Windows Media Audio (WMA) is a series of audio codecs and their corresponding audio coding formats developed by Microsoft. It is a proprietary technology that forms part of the Windows Media framework. WMA consists of four distinct codecs. The original WMA codec, known simply as WMA, was conceived as a competitor to the popular MP3 and RealAudio codecs. WMA Pro, a newer and more advanced codec, supports multichannel and high resolution audio. A lossless codec, WMA Lossless, compresses audio data without loss of audio fidelity. WMA Voice, targeted at voice content, applies compression using a range of low bit rates. Microsoft has also developed a digital container format called Advanced Systems Format to store audio encoded by WMA.
Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding (ATRAC) is a family of proprietary audio compression algorithms developed by Sony. MiniDisc was the first commercial product to incorporate ATRAC in 1992. ATRAC allowed a relatively small disc like MiniDisc to have the same running time as CD while storing audio information with minimal loss in perceptible quality. Improvements to the codec in the form of ATRAC3, ATRAC3plus, and ATRAC Advanced Lossless followed in 1999, 2002, and 2006 respectively.
G.723.1 is an audio codec for voice that compresses voice audio in 30 ms frames. An algorithmic look-ahead of 7.5 ms duration means that total algorithmic delay is 37.5 ms. Its official name is Dual rate speech coder for multimedia communications transmitting at 5.3 and 6.3 kbit/s. It is sometimes associated with a Truespeech trademark in coprocessors produced by DSP Group.
Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is an audio coding standard for lossy digital audio compression. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at the same bit rate. The confusingly named AAC+ (HE-AAC) does so only at low bit rates and less so at high ones.
The Environmental Audio Extensions are a number of digital signal processing presets for audio, present in Creative Technology Sound Blaster sound cards starting with the Sound Blaster Live and the Creative NOMAD/Creative ZEN product lines. Due to the release of Windows Vista which deprecated the DirectSound3D API EAX was based on in 2007, Creative discouraged EAX implementation in favor of its OpenAL-based EFX equivalent – though at that point relatively few games used the API.
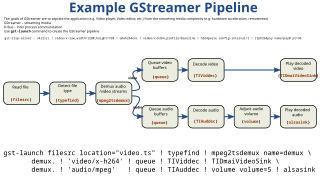
GStreamer is a pipeline-based multimedia framework that links together a wide variety of media processing systems to complete complex workflows. For instance, GStreamer can be used to build a system that reads files in one format, processes them, and exports them in another. The formats and processes can be changed in a plug and play fashion.
Cinepak is a lossy video codec developed by Peter Barrett at SuperMac Technologies, and released in 1991 with the Video Spigot, and then in 1992 as part of Apple Computer's QuickTime video suite. One of the first video compression tools to achieve full motion video on CD-ROM, it was designed to encode 320×240 resolution video at 1× CD-ROM transfer rates. The original name of this codec was Compact Video, which is why its FourCC identifier is CVID. The codec was ported to the Microsoft Windows platform in 1993. It was also used on first-generation and some second-generation CD-ROM game consoles, such as the Atari Jaguar CD, Sega CD, Sega Saturn, and 3DO. libavcodec includes a Cinepak decoder and an encoder, both licensed under the terms of the LGPL.
High Definition Compatible Digital (HDCD) is a proprietary audio encode-decode process that claims to provide increased dynamic range over that of standard Red Book audio CDs, while retaining backward compatibility with existing compact disc players.

The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of web browsers.
The following comparison of video players compares general and technical information for notable software media player programs.
SMPTE 421M, informally known as VC-1, is a video coding format. Most of it was initially developed as the proprietary video format Windows Media Video 9 by Microsoft in 2003. With some enhancements including the development of a new Advanced Profile, it was officially approved as a SMPTE video codec standard on April 3, 2006.

Microsoft NetMeeting is a discontinued VoIP and multi-point videoconferencing client included in many versions of Microsoft Windows. It uses the H.323 protocol for videoconferencing, and is interoperable with OpenH323-based clients such as Ekiga, OpenH323, and Internet Locator Service (ILS) as reflector. It also uses a slightly modified version of the T.120 Protocol for whiteboarding, application sharing, and file transfers.

Indeo Video is a family of audio and video formats and codecs designed for real-time video playback on desktop CPUs first released in 1992. While its original version was related to Intel's DVI video stream format, a hardware-only codec for the compression of television-quality video onto compact discs, Indeo was distinguished by being one of the first codecs allowing full-speed video playback without using hardware acceleration. Also unlike Cinepak and TrueMotion S, the compression used the same Y'CbCr 4:2:0 colorspace as the ITU's H.261 and ISO's MPEG-1. Indeo use was free of charge to allow for broadest usage.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a variety of audio coding formats. For listening tests comparing the perceived audio quality of audio formats and codecs, see the article Codec listening test.
The Speech Application Programming Interface or SAPI is an API developed by Microsoft to allow the use of speech recognition and speech synthesis within Windows applications. To date, a number of versions of the API have been released, which have shipped either as part of a Speech SDK or as part of the Windows OS itself. Applications that use SAPI include Microsoft Office, Microsoft Agent and Microsoft Speech Server.
Adaptive differential pulse-code modulation (ADPCM) is a variant of differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) that varies the size of the quantization step, to allow further reduction of the required data bandwidth for a given signal-to-noise ratio.

Libav is a free software project, forked from FFmpeg in 2011, that produces libraries and programs for handling multimedia data.

Opus is a lossy audio coding format developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation and standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force, designed to efficiently code speech and general audio in a single format, while remaining low-latency enough for real-time interactive communication and low-complexity enough for low-end embedded processors. Opus replaces both Vorbis and Speex for new applications, and several blind listening tests have ranked it higher-quality than any other standard audio format at any given bitrate until transparency is reached, including MP3, AAC, and HE-AAC.
Sorenson Media was an American software company specializing in video encoding technology. Established in December 1995 as Sorenson Vision, the company developed technology which was licensed and ultimately acquired from Utah State University. The company first announced its codec at a developer’s preview at MacWorld Expo in January 1997.







