some of the mass graves were first discovered by German Nazi forces.

The Nuremberg Trials is a 1947 Soviet-made documentary film about the trials of individual members of the former Nazi leadership after World War II. It was directed by Elizaveta Svilova, produced by Roman Karmen, and was an English-language version of the Russian-language film Суд народов.
Systematic POW labor in the Soviet Union is associated primarily with the outcomes of World War II and covers the period of 1939–1956, from the official formation of the first POW camps, to the repatriation of the last POWs, from the Kwantung Army.
As a result of the Soviet invasion of Poland in 1939, hundreds of thousands of Polish soldiers became prisoners of war. Many of them were executed; 22,000 Polish military personnel and civilians perished in the Katyn massacre alone.

The Przyszowice massacre was a massacre perpetrated by the Red Army against civilian inhabitants of the Polish village of Przyszowice in Upper Silesia during the period January 26 to January 28, 1945. Sources vary on the number of victims, which range from 54 to over 60 – and possibly as many as 69. The Institute of National Remembrance, a Polish organization that carried out research into these events, has declared that the Przyszowice massacre was a crime against humanity.

Katyń is a 2007 Polish historical drama film about the 1940 Katyn massacre, directed by Academy Honorary Award winner Andrzej Wajda. It is based on the book Post Mortem: The Story of Katyn by Andrzej Mularczyk. It was nominated for Best Foreign Language Film for the 80th Academy Awards.

The occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union during World War II (1939–1945) began with the German-Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe.

SS-Truppenübungsplatz Heidelager was a World War II SS military complex and Nazi concentration camp in Pustków and Pustków Osiedle, Occupied Poland. The Nazi facility was built to train collaborationist military units, including the Ukrainian 14th Waffen SS Division "Galician", and units from Estonia. This training included killing operations inside the concentration camps – most notably at the nearby Pustków and Szebnie camps – and Jewish ghettos in the vicinity of the 'Heidelager'. The military area was situated in the triangle of the Wisła and San rivers, dominated by large forest areas. The centre of the Heidelager was at Blizna, the location of the secret Nazi V-2 missile launch site, which was built and staffed by prisoners from the concentration camp at Pustków.

Kornilyevo is a rural locality in Rostilovskoye Rural Settlement, Gryazovetsky District, Vologda Oblast, Russia. The population was 99 as of 2002.

















