
Mach number is a dimensionless quantity in fluid dynamics representing the ratio of flow velocity past a boundary to the local speed of sound. It is named after the Austrian physicist and philosopher Ernst Mach.

In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds five times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above.

In physics, a shock wave, or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium.

The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At 20 °C (68 °F), the speed of sound in air is about 343 metres per second, or one kilometre in 2.91 s or one mile in 4.69 s. It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At 0 °C (32 °F), the speed of sound in air is about 331 m/s. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel.
Compressible flow is the branch of fluid mechanics that deals with flows having significant changes in fluid density. While all flows are compressible, flows are usually treated as being incompressible when the Mach number is smaller than 0.3. The study of compressible flow is relevant to high-speed aircraft, jet engines, rocket motors, high-speed entry into a planetary atmosphere, gas pipelines, commercial applications such as abrasive blasting, and many other fields.

The Prandtl–Glauert singularity is a theoretical construct in flow physics, often incorrectly used to explain vapor cones in transonic flows. It is the prediction by the Prandtl–Glauert transformation that infinite pressures would be experienced by an aircraft as it approaches the speed of sound. Because it is invalid to apply the transformation at these speeds, the predicted singularity does not emerge. The incorrect association is related to the early-20th-century misconception of the impenetrability of the sound barrier.
In aeronautics, wave drag is a component of the aerodynamic drag on aircraft wings and fuselage, propeller blade tips and projectiles moving at transonic and supersonic speeds, due to the presence of shock waves. Wave drag is independent of viscous effects, and tends to present itself as a sudden and dramatic increase in drag as the vehicle increases speed to the critical Mach number. It is the sudden and dramatic rise of wave drag that leads to the concept of a sound barrier.

In fluid dynamics, a Mach wave is a pressure wave traveling with the speed of sound caused by a slight change of pressure added to a compressible flow. These weak waves can combine in supersonic flow to become a shock wave if sufficient Mach waves are present at any location. Such a shock wave is called a Mach stem or Mach front. Thus, it is possible to have shockless compression or expansion in a supersonic flow by having the production of Mach waves sufficiently spaced. A Mach wave is the weak limit of an oblique shock wave where time averages of flow quantities don't change. If the size of the object moving at the speed of sound is near 0, then this domain of influence of the wave is called a Mach cone.
In fluid dynamics, drag is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers or between a fluid and a solid surface.
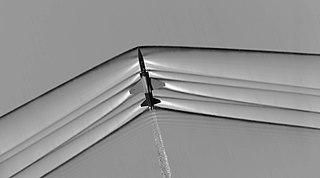
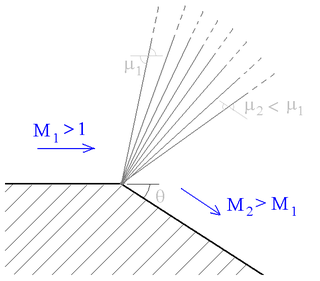
An oblique shock wave is a shock wave that, unlike a normal shock, is inclined with respect to the incident upstream flow direction. It will occur when a supersonic flow encounters a corner that effectively turns the flow into itself and compresses. The upstream streamlines are uniformly deflected after the shock wave. The most common way to produce an oblique shock wave is to place a wedge into supersonic, compressible flow. Similar to a normal shock wave, the oblique shock wave consists of a very thin region across which nearly discontinuous changes in the thermodynamic properties of a gas occur. While the upstream and downstream flow directions are unchanged across a normal shock, they are different for flow across an oblique shock wave.

The Stokes number (Stk), named after George Gabriel Stokes, is a dimensionless number characterising the behavior of particles suspended in a fluid flow. The Stokes number is defined as the ratio of the characteristic time of a particle to a characteristic time of the flow or of an obstacle, or

A supersonic wind tunnel is a wind tunnel that produces supersonic speeds (1.2<M<5) The Mach number and flow are determined by the nozzle geometry. The Reynolds number is varied by changing the density level. Therefore, a high pressure ratio is required. Apart from that, condensation of moisture or even gas liquefaction can occur if the static temperature becomes cold enough. This means that a supersonic wind tunnel usually needs a drying or a pre-heating facility. A supersonic wind tunnel has a large power demand, so most are designed for intermittent instead of continuous operation.
Gas kinetics is a science in the branch of fluid dynamics, concerned with the study of motion of gases and its effects on physical systems. Based on the principles of fluid mechanics and thermodynamics, gas dynamics arises from the studies of gas flows in transonic and supersonic flights. To distinguish itself from other sciences in fluid dynamics, the studies in gas dynamics are often defined with gases flowing around or within physical objects at speeds comparable to or exceeding the speed of sound and causing a significant change in temperature and pressure. Some examples of these studies include but are not limited to: choked flows in nozzles and valves, shock waves around jets, aerodynamic heating on atmospheric reentry vehicles and flows of gas fuel within a jet engine. At the molecular level, gas dynamics is a study of the kinetic theory of gases, often leading to the study of gas diffusion, statistical mechanics, chemical thermodynamics and non-equilibrium thermodynamics. Gas dynamics is synonymous with aerodynamics when the gas field is air and the subject of study is flight. It is highly relevant in the design of aircraft and spacecraft and their respective propulsion systems.
A supersonic expansion fan, technically known as Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan, a two-dimensional simple wave, is a centered expansion process that occurs when a supersonic flow turns around a convex corner. The fan consists of an infinite number of Mach waves, diverging from a sharp corner. When a flow turns around a smooth and circular corner, these waves can be extended backwards to meet at a point.

A Machmeter is an aircraft pitot-static system flight instrument that shows the ratio of the true airspeed to the speed of sound, a dimensionless quantity called Mach number. This is shown on a Machmeter as a decimal fraction. An aircraft flying at the speed of sound is flying at a Mach number of one, expressed as Mach 1.
The drag-divergence Mach number is the Mach number at which the aerodynamic drag on an airfoil or airframe begins to increase rapidly as the Mach number continues to increase. This increase can cause the drag coefficient to rise to more than ten times its low-speed value.
In aerodynamics, the normal shock tables are a series of tabulated data listing the various properties before and after the occurrence of a normal shock wave. With a given upstream Mach number, the post-shock Mach number can be calculated along with the pressure, density, temperature, and stagnation pressure ratios. Such tables are useful since the equations used to calculate the properties after a normal shock are cumbersome.
The term shock polar is generally used with the graphical representation of the Rankine–Hugoniot equations in either the hodograph plane or the pressure ratio-flow deflection angle plane. The polar itself is the locus of all possible states after an oblique shock.
The Prandtl condition was suggested by the German physicist Ludwig Prandtl to identify possible boundary layer separation points of incompressible flows.















