
A tithe is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques, whereas historically tithes were required and paid in kind, such as agricultural products. Several European countries operate a formal process linked to the tax system allowing some churches to assess tithes.
Commute, commutation or commutative may refer to:

Richard Jones was an English economist who criticised the theoretical views of David Ricardo and T. R. Malthus on economic rent and population.
In the pre-Reformation church, a parson is the priest of an independent parish church, that is, a parish church not under the control of a larger ecclesiastical or monastic organization. The term is similar to rector and is in contrast to a vicar, a cleric whose revenue is usually, at least partially, appropriated by a larger organization. Today the term is normally used for some parish clergy of non-Roman Catholic churches, in particular in the Anglican tradition in which a parson is the incumbent of a parochial benefice: a parish priest or a rector; in this sense a parson can be compared with a vicar. The title parson can be applied to clergy from certain other Protestant denominations. A parson is often housed in a church-owned home known as a parsonage.
The Tithe War was a campaign of mainly nonviolent civil disobedience, punctuated by sporadic violent episodes, in Ireland between 1830 and 1836 in reaction to the enforcement of tithes on the Roman Catholic majority for the upkeep of the established state church – the Church of Ireland. Tithes were payable in cash or kind and payment was compulsory, irrespective of an individual's religious adherence.
In law, a commutation is the substitution of a lesser penalty for that given after a conviction for a crime. The penalty can be lessened in severity, in duration, or both. Unlike most pardons by government and overturnings by the court, a commutation does not affect the status of a defendant's underlying criminal conviction.
The Lichfield House Compact was an 1835 agreement between the Whig government, the Irish Repeal Party and the Radicals to act as one body against the Conservative Party. It allowed O'Connell to push for further reforms for Ireland. It was signed in February 1835 in Lichfield House, St James's, residence of Thomas Anson, 1st Earl of Lichfield.
A tithing or tything was a historic English legal, administrative or territorial unit, originally ten hides. Tithings later came to be seen as subdivisions of a manor or civil parish. The tithing's leader or spokesman was known as a tithingman.
Chancel repair liability is a legal obligation on some property owners in England and Wales to pay for certain repairs to a church which may or may not be the local parish church.
William Blamire was a British landowner, civil servant, and Whig politician.

The Tithe Commutation Act 1836 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom with the long title "An Act for the Commutation of Tithes in England and Wales". It replaced the ancient system of payment of tithes in kind with monetary payments. It is especially noted for the tithe maps which were needed for the valuation process required by the Act. British Parliamentary Paper 1837 XLI 405 was published to give guidance on how landscape features were to be indicated on the maps. It is entitled ′Conventional signs to be used in the plans made under the Act for the Commutation of Tithes in England and Wales′

The Enrollment Act, 12 Stat. 731, enacted March 3, 1863, also known as the Civil War Military Draft Act, was legislation passed by the United States Congress during the American Civil War to provide fresh manpower for the Union Army. A form of conscription, the controversial act required the enrollment of every male citizen and those immigrants who had filed for citizenship between ages twenty and forty-five. Federal agents established a quota of new troops due from each congressional district. In some cities, particularly New York City, enforcement of the act sparked civil unrest as the war dragged on, leading to the New York City draft riots on July 13–16. It replaced the previous Militia Act of 1862.
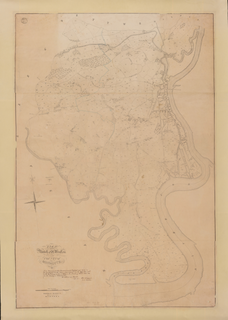
The term Tithe map is usually applied to a map of an English or Welsh parish or township, prepared following the Tithe Commutation Act 1836. This act allowed tithes to be paid in cash rather than goods. The map and its accompanying schedule gave the names of all owners and occupiers of land in the parish. Individual tithe owners sometimes prepared maps for their own use to show who owned what land. These maps are sometimes also called tithe maps, although such maps are not common before 1836.
Mjr.Aubrey William de Vere Beauclerk was a Radical British Member of Parliament (MP), who was elected to serve the dual-member East Surrey, making contributions in the Commons between 1833 and 1837, when he did not stand for re-election. One of his great-grandfathers was a younger son of the 1st Duke of St Albans (paternal-line-only), two of the others were the 3rd Duke of Marlborough and 2nd Duke of Richmond.

The Composition for Tithes Act of 1823, also known as the Tithe Composition Act, was an act of the British Parliament requiring all citizens of Ireland to pay monetary tithes to support the Anglican Church in Ireland, instead of a percentage of agricultural yield. The act also allowed for those who paid a large tithe to be able to negotiate the composition of the tithes for their parish; that is to decide on what monetary basis the tithes would be based, so that the tithes would be reasonable in comparison to income for the tithe-payers and sufficient for the subsistence of the parishes. It was thought by some members of Parliament to be a conciliatory measure that would reduce the oppressive nature of the then current tithe system.

Gayton le Wold is a village and civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It lies 6 miles (10 km) west from Louth, 3 miles (5 km) north from Donington on Bain, and to the south of the A157. The parish includes Biscathorpe 1 mile (1.6 km) to the south-west.

Searby cum Owmby is a civil parish situated to the north of the West Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The only parish settlements are Searby village and Owmby hamlet, separated by 1,000 yards (900 m), and approximately 4 miles (6 km) east from Brigg and 3.5 miles (6 km) north-east from Caistor. The A1084 Brigg to Caistor road runs through the centre of the parish.

Aneurin Owen was a Welsh historical scholar.
The Church Temporalities Act 1833, sometimes called the Church Temporalities (Ireland) Act 1833, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland which undertook a major reorganisation of the Church of Ireland, then the established church in Ireland. The Act suppressed ten bishoprics and merged the corresponding dioceses, with effect from the next vacancy.
Tithe commutation was a 19th century reform of land tenure in Great Britain and Ireland, which implemented an exchange of the payment of a tithe to the clergy of the established church, which were traditionally paid in kind, to a system based in an annual cash payment, or once-for-all payment. The system had become complex, with lay owners by impropriation entitled to some tithes, which were of a number of kinds.








