See also
- Tin foil hat, a headpiece associated with paranoia
Tin hat can refer to:
As a proper noun, Tin Hat can refer to:

A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and often a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.

The Yellowdog Updater Modified (YUM) is a free and open-source command-line package-management utility for computers running the Linux operating system using the RPM Package Manager. Though YUM has a command-line interface, several other tools provide graphical user interfaces to YUM functionality.
Red Hat is an American software company that provides open source software products.

Within the free software and the open-source software communities there is controversy over whether to refer to computer operating systems that use a combination of GNU software and the Linux kernel as "GNU/Linux" or "Linux" systems.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is a commercial open-source Linux distribution developed by Red Hat for the commercial market. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is released in server versions for x86-64, Power ISA, ARM64, and IBM Z and a desktop version for x86-64. Fedora Linux and CentOS Stream serve as its upstream sources. All of Red Hat's official support and training, together with the Red Hat Certification Program, focuses on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform.
In computing, the Global File System 2 or GFS2 is a shared-disk file system for Linux computer clusters. GFS2 allows all members of a cluster to have direct concurrent access to the same shared block storage, in contrast to distributed file systems which distribute data throughout the cluster. GFS2 can also be used as a local file system on a single computer.

CentOS is a discontinued Linux distribution that provided a free and open-source community-supported computing platform, functionally compatible with its upstream source, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). In January 2014, CentOS announced the official joining with Red Hat while staying independent from RHEL, under a new CentOS governing board.
BioLinux is a term used in a variety of projects involved in making access to bioinformatics software on a Linux platform easier using one or more of the following methods:

Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by the Fedora Project. It was originally developed in 2003 as a continuation of the Red Hat Linux project. It contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of open-source technologies. It is now the upstream source for CentOS Stream and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.

Tinfoil Hat Linux (THL) was a compact security-focused Linux distribution designed for high security developed by The Shmoo Group. The first version (1.000) was released in February 2002. By 2013, it had become a low-priority project. Its image files and source are available in gzip format. THL can be used on modern PCs using an Intel 80386 or better, with at least 8 MB of RAM. The distribution fits on a single HD floppy disk. The small footprint provides additional benefits beyond making the system easy to understand and verify. The computer need not even have a hard drive, making it easier to "sanitize" the computer after use.
Ceph is a free and open-source software-defined storage platform that provides object storage, block storage, and file storage built on a common distributed cluster foundation. Ceph provides completely distributed operation without a single point of failure and scalability to the exabyte level, and is freely available. Since version 12 (Luminous), Ceph does not rely on any other conventional filesystem and directly manages HDDs and SSDs with its own storage backend BlueStore and can expose a POSIX filesystem.
A fedora is a type of hat.
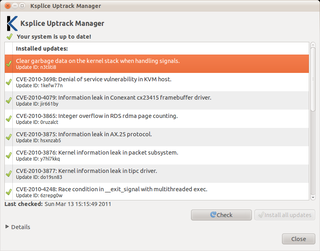
Ksplice is an open-source extension of the Linux kernel that allows security patches to be applied to a running kernel without the need for reboots, avoiding downtimes and improving availability. Ksplice supports only the patches that do not make significant semantic changes to kernel's data structures.

RPM Package Manager (RPM) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the .rpm file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base.

OpenShift is a family of containerization software products developed by Red Hat. Its flagship product is the OpenShift Container Platform — a hybrid cloud platform as a service built around Linux containers orchestrated and managed by Kubernetes on a foundation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. The family's other products provide this platform through different environments: OKD serves as the community-driven upstream, Several deployment methods are available including self-managed, cloud native under ROSA, ARO and RHOIC on AWS, Azure, and IBM Cloud respectively, OpenShift Online as software as a service, and OpenShift Dedicated as a managed service.
Ansible is a suite of software tools that enables infrastructure as code. It is open-source and the suite includes software provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment functionality.
kdump is a feature of the Linux kernel that creates crash dumps in the event of a kernel crash. When triggered, kdump exports a memory image that can be analyzed for the purposes of debugging and determining the cause of a crash. The dumped image of main memory, exported as an Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) object, can be accessed either directly through /proc/vmcore during the handling of a kernel crash, or it can be automatically saved to a locally accessible file system, to a raw device, or to a remote system accessible over network.
AlmaLinux is a free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the AlmaLinux OS Foundation, a 501(c) organization, to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system that is binary-compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). The name of the distribution comes from the word "alma", meaning "soul" in Spanish and other Latin languages. It was chosen to be a homage to the Linux community.