
Hair coloring, or hair dyeing, is the practice of changing the color of the hair on humans' heads. The main reasons for this are cosmetic: to cover gray or white hair, to alter hair to create a specific look, to change a color to suit preference or to restore the original hair color after it has been discolored by hairdressing processes or sun bleaching.

p-Phenylenediamine (PPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This derivative of aniline is a white solid, but samples can darken due to air oxidation. It is mainly used as a component of engineering polymers and composites like kevlar. It is also an ingredient in hair dyes and is occasionally used as a substitute for henna.
IARC group 2B substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances are those that have been classified as "possibly carcinogenic to humans" by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as This category is used when there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans and less than sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. It may also be used when there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some instances, an agent, mixture or exposure circumstance for which there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans, but limited evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals together with supporting evidence from other relevant data may be placed in this group.
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH or DNPH) is the organic compound C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2. DNPH is a red to orange solid. It is a substituted hydrazine. The solid is relatively sensitive to shock and friction. For this reason DNPH is usually handled as a wet powder. DNPH is a precursor to the drug Sivifene.
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction.
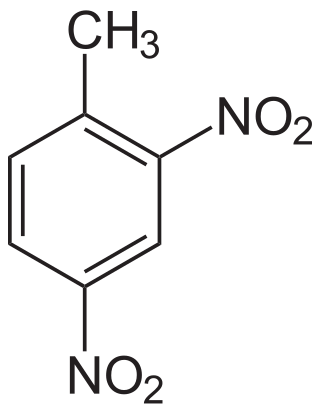
2,4-Dinitrotoluene (DNT) or dinitro is an organic compound with the formula C7H6N2O4. This pale yellow crystalline solid is well known as a precursor to trinitrotoluene (TNT) but is mainly produced as a precursor to toluene diisocyanate.

Dinitrophenols are chemical compounds which are nitro derivatives of phenol.
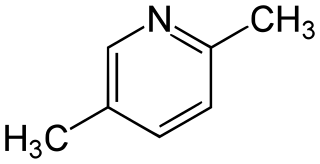
Lutidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are dimethyl derivatives of pyridine. Their chemical properties resemble those of pyridine, although the presence of the methyl groups may prohibit some of the more straightforward reactions. Lutidine comes in several isomers:
Arylide yellow, also known as Hansa yellow and monoazo yellow, is a family of organic compounds used as pigments. They are primarily used as industrial colorants including plastics, building paints and inks. They are also used in artistic oil paints, acrylics and watercolors. These pigments are usually semi-transparent and range from orange-yellow to yellow-greens. Related organic pigments are the diarylide pigments. Overall, these pigments have partially displaced the toxic cadmium yellow in the marketplace. Painters such as Alexander Calder and Jackson Pollock are known to have employed arylide yellow in their artworks.
A trichlorophenol is any organochloride of phenol that contains three covalently bonded chlorine atoms. Trichlorophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine. Different isomers of trichlorophenol exist according to which ring positions on the phenol contain chlorine atoms. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, for example, has two chlorine atoms in the ortho positions and one chlorine atom in the para position.
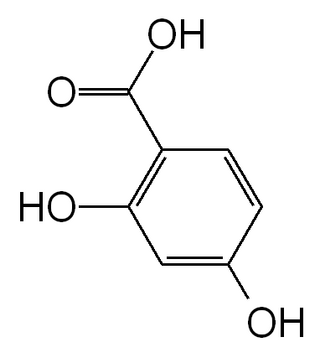
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.
Dichlorophenols (DCPs) are any of several chemical compounds which are derivatives of phenol containing two chlorine atoms. There are six isomers:
The molecular formula C7H10N2 may refer to:
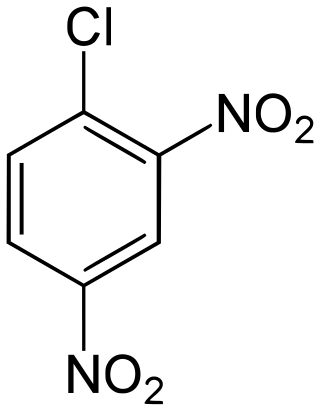
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (O2N)2C6H3Cl. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an important intermediate for the industrial production of other compounds.
Dinitrotoluenes could refer to one of the following compounds:

Nitrobenzoic acids are derivatives of benzoic acid. Two are commercially important. They are about ten times more acidic than the parent benzoic acid.
Dihydroxycinnamic acid may refer to several molecules with the molecular formula C9H8O4 including:
2,4-Dinitroaniline is a chemical compound with a formula of C6H5N3O4. It is used as an explosive and as a reagent to detect and characterize aldehydes and ketones.

2,4-Diaminotoluene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(NH2)2CH3. It is one isomer of six with this formula. It is a white solid, although commercial samples are often yellow-tan.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.









