External links
| Scholia has an author profile for Torsten Zuberbier . |
Torsten Zuberbier | |
|---|---|
| Born | 28 February 1962 (age 59) |
| Nationality | German |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Medicine |
Torsten Zuberbier (born 28 February 1962) is a German dermatologist and allergologist.
After completing his Abitur (secondary school education) in 1981, Torsten Zuberbier studied medicine at Free University of Berlin from 1983 to 1990. From 1990 to 1994, he completed his specialist training in the Department of Dermatology at the Virchow Clinic in Berlin, where he also became a senior physician in 1995 and qualified as a professor in 1996 with his work on the topic of differentiation and functional relations in human mast cells.[ citation needed ]
In 1996 he was named head of the allergy section at the Clinic for Dermatology, Venereology and Allergology at the Charité Berlin. In September 2001, he was appointed to an extraordinary professorship. In 2003, he was named to a foundation professorship (level C4) for research on the effects of allergies and in the same year he became head of the European Centre for Allergy Research Foundation (ECARF) at the Clinic for Dermatology, Venereology and Allergology at the Charité. He has been Director of the Allergie-Centrum-Charité at the Dermatology Clinic in Berlin-Mitte since 2004. He served as co-director of the Clinic for Dermatology, Venerology and Allergology at the Charité before being named its Managing Director in January 2012. Zuberbier received an honorary doctorate from the University of Athens in 2012.[ citation needed ]
Zuberbier's clinical research focuses on urticaria, neurodermatitis, respiratory and food allergies and allergic rhinitis. He is assistant editor of the Journal of the German Dermatologic Society and a member of the scientific advisory board of the Allergo Journal.[ citation needed ]
Zuberbier is married and has two children.[ citation needed ]
| Scholia has an author profile for Torsten Zuberbier . |

Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are a number of conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions.

Allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, itchy, and watery eyes, and swelling around the eyes. The fluid from the nose is usually clear. Symptom onset is often within minutes following allergen exposure, and can affect sleep and the ability to work or study. Some people may develop symptoms only during specific times of the year, often as a result of pollen exposure. Many people with allergic rhinitis also have asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, or atopic dermatitis.

Rhinitis, also known as coryza, is irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. Common symptoms are a stuffy nose, runny nose, sneezing, and post-nasal drip.

Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. They may also burn or sting. Often the patches of rash move around. Typically they last a few days and do not leave any long-lasting skin changes. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs.

Cold urticaria is a disorder where hives (urticaria) or large red welts form on the skin after exposure to a cold stimulus. The welts are usually itchy and often the hands and feet will become itchy and swollen as well. Hives vary in size from about 7mm in diameter to as big as about 27mm diameter or larger. This disorder, or perhaps two disorders with the same clinical manifestations, can be inherited or acquired. The acquired form is most likely to occur between ages 18–25, although it can occur as early as 5 years old in some cases. Life-threatening risks include suffocation resulting from pharyngeal angioedema induced by cold foods or beverages, drowning after shock from swimming in cold water and anaphylactic shock.

Aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD), also termed aspirin-induced asthma, is a medical condition initially defined as consisting of three key features: asthma, respiratory symptoms exacerbated by aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and nasal polyps. The symptoms of respiratory reactions in this syndrome are hypersensitivity reactions to NSAIDs rather than the typically described true allergic reactions that trigger other common allergen-induced asthma, rhinitis, or hives. The NSAID-induced reactions do not appear to involve the common mediators of true allergic reactions, immunoglobulin E or T cells. Rather, AERD is a type of NSAID-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. EAACI/WHO classifies the syndrome as one of five types of NSAID hypersensitivity or NSAID hypersensitivity reactions.

Allergen immunotherapy, also known as desensitization or hypo-sensitization, is a medical treatment for environmental allergies, such as insect bites, and asthma. Immunotherapy involves exposing people to larger and larger amounts of allergen in an attempt to change the immune system's response.

