
The War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1714) was a European conflict of the early 18th century, triggered by the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, the last Habsburg monarch of Spain. His closest heirs were members of the Austrian Habsburg and French Bourbon families; acquisition of an undivided Spanish Empire by either threatened the European balance of power and thus involved the other leading powers. Related conflicts include Rákóczi's War of Independence in Hungary, the Camisard revolt in Southern France, Queen Anne's War in North America, and minor struggles in Colonial India. The 1700-1721 Great Northern War is viewed as connected but separate.

The United Provinces of the Netherlands, or simply United Provinces, and commonly referred to historiographically as the Dutch Republic, was a federal republic formally established from the formal creation of a federal state in 1581 by several Dutch provinces—seceded from Spanish rule—until the Batavian Revolution of 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state.
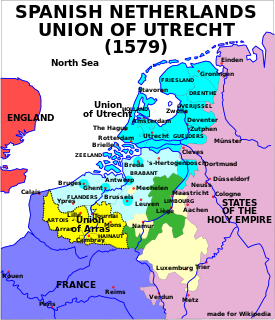
The Union of Utrecht was a treaty signed on 23 January 1579 in Utrecht, the Netherlands, unifying the northern provinces of the Netherlands, until then under the control of Habsburg Spain.

The Peace of Utrecht is a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715.

Lillers is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France.

Events from the year 1702 in Canada.

Events from the year 1713 in Canada.

The War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718-1720) was caused by Spanish attempts to recover territorial losses agreed by the 1713 Peace of Utrecht. Primarily conducted in Italy, it included minor engagements in the Americas and Northern Europe, as well as the Spanish-backed 1719 Jacobite Rising.

The Treaty of Baden was the treaty that ended formal hostilities between France and the Holy Roman Empire, which had been at war since the start of the War of the Spanish Succession. It was signed on 7 September 1714 in Baden, Switzerland, and complemented the Treaties of Utrecht and of Rastatt.
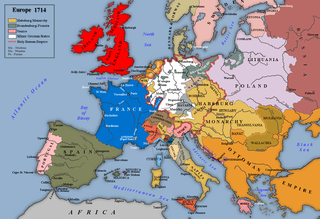
The Treaty of Rastatt was a peace treaty between France and Austria, concluded on 7 March 1714 in the Baden city of Rastatt, to put an end to state of war between them from the War of the Spanish Succession. The treaty followed the earlier Treaty of Utrecht of 11 April 1713, which ended hostilities between France and Spain, on the one hand, and Britain and the Dutch Republic, on the other hand. A third treaty at Baden, Switzerland was required to end the hostilities between France and the Holy Roman Empire.
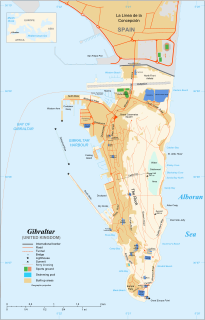
The Gibraltar territory currently contains an 800-metre (2,625 ft) long section of the isthmus that links the Rock with mainland Spain. Spain does not acknowledge British sovereignty over Gibraltar beyond the fortified perimeter of the town as at 1704. The United Kingdom claims the southern part of the isthmus on the basis of continuous possession over a long period.

Île-Royale was a French colony in North America that existed from 1713 to 1763, consisting of two islands, Île Royale and Île Saint-Jean. Its territory is known now as Cape Breton Island and Prince Edward Island.

The Siege of Barcelona was a battle at the end of the War of Spanish Succession, which pitted Archduke Charles of Austria, against Philip V of Spain, backed by France in a contest for the Spanish crown.
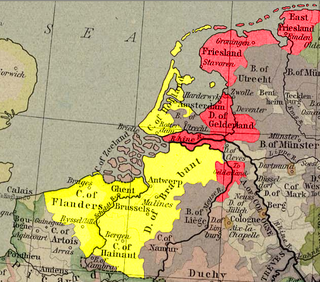
The Guelders Wars were a series of conflicts in the Low Countries between the Duke of Burgundy, who controlled Holland, Flanders, Brabant and Hainaut on the one side, and Charles, Duke of Guelders, who controlled Guelders, Groningen and Frisia on the other side.

The 1720 Treaty of The Hague was signed on 17 February 1720 between Spain and the Quadruple Alliance, established by the 1718 Treaty of London. Its members included Britain, France, the Dutch Republic and Austria.

The Treaty of Utrecht was signed in 1474 after the Anglo-Hanseatic War between England and the Hanseatic League.
The Anglo-French Alliance is the name for the alliance between Great Britain and France between 1716 and 1731. It formed part of the stately quadrille in which the Great Powers of Europe repeatedly switched partners to try to build a superior alliance.

Henry of the Palatinate was bishop of Utrecht from 1524 to 1529, bishop of Worms from 1523 to 1552 and bishop of Freising from 1541 to 1552.

The Gibraltar–Spain border is the international boundary between the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar and the Kingdom of Spain. It is also referred to as "The Fence of Gibraltar" or simply "The Fence".

Netherlands–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Spain has an embassy in The Hague and a consulate general in Amsterdam. The Netherlands has an embassy in Madrid and nine honorary consulates in Barcelona, Bilbao, Ceuta, Gijón, Palma, Benidorm, Sevilla, Tenerife, Torremolinos and Valencia. The relations between both countries are defined mainly by their membership in the European Union and by being allies in the NATO, as well as belonging to numerous International Organizations.

















