
Natural gas is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane (97%) in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Traces of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Methane is colorless and odorless, and the second largest greenhouse gas contributor to global climate change after carbon dioxide. Because natural gas is odorless, odorizers such as mercaptan are commonly added to it for safety so that leaks can be readily detected.
The Filitelnic gas field is a natural gas field in the Filitelnic village of Bălăușeri commune, Mureș County, Romania lying in the center of the Transylvanian Basin, a major natural gas-producing region. It was discovered in 1958 and is developed by Romgaz. It began production in 1961 and produces natural gas and condensates.

Tin Cup Oil Field is located in San Juan County, approximately 21 miles (34 km) southeast of Blanding, Utah. Production is from a northwest–southeast trending 120-foot-thick (37 m) carbonate buildup in the Pennsylvanian Upper Ismay. The field is part of the Paradox Basin that extends from the states of Colorado to Utah and New Mexico.
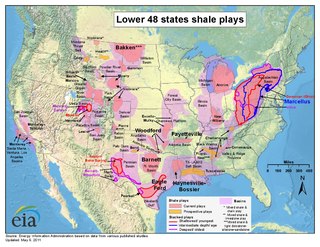
Shale gas in the United States is an available source of unconventional natural gas. Led by new applications of hydraulic fracturing technology and horizontal drilling, development of new sources of shale gas has offset declines in production from conventional gas reservoirs, and has led to major increases in reserves of U.S. natural gas. Largely due to shale gas discoveries, estimated reserves of natural gas in the United States in 2008 were 35% higher than in 2006.
The Lebăda Vest oil field is an oil field located on the continental shelf of the Black Sea. It was discovered in 1980 and developed by Petrom. It began production in 1993 and produces oil. The total proven reserves of the Lebăda Vest oil field are around 50 million barrels (6.8×106tonnes), and production is centered on 10,000 barrels per day (1,600 m3/d). The field also produces around 35.8 million cubic feet/day (1×105m3) of gas and has reserves of 200 billion cubic feet (5.7×109m3).
The Deleni gas field is a natural gas field located in Băgaciu, Mureș County. It was discovered in 1912 and developed by and Romgaz. It began production in 1915 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Deleni gas field are around 3 trillion cubic feet (85 km3), and production is slated to be around 178 million cubic feet per day (5,000,000 m3/d) in 2010.
The Jodłówka gas field in Poland was discovered in 1980. It began production in 1985 and produces natural gas. The total proven reserves of the Jodłówka gas field are around 106 billion cubic feet (3×109m³).
The Radlin gas field in Poland was discovered in 1980. It began production in 1982 and produces natural gas. The total proven reserves of the Radlin gas field are around 390 billion cubic feet (11×109m³).
The Odeske gas field natural gas field located on the continental shelf of the Black Sea. It was discovered in 2009 and developed by Chornomornaftogaz in cooperation with the China National Offshore Oil Corporation. It started commercial production on 5 September 2012. The total proven reserves of the Odesa gas field are around 746 billion cubic feet, and production is slated to be around 35 million cubic feet per day in 2015.
The Akçakoca gas field is a natural gas field located on the continental shelf of the Black Sea. It was discovered in 2004 and developed by a consortium consisting of Türkiye Petrolleri Anonim Ortaklığı, Petrol Ofisi, Tiway Oil and Stratic Oil. It began production in 2007 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Akçakoca gas field are around 127 billion cubic feet (3.6×109m³), and production is slated to be around 50 million cubic feet/day (1.4×106m³) in 2015.
The Holitsynske gas field natural gas field located on the continental shelf of the Black Sea. It was discovered in 1974 and developed by Chornomornaftogaz. It started commercial production in 1975. The total proven reserves of the Holitsynske gas field are around 544 billion cubic feet, and production is slated to be around 20 million cubic feet per day in 2015.
The Pivdenno-Holitsynske gas field natural gas field located on the continental shelf of the Black Sea. It was discovered in 1981 and developed by Chornomornaftogaz. It started commercial production in 1982. The total proven reserves of the Pivdenno-Holitsynske gas field are around 124 billion cubic feet, and production is slated to be around 20 million cubic feet per day in 2015.
The Bezimenne gas field natural gas field located on the continental shelf of the Black Sea. It was discovered in 1997 and developed by Chornomornaftogaz. It started commercial production in 1997. The total proven reserves of the Bezimenne gas field are around 140 billion cubic feet, and production is slated to be around 20 million cubic feet per day in 2015.
The Foroska gas field natural gas field located on the continental shelf of the Black Sea. It was discovered in 1974 and developed by Chornomornaftogaz. It started commercial production in 1975. The total proven reserves of the Foroska gas field are around 900 billion cubic feet, and production is slated to be around 67 million cubic feet per day in 2018.
The Shatlyk Gas Field is a natural gas field located in the Mary Province near the city of Şatlyk. It was discovered in 1974 and developed by Türkmengaz. It began production in 1980 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Shatlyk gas field are around 33 trillion cubic feet (943 km3), and production was slated to be around 287 million cubic feet/day (8.2×105m3) as of 2013.
The Tabnak gas field is an Iranian natural gas field discovered in 1967 that began production in 1980 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Tabnak gas field are around 30 trillion cubic feet (857×109m3), and production was estimated to be around 1.5 billion cubic feet/day (43×106m3) in 2000.
The Kangan gas field is an Iranian natural gas field that was discovered by the NIOC-EGOCO consortium (contract signed in March 1969) with the Kangan #2 well drilled in 1972. It began production in 1980 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Kangan gas field are around 29 trillion cubic feet (829×109m3) and production is slated to be around 800 million cubic feet/day (23×106m3). Nar gas field is located a few kilometers away from kangan gas field. That's why Nar & Kangan appear together most of the time. The produced gas from Nar & Kangan fields delivers to Fajr gas refinery in the downstream. Nar & Kangan is the major onshore natural gas provider for domestic consumption. The two fields together hold the record of maximum gas production rate from onshore fields in Iran, 120 million cubic meter per day at standard conditions.
The Khangiran gas field is an Iranian natural gas field that was discovered in 1967. It began production in 1980 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Khangiran gas field are around 17 trillion cubic feet (480×109m3) and production is slated to be around 600 million cubic feet/day (17×106m3).
The Badak gas field is a natural gas field located in the South China Sea. It was discovered in 1970 and developed by and Pertamina. It began production in 1971 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Badak gas field are around 7 trillion cubic feet (200×109m³), and production is slated to be around 500 million cubic feet/day (14.2×105m³).
The Rhourde Nouss gas field is a natural gas field located in the Ouargla Province. It was discovered in 1980 and developed by Sonatrach. It began production in 1956 and produces natural gas and condensates. The total proven reserves of the Rhourde Nouss gas field are around 13 trillion cubic feet (370×109m³), and production is slated to be around 1.69 billion cubic feet/day (48.3×105m³).


