
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spans 513,115 square kilometres (198,115 sq mi). Thailand is bordered to the northwest by Myanmar, to the northeast and east by Laos, to the southeast by Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the southwest by the Andaman Sea; it also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the state capital and largest city.

Tael, or liang, also known as the tahil and by other names, can refer to any one of several weight measures used in East and Southeast Asia. It usually refers to the Chinese tael, a part of the Chinese system of weights and currency. The Chinese tael was standardized to 50 grams in 1959.

The baht is the official currency of Thailand. It is divided into 100 satang. Prior to decimalisation, the baht was divided into eight fueang, each of eight at. The issuance of currency is the responsibility of the Bank of Thailand. SWIFT ranked the Thai baht as the 10th-most-frequently used world payment currency as of December 2023.
The ounce is any of several different units of mass, weight, or volume and is derived almost unchanged from the uncia, an Ancient Roman unit of measurement.

Phra Bat Somdet Phra Phutthayotfa Chulalok Maharat, personal name Thongduang (ทองด้วง), also known as Rama I, was the founder of the Rattanakosin Kingdom and the first King of Siam from the reigning Chakri dynasty. His full title in Thai is Phra Bat Somdet Phra Paramoruracha Maha Chakri Boromanat Phra Phutthayotfa Chulalok. He ascended the throne in 1782, following the deposition of King Taksin of Thonburi. He was also celebrated as the founder of Rattanakosin as the new capital of the reunited kingdom.
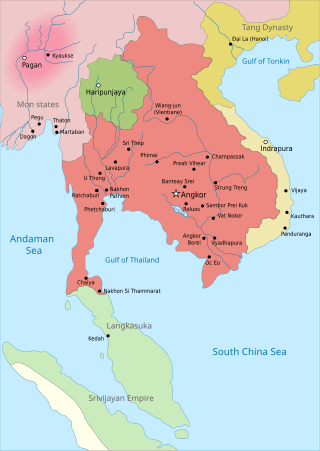
The Khmer Empire was a Hindu-Buddhist empire in Southeast Asia, centered around hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilisation of Chenla and lasted from 802 to 1431. Historians call this period of Cambodian history the Angkor period, after the empire's most well-known capital, Angkor. The Khmer Empire ruled or vassalised most of mainland Southeast Asia and stretched as far north as southern China. At its peak, the Empire was larger than the Byzantine Empire, which existed around the same time.

The post-Angkor period of Cambodia, also called the Middle period, refers to the historical era from the early 15th century to 1863, the beginning of the French protectorate of Cambodia. As reliable sources are very rare, a defensible and conclusive explanation that relates to concrete events that manifest the decline of the Khmer Empire, recognised unanimously by the scientific community, has so far not been produced. However, most modern historians have approached a consensus in which several distinct and gradual changes of religious, dynastic, administrative and military nature, environmental problems and ecological imbalance coincided with shifts of power in Indochina and must all be taken into account to make an interpretation. In recent years scholars' focus has shifted increasingly towards human–environment interactions and the ecological consequences, including natural disasters, such as flooding and droughts.

Naresuan, commonly known as Naresuan the Great, or Sanphet II was the 18th king of the Ayutthaya Kingdom and 2nd monarch of the Sukhothai dynasty. He was the king of the Ayutthaya Kingdom from 1590 and overlord of Lan Na from 1602 until his death in 1605. Naresuan is one of Thailand's most revered monarchs as he is known for his campaigns to free Ayutthaya from the vassalage of the Taungoo Empire. During his reign, numerous wars were fought against Taungoo Burma. Naresuan also welcomed the Dutch.

The Rattanakosin Kingdom, the Kingdom of Siam, or the RattanakosinEmpire, were names used to reference the fourth and current Thai kingdom in the history of Thailand. It was founded in 1782 with the establishment of Rattanakosin (Bangkok), which replaced the city of Thonburi as the capital of Siam. This article covers the period until the Siamese revolution of 1932.

Pailin is a province in western Cambodia at the northern edge of the Cardamom Mountains near the border of Thailand. This province is surrounded by Battambang province, and was officially carved out of Battambang to become a separate administrative division after the surrender of the Ieng Sary faction of the Khmer Rouge in 1996. Pailin is known to much of the world for having long been a stronghold of the Khmer Rouge, remaining under their control long after they were defeated in 1979 and serving from 1994 to 1998 as the capital of the Provisional Government of National Union and National Salvation of Cambodia. Within Cambodia, Pailin is known for its natural resources, namely precious gems and timber.

The military history of Thailand encompasses a thousand years of armed struggle, from wars of independence from the powerful Khmer Empire, through to struggles with her regional rivals of Burma and Vietnam and periods of tense standoff and conflict with the colonial empires of Britain and France. Thailand's military history, dominated by her centrality in the south-eastern Asian region, the significance of her far flung and often hostile terrain, and the changing nature of military technology, has had a decisive impact on the evolution of both Thailand and her neighbours as modern nation states. In the post-war era, Thailand's military relationship with the United States has seen her play an important role in both the Cold War and the recent War on Terror, whilst her military's involvement in domestic politics has brought frequent international attention.

Dance in Thailand is the main dramatic art form in Thailand. Thai dance can be divided into two major categories, high art and low art.

The Lavo Kingdom was a political entity (mandala) on the left bank of the Chao Phraya River in the Upper Chao Phraya valley from the end of Dvaravati civilization, in the 7th century, until 1388. The original center of Lavo civilization was Lavo.
Chula Sakarat or Chulasakarat is a lunisolar calendar derived from the Burmese calendar, whose variants were in use by most mainland Southeast Asian kingdoms down to the late 19th century. The calendar is largely based on an older version of the Hindu calendar though unlike the Indian systems, it employs a version of the Metonic cycle. The calendar therefore has to reconcile the sidereal years of the Hindu calendar with Metonic cycle's tropical years by adding intercalary months and intercalary days on irregular intervals.

Curry paste is a mixture of ingredients in the consistency of a paste used in the preparation of a curry. There are different varieties of curry paste depending from the region and also within the same cuisine.

Steamed curry is a Southeast Asian type of curry steam-cooked in banana leaves and served with cooked rice. In Laos, it is also roasted on embers. The base of the curry is made with a curry paste with or without the addition of coconut cream or coconut milk and eggs. A wide range of leaves and staple ingredients are also added to the dish, such as:
Thailand adopted the metric system on 17 December 1923.
Anti-Thai sentiment involves hostility, discrimination or hatred that is directed towards people in Thailand, or the state of Thailand.

Lat money refers to the bar-shaped coinage minted and used as currency in the kingdom of Lan Xang and its successor kingdoms of Vientiane, Luang Prabang, and Champasak. "Lat" is a Lao abbreviation for "talat" or "market," referring to the small denomination currency which may also be referred to as "boat money" or "Ngern Heua." The bar-shaped coinage of Lan Xang could be differentiated according to shape, weight, metal, alloy, and mint marks.

Folding-book manuscripts are a type of writing material historically used in Mainland Southeast Asia, particularly in the areas of present-day Myanmar, Thailand, Laos and Cambodia. They are known as parabaik in Burmese, samut thai in Thai or samut khoi in Thai and Lao, phap sa in Northern Thai and Lao, and kraing in Khmer.
