Ketotifen, sold under the brand name Zaditor among others, is a second-generation noncompetitive H1-antihistamine and mast cell stabilizer. It is most commonly sold as a salt with fumaric acid, ketotifen fumarate, and is available in two forms. In its ophthalmic form, it is used to treat allergic conjunctivitis. In its oral form, it is used to prevent asthma attacks or anaphylaxis, as well as various mast cell, allergic-type disorders.
ALK-Abelló A/S, also commonly known as ALK, is a Denmark-based pharmaceutical company which specializes in the development and manufacture of allergy immunotherapy (AIT) products for the prevention and treatment of allergy. It is one of the world’s largest makers of allergy immunotherapy products with 81% of its revenue coming from sales in Europe.

Cholinergic urticaria (CU) is a type of physical urticaria that appears when a person is sweating or their core body temperature increases.
Aquagenic urticaria, also known as water allergy and water urticaria, is a rare form of physical urticaria in which hives develop on the skin after contact with water, regardless of its temperature. It is sometimes described as an allergy, although it is not a true histamine-releasing allergic reaction like some other forms of urticaria. The condition typically results from contact with water of any type, temperature or additive.
GA²LEN, or Global Allergy and Asthma European Network, is a consortium of leading European research centres specialized in allergic diseases, which include asthma. Funded by the European Union under the 6th Framework Programme, GA²LEN addresses the growing public health concern of allergic diseases.
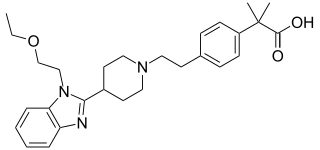
Bilastine, is a second-generation antihistamine medication which is used in the treatment of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and urticaria (hives).
ECARF - European Centre for Allergy Research Foundation is a non-profit foundation in the area of allergology.
Igor Petrovych Kaidashev is a Ukrainian immunologist and allergist, MD, and Professor. Igor Kaidashev is President of the Ukrainian Society of Immunology, Allergy and Immunorehabilitation, Professor of the Department of Internal Medicine No. 3 with Phthisiology, and Vice-Rector for Research & Development at Ukrainian Medical Stomatological Academy (UMSA) since 2010.
NSAID or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug hypersensitivity reactions encompasses a broad range of allergic or allergic-like symptoms that occur within minutes to hours after ingesting aspirin or other NSAID nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Hypersensitivity drug reactions differ from drug toxicity reactions in that drug toxicity reactions result from the pharmacological action of a drug, are dose-related, and can occur in any treated individual ; hypersensitivity reactions are idiosyncratic reactions to a drug. Although the term NSAID was introduced to signal a comparatively low risk of adverse effects, NSAIDs do evoke a broad range of hypersensitivity syndromes. These syndromes have recently been classified by the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology Task Force on NSAIDs Hypersensitivity.

Alexander Kapp is a German dermatologist and allergist. He is chairman and medical director of the department of dermatology and allergy at the Hannover Medical School. He is known for his work in the field of pathophysiology of inflammatory skin diseases, his research on neuro-immunological interactions in allergic inflammation and on the role of eosinophilic granulocytes in allergy and dermatology.
A sweat allergy is the exacerbation of atopic dermatitis associated with an elevated body temperature and resulting increases in the production of sweat. It appears as small reddish welts that become visible in response to increased temperature and resulting production of sweat. It can affect all ages. Sweating can trigger intense itching or cholinergic urticaria. The protein MGL_1304 secreted by mycobiota present on the skin such as Malassezia globosa acts as a histamine or antigen. People can be desensitized using their own samples of sweat that have been purified that contains small amounts of the allergen. The allergy is not due to the sweat itself but instead to an allergy-producing protein secreted by bacteria found on the skin.
Cezmi Akdis is a medical researcher in the field of immunology. He is director of the Swiss Institute of Allergy and Asthma Research (SIAF) in Davos, Switzerland and the editor in chief of the journal Allergy.
Giorgio Walter Canonica is an Italian medical scientist and professor at Allergy and Respiratory Diseases, Dept. of Internal Medicine, Humanitas University, Milano. He is known for his research work related to innovative treatment strategies for allergic diseases which includes biological response modifier in form of targeted immunotherapy with primary emphasis on sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT). He has served as Secretary General and President elect of World Allergy Organisation for six consecutive years and has served as president of the same organization during 2007–09. He is also the vice-president of INTERASMA.