An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which combatants take advantage of concealment and the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind hilltops. Ambushes have been used consistently throughout history, from ancient to modern warfare. In the 20th century, an ambush might involve thousands of soldiers on a large scale, such as over a choke point such as a mountain pass, or a small irregular band or insurgent group attacking a regular armed force patrol. Theoretically, a single well-armed and concealed soldier could ambush other troops in a surprise attack.

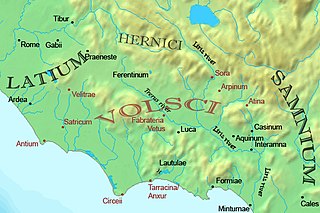
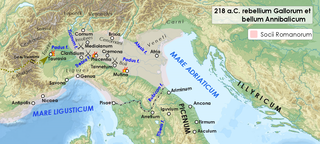
Year 218 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Longus. The denomination 218 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The pincer movement, or double envelopment, is a military maneuver in which forces simultaneously attack both flanks (sides) of an enemy formation.

Publius Cornelius Scipio was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic and the father of Scipio Africanus.

The Battle of the Trebia was the first major battle of the Second Punic War, fought between the Carthaginian forces of Hannibal and the Roman Republic in December of 218 BC, on or around the winter solstice. It was a resounding Roman defeat with heavy losses, with only about 10,000 out of 40,000 Romans surviving and retreating to Placentia (Piacenza). In this battle, Hannibal got the better of the Romans by exercising the careful and innovative planning for which he was famous. The impetuous and short-sighted opposing general, the consul Tiberius Sempronius Longus, allowed himself to be provoked into a frontal assault under physically difficult circumstances and failed to see that he was being led into a trap.

The Battle of Lake Trasimene was a major battle in the Second Punic War. The Carthaginians under Hannibal defeated the Romans under the consul Gaius Flaminius. Hannibal's victory over the Roman army at Lake Trasimene remains, in terms of the number of men involved, the largest ambush in military history. In the prelude to the battle, Hannibal also achieved the earliest known example of a strategic turning movement.

The Trebbia is a river predominantly of Liguria and Emilia Romagna in northern Italy. It is one of the four main right-bank tributaries of the river Po, the other three being the Tanaro, the Secchia and the Panaro.
The Battle of Ticinus was a battle of the Second Punic War fought between the Carthaginian forces of Hannibal and the Romans under Publius Cornelius Scipio in late November 218 BC. The battle took place in the flat country of Pavia county on the right bank of the Ticino River, not far north from its confluence with the Po River. The battle is named from the river, not the nearby contemporaneous settlement of Ticinum. Although the precise location is not known, it is generally accepted that a settlement known today as Vigevano is mentioned in Livy's text and that Scipio's camp was to the south at Gambolo, whose coordinates are given on the map. The conflict would have been west of there. It was the first battle of the war against the Romans that was fought on Italian soil and the first battle of the war to employ legion-sized forces. Its loss by the Romans, and the temporary disablement of Scipio's command, set the stage for the Roman disaster at the Battle of the Trebia in December.
SPQR is a board wargame designed by Richard Berg and Mark Herman, and released in 1992 by GMT Games, as part of the Great Battles of History (GBoH) series of games on ancient warfare. SPQR deals with battles fought by the Roman Republic, and is designed to showcase the strengths and weaknesses of the Roman manipular legion.

The Civic Crown was a military decoration during the Roman Republic and the subsequent Principate, regarded as the second highest to which a citizen could aspire. It took the form of a chaplet of common oak leaves woven to form a crown. It was reserved for Roman citizens who saved the lives of fellow citizens by slaying an enemy on a spot held by the enemy that same day. The citizen saved must admit it; no one else could be a witness.
Trebia or Trebbia can refer to:

The Third Battle of Nola was fought in 214 BC between Hannibal and a Roman army led by Marcus Claudius Marcellus. It was Hannibal's third attempt to take the town of Nola. Once again, Marcellus successfully prevented the town's capture.
Tiberius Sempronius Longus was a Roman consul during the Second Punic War and a contemporary of Publius Cornelius Scipio. In 218 BC, Sempronius was sent to Africa with 160 quinqueremes to gather forces and supplies, while Scipio was sent to Iberia to intercept Hannibal. It was at this time, striking from Lilybaeum, on the island of Sicily, that Sempronius Longus captured Malta from the Carthaginians.

The Siege of Saguntum was a battle which took place in 219 BC between the Carthaginians and the Saguntines at the town of Saguntum, near the modern town of Sagunto in the province of Valencia, Spain. The battle is mainly remembered today because it triggered one of the most important wars of antiquity, the Second Punic War.

Gragnano Trebbiense is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Piacenza in the Italian region, Emilia-Romagna, located about 150 kilometres (93 mi) northwest of Bologna and about 11 kilometres (7 mi) southwest of Piacenza.

Sergio Guerri was an Italian Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church who served as personal theologian to five popes from 1955 to 1989, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1969.
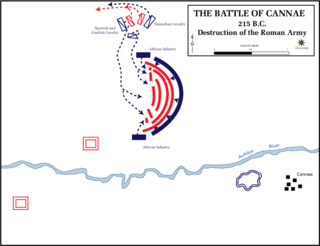
Numidian cavalry was a type of light cavalry developed by the Numidians. After they were used by Hannibal during the Second Punic War, they were described by the Roman historian Livy as "by far the best horsemen in Africa."

Battles BC is a 2009 documentary series looking at key battles in ancient history. The show was known for its very gritty nature, visual effects similar to the film 300 and its highly choreographed fight scenes with various weapons.
Michael, Freiherr von Fröhlich was a German general officer serving in army of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, notably during the Wars of the French Revolution.