External links
- Brief biography at "Here of a Sunday Morning"
- IMSLP Free scores, Ground Upon la mi re.
Thomas Preston (died c. 1563) was an English organist and composer who held posts at Magdalen College, Oxford, Trinity College, Cambridge, and St George's Chapel at Windsor Castle.
According to John Caldwell, his music features fine 4-part counterpoint, intricacies of rhythm, and a virtuosic approach to the keyboard, even though all the surviving music is liturgical.
12 Offertory settings for keyboard, including Felix namque, and Mass versets for Easter, containing the only known sequence setting of the time (only part of the sequence survives.)
The anonymous ground for keyboard Uppon la mi re (MB, LXVI, 1995) in the collection Add.29996 (London British Library) is often attributed to him.

In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the pre-eminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to Margaret Bent, "a piece of music in several parts with words" is as precise a definition of the motet as will serve from the 13th to the late 16th century and beyond. The late 13th-century theorist Johannes de Grocheo believed that the motet was "not to be celebrated in the presence of common people, because they do not notice its subtlety, nor are they delighted in hearing it, but in the presence of the educated and of those who are seeking out subtleties in the arts".

William Byrd was an English Renaissance composer. Considered among the greatest composers of the Renaissance, he had a profound influence on composers both from his native country and on the Continent. He is often considered along with John Dunstaple and Henry Purcell as one of England's most important composers of early music.
In music, solfège or solfeggio, also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a mnemonic used in teaching aural skills, pitch and sight-reading of Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably.

Orlando Gibbons was an English composer and keyboard player who was one of the last masters of the English Virginalist School and English Madrigal School. The best known member of a musical family dynasty, by the 1610s he was the leading composer and organist in England, with a career cut short by his sudden death in 1625. As a result, Gibbons's oeuvre was not as large as that of his contemporaries, like the elder William Byrd, but he made considerable contributions to many genres of his time. He is often seen as a transitional figure from the Renaissance to the Baroque periods.

Robert Smith was an English mathematician.
John Sheppard was an English composer of the Renaissance.

The Fitzwilliam Virginal Book is a primary source of keyboard music from the late Elizabethan and early Jacobean periods in England, i.e., the late Renaissance and very early Baroque. It takes its name from Viscount Fitzwilliam who bequeathed this manuscript collection to Cambridge University in 1816. It is now housed in the Fitzwilliam Museum at Cambridge. The word virginals does not necessarily denote any specific instrument and might refer to any instrument with a keyboard.
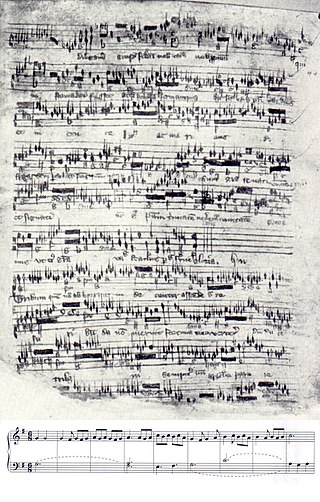
The Robertsbridge Codex (1360) is a music manuscript of the 14th century. It contains the earliest surviving music written specifically for keyboard.
Hugh Aston was an English composer of the early Tudor period. While little of his music survives, he is notable for his innovative keyboard and church music writing. He was also politically active, a mayor, Member of Parliament, and Alderman.
Leonel Power, c. 1380–1445, was an English composer of the early Renaissance. Along with John Dunstaple he was a dominant figure of 15th-century English music. Mainly a composer of motets and of sections of the Mass, he is the best-represented contributor in the Old Hall Manuscript. Occasionally he is referred to by his Christian name only.
Robert White probably born in Holborn, a district of London, was an English composer whose liturgical music to Latin texts is considered particularly fine. His surviving works include a setting of verses from Lamentations, and instrumental music for viols.

Peter Philips was an eminent English composer, organist, and Catholic priest exiled to Flanders in the Spanish Netherlands. He was one of the greatest keyboard virtuosos of his time, and transcribed or arranged several Italian motets and madrigals by such composers as Lassus, Palestrina, and Giulio Caccini for his instruments. Some of his keyboard works are found in the Fitzwilliam Virginal Book. Philips also wrote many sacred choral works.

Durham College was a college of the University of Oxford, founded by the monks of Durham Priory in the late 13th century and endowed by Bishop Thomas Hatfield in 1381.
Nicholas Ludford was an English composer of the Tudor period. He is known for his festal masses, which are preserved in two early-16th-century choirbooks, the Caius Choirbook at Caius College, Cambridge, and the Lambeth Choirbook at Lambeth Palace, London. His surviving antiphons, all incomplete, are copied in the Peterhouse partbooks, which disappeared from view until some were rediscovered in 1850, and the rest only in 1926.

Early music of Britain and Ireland, from the earliest recorded times until the beginnings of the Baroque in the 17th century, was a diverse and rich culture, including sacred and secular music and ranging from the popular to the elite. Each of the major nations of England, Ireland, Scotland, and Wales retained unique forms of music and of instrumentation, but British music was highly influenced by continental developments, while British composers made an important contribution to many of the major movements in early music in Europe, including the polyphony of the Ars Nova and laid some of the foundations of later national and international classical music. Musicians from the British Isles also developed some distinctive forms of music, including Celtic chant, the Contenance Angloise, the rota, polyphonic votive antiphons, and the carol in the medieval era and English madrigals, lute ayres, and masques in the Renaissance era, which would lead to the development of English language opera at the height of the Baroque in the 18th century.

Trinity College Chapel is the chapel of Trinity College, Cambridge, a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. Part of a complex of Grade I listed buildings at Trinity, it dates from the mid 16th century. It is an Anglican church in the Anglo-Catholic tradition.

Osbert Parsley was an English Renaissance composer and chorister. Few details of his life are known, but he evidently married in 1558, and lived for a period in the parish of St Saviour's Church, Norwich. A boy chorister at Norwich Cathedral, Parsley worked there throughout his musical career. He was first mentioned as a lay clerk, was appointed a "singing man" in c. 1534, and was probably the cathedral's unofficial organist for half a century. His career spanned the reigns of Henry VIII and all three of his children. After the Reformation of 1534, the lives of English church musicians changed according to the official policy of each monarch.
The Forrest-Heyther partbooks are a set of six manuscript partbooks copied in England in the sixteenth century. They are an important source of polyphonic Mass Ordinary settings by composers from the reign of Henry VIII, including John Taverner and Robert Fayrfax.
Benjamin Cosyn was an English composer, organist and virginalist. He was organist of St Laurence's Church, Ludlow, Dulwich College and Charterhouse School.

The American Institute of Musicology (AIM) is a musicological organization that researches, promotes and produces publications on early music. Founded in 1944 by Armen Carapetyan, the AIM's chief objective is the publication of modern editions of medieval, Renaissance and early Baroque compositions and works of music theory. The breadth and quality of publications produced by the AIM constitutes a central contribution to the study, practice and performance of early music.